Chapter 17: Oral Manifestations of Systemic Diseases Flashcards
___ is characterized by excess bilirubin in the bloodstream that accumulates in the tissues, which results in a yellowish discoloration of the skin and mucosa
jaundice
what are the causes of jaundice?
numerous causes; some are physiologic, many are pathologic
___ is an inherited, innocuous problem seen in 5% of americans and is characterized by impaired processing of bilirubin by the liver
gilbert syndrome
other than gilbert syndrome, what are 3 other causes of jaundice?
- sickle cell anemia
- liver infections or toxins
- cancer
___ fibers have an affinity for bilirubin, so what areas are more prominently affected?
- elastin fibers
- sclera, lingual frenum, soft palate
what are some signs and symptoms due to hyperbilirubinemia that may occur with jaundice?
fever, abdominal pain, anorexia, fatigue
patients with jaundice should be evaluated for ___
undelrying condition
what is the prognosis of patients with jaundice?
depends on the etiology of the jaundice

jaundice
___ is a group of conditions characterized by the deposition of an extracellular, proteinaceous substance that gives the condition its name
amyloidosis
(amyloid is the extracellular, proteinaceous substance)
what are the classifications of amyloidosis?
- organ-limited
- systemic
- primary
- myeloma associated
- secondary
- hemodialysis associated
- heredofamilial
which classification of amyloidosis can occur in a variety of organs, but is rarely seen in the oral cavity, and has no association with any systemic condition?
organ-limited amyloidosis
what is an example of organ-limited amyloidosis?
amyloid nodule, which is a solitary, asymptomatic, submucosal deposit
which classifications of amyloidosis affect older adults, has a male predominance, with initial signs that are nonspecific but eventually develop carpal tunnel syndrome, mucocutaneous lesions, hepatomegaly, and macroglossia?
primary and myeloma-associated systemic amyloidosis
20% of primary and myeloma-associated systemic amyloidosis cases are due to ___
multiple myeloma
describe skin lesions associated with primary and myeloma-associated systemic amyloidosis
appear as smooth-surfaced, firm, waxy papules and plaques
what are the most commonly affected areas in primary and myeloma-associated systemic amyloidosis?
eyelid, neck, and lips
which classification of amyloidosis develops as a result of a chronic inflammatory process, such as TB, sarcoidosis, or osteomyelitis?
secondary systemic amyloidosis
what organs are affected by secondary systemic amyloidosis?
the heart is spared, but it affects the liver, kidney, and spleen
is secondary systemic amyloidosis common? why or why not?
not common after advent of modern antibiotic therapy
which classification of amyloidosis is characterized by an accumulation of protein in plasma (as a result of not being removed by dialysis), which eventually deposits in the bones and joints?
hemodialysis-associated systemic amyloidosis
which classification of amyloidosis is uncommon but a significant form of the disease, is autosomal dominant, and patients have polyneuropathies primarily
heredofamilial systemic amyloidosis
what are other conditions associated with heredofamilial systemic amyloidosis?
cardiomyopathy, cardiac arrhythmias, congestive heart failure, and renal failure develops as the condition progresses
what is the treatment for amyloidosis?
in most instances, no effective therapy is available
most patients with systemic amyloidosis succomb to ___, ___, or ___ within months to a few years after diagnosis
cardiac failure, arrhythmia, or renal disease

amyloidosis
are significant vitamin deficiencies common in the US?
no
what patients are commonly affected by vitamin deficiencies?
patients with malabsorption syndromes or eating disorders, those following “fad diets”, and alcoholics
describe vitamin A deficiency
- vitamin A = retinol
- essential for vision
- may lead to blindness
describe vitamin B1
- vitamin B1 = thiamin
- maintain proper functioning of neurons
- beriberi
describe vitamin B2
- aka riboflavin
- necessary for cellular oxidation-reduction reactions
- oral alterations like angular cheilitis, glossitis
describe vitamin B3
- aka niacin
- acts as a coenxyme for oxidation-reduction reactions
- pellagra (shown) = dermatitis, dementia, diarrhea

describe vitamin B6
- aka pyridoxine
- cofactor associated with enxymes that participate in amino acid synthesis
describe vitamin C
- ascorbic acid
- necessary for the proper synthesis of collagen
- scurvy (shown)

describe vitamin D
- considered a hormone, necessary for calcium absorption from the gut
- rickets, osteomalacia
describe vitamin E
- aka alpha-tocopherol
- antioxidant
describe vitamin K
- necessary for proper clotting (needed in clotting factors II, VII, IX, X)
- coagulopathy because of inadequate synthesis or prothrombin
___ is the most common cause of anemia in the US and the world
iron deficiency anemia
iron deficiency anemia develops from what 4 possible things?
- excessive blood loss
- increased demand for RBCs
- decreased uptake of iron
- decreased absorption of iron
20% of women of childbearing years (menorrhagia) have iron deficiency anemia. why?
chronic blood loss
what are the oral manifestations of iron deficiency anemia?
angular cheilitis, atrophic glossitis
what are the lab findings in iron deficiency anemia
hypochromic microcytic RBCs
___ is a system complex characterized by iron deficiency anemia, glossitis, and dysphagia
plummer-vinson syndrome
the incidence of plummer-vinson syndrome is declining; why?
likely due to improved nutritional status
plummer-vinson syndrome has been associated with a high frequency of what two things?
oral and esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
plummer-vinson syndrome is considered a ___ process
pre-malignant
most patients with plummer-vinson syndrome are what gender, with what background, and of what ages?
- women
- scandinavian or northern european background
- between 30-50yo
patients with plummer-vinson syndrome complain of what?
burning sensation associated with the tongue and oral mucosa
___ is often present in plummer-vinson syndrome
angular cheilitis
patients with plummer-vinson have marked atrophy of the ___; what does this cause?
- lingual papilla
- produces a smooth, red appearance of the dorsal tongue
patients with plummer-vinson syndrome have pain or difficulty upon ___
swallowing
evaluation of the esophagus in patients with plummer-vinson syndrome shows the presence of ___
abnormal bands of tissue termed esophageal webs
describe the nails in patients with plummer-vinson syndrome
- alteration of the growth pattern of nails
- results in a spoon-shaped configuration (koilonychia)
- nails are also brittle
what is the treatment for plummer-vinson syndrome?
directed at correcting the iron-deficiency anemia by means of dietary iron supplementation
patients with plummer-vinson syndrome should be evaluated periodically for what 3 things?
oral, pharyngeal, and esophageal carcinoma
patients with plummer-vinson syndrome have anywhere from 5-50% chance of developing ___
an upper aerodigestive tract malignancy

plummer-vinson syndrome
angular cheilitis and glossitis
what is another name for pernicious anemia?
megaloblastic anemia
what is pernicious anemia caused by?
poor absorption of cobalamin (vitamin B12, intrinsic factor)
why do most patients with pernicious anemia lack intrinsic factor?
autoimmune destruction of th parietal cells of the stomach, which results in decreased absorption of cobalamin
what are the oral manifestations of pernicious anemia?
atrophic glossitis

___ is a result of increased production of growth hormone, usually related to a functioning pituitary adenoma
gigantism
when does gigantism take place?
before the closure of the epiphyseal plates
what are the oral findings of gigantism?
generalized macrodontia
___ is characterized by excessive production of growth hormone after the closure of epiphyseal plates, and includes increased growth of the mandible (prognathism) with diastema formation and macroglossia
acromegaly
photo shows mandibular enlargement

hypothyroidism is characterized by decreased levels of ___
thyroid hormone
what is cretinism?
hypothyroidism that occurs during infancy
what is myxedema?
hypothyroidism that occurs in adulthood

hypothyroidism
before and after
many oral complications of diabetes mellitus are due to ___, which results in occlusion of the small blood vessels, causing a decrease in tissue perfusion
microangiopathy
patients with diabetes mellitus have an impairment of ___ function
neutrophil
oral manifestations of diabetes mellitus are limited to those with which type of DM?
type I
what are the oral manifestations of DM?
- periodontal disease
- occurs more frequently and progresses more rapidly than in normal patients
- delayed healing
- increasing probability of infection
- enlargement and erythema of the attached gingiva
- oral candidiasis (30%)
- zygomycosis - poorly controlled
- xerostomia (30%)
- diabetic sialadenosis
- diffuse, nontender, bilateral enlargement of the parotid glands
what is the treatment of oral manifestations of diabetes mellitus?
geared toward controlling the DM

diabetes mellitus
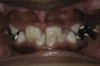
This diffuse, erythematous enlargement of the gingival tissues developed in a diabetic patient who discontinued taking her insulin. B, The gingival tissues have greatly improved after reinstitution of regular insulin injections. Several incisors were extracted because of severe periodontal bone loss.

___ is an inflammatory and immunologically mediated condition of unknown cause, whose manifestations can be seen a nywhere along the GI tract (from mouth to anus)
crohn’s disease
why are oral lesions associated with crohn’s disease significant?
they precede GI lesions 30% of the time
most patients with crohn’s disease are what age when the disease first becomes evident?
teenagers
what are the GI signs of crohn’s disease?
abdominal cramping, diarrhea, pain, nausea, and fever
___ and ___ may develop with crohn’s disease
weight loss and malnutrition
describe the oral lesions associated with crohn’s disease
- nonspecific
- diffuse, nodular swellings
- “cobblestone appearance” of the oral mucosa
- linear ulcerations of the buccal vestibule

what is the treatment for crohn’s disease?
- usually sulfa drugs
- systemic prednisone is used in more severe cases
oral lesions associated with crohn’s disease clear with the treatment of ___
GI disease


