Chapter 15: Odontogenic Cysts and Tumors Part II Flashcards
___ is a developmental odontogenic cyst which typically occurs along the lateral root surface
lateral periodontal cyst
lateral periodontal cysts arise from ___
cell rests of the dental lamina
which 3 odontogenic cysts are derived from cell rests of the dental lamina?
- odontogenic keratocyst
- gingival cyst of the adult
- lateral periodontal cyst
lateral periodontal cysts are the intrabody counterpart of the ___
gingival cyst of the adult
lateral periodontal cysts are found in patients of what age?
40-60
lateral periodontal cysts have a striking predilection to occur in what location?
mandibular premolar-canine-lateral incisor area
are teeth affected by lateral periodontal cysts vital or non-vital?
vital
how do lateral periodontal cysts present radiographically?
- well-circumscribed RL
- occasionally, the lesion may appear polycystic, termed botryoid odontogenic cysts
___ usually appear multilocular via xray and represent a rare variant of the lateral periodontal cyst
botryoid odontogenic cysts
what is the treatment of lateral periodontal cysts?
conservative enucleation
what is the recurrance and malignant transformation of lateral periodontal cyst?
recurrence and malignant transformation are exceedingly rare

lateral periodontal cyst

lateral periodontal cyst

lateral periodontal cyst
calcifying odontogenic cyst is also called ___
gorlin cyst
the WHO reclassified calcifying odontogenic cyst to be ___, but most clinicians refer to it as ___
- calcifying cystic odontogenic tumor
- gorlin cyst
65% of calcifying odontogenic cysts are found in what location?
- incisor-canine areas
- mx = md
what is the average age patient with a calcifying odontogenic cyst?
35
20% of calcifying odontogenic cysts are associated with ___
odontomas
what are the radiographic features of calcifying odontogenic cysts?
- unilocular, well-defined radiolucency
- radiopaque structures are seen within the RL in 50%
1/3 of calcifying odontogenic cysts are associated with a ___
unerupted tooth (usually canine)
what are the histopathologic features of calcifying odontogenic cysts?
has ghost cells, which can calcify

what is the recurrence of calcifying odontogenic cysts? what is the prognosis?
rare recurrences have been reported after enucleation
prognosis is good

calcifying odontogenic cyst

calcifying odontogenic cyst

calcifying odontogenic cyst
___ is a developmental cyst with glandular and/or salivary gland features
glandular odontogenic cyst
what is the average age of someone with a glandular odontogenic cyst?
50 years old
75% of glandular odontogenic cyst cases occur in what location?
mandible, with a predilection for the anterior jaws
describe the size of glandular odontogenic cysts
can vary from small to very large
what are the radiographic features of glandular odontogenic cysts?
- either unilocular or multilocular radiolucency
- well-defined margins
- sclerotic rim

what is the treatment for a glandular odontogenic cyst? what is the recurrence rate?
- enucleation with curettage
- 30% will recur

lateral periodontal cyst
of multilocular vs unilocular glandular odontogenic cyst lesions, which is more likely to recur?
multilocular (because they’re harder to get out)
because multilocular glandular odontogenic cyst lesions are more likely to recur than unilocular lesions, ___ is used at times
en bloc resection
*difference between en bloc vs complete resection: complete resection is complete, through-through removal; en bloc leaves a border of the mandlbe there

glandular odontogenic cyst
___ is an inflammatory cyst with uncertain pathogenesis, which characteristically develops on the buccal aspect of the mandibular first permanent molar
buccal bifurcation cyst
what age patient do buccal bifurcation cysts commonly affect?
children, average age 10
what are some common experiences a patient may have with a buccal bifurcation cyst?
- tenderness
- swelling
- foul-tasting discharge
in a patient with a buccal bifurcation cyst, what does perio probing usually reveal?
pocket formation on the buccal aspect
1/3 of buccal bifurcation cysts have ___ involvement
bilateral
what are the radiographic features of buccal bifurcation cysts?
- well-circumscribed, unilocular radiolucency involving the buccal bifurcation and root
- average size is 1.5 cm
- an occlusal xray can demonstrate buccal location
- the root apices are characteristically tipped toward the lingual mandibular cortex

what is the treatment of buccal bifurcation cysts?
enucleation
no need to extract the tooth
when is complete healing usually achieved with the treatment of a buccal bifurcation cyst?
within 1 year of surgery

buccal bifurcation cyst

buccal bifurcation cyst
___ is a carcinoma arising within bone, is rare, and essentially limited to the jaws
carcinoma arising in odontogenic cysts
carcinomas arising in odontogenic cysts are collectively known as ___
odontogenic carcinomas
most odontogenic carcinomas arise from ___
odontogenic cysts
1-2% of all oral cavity carcinomas originate from ___
odontogenic cysts
what is the pathogenesis of carcinomas arising in odontogenic cysts?
unknown
carcinomas arising in odontogenic cysts are typically seen in what age patient?
older patients
___ and ___ are the two most common presenting symptoms of carcinomas arising in odontogenic cysts; however, some patients are asymptomatic
pain and swelling
radiographically, carcinomas arising in odontogenic cysts mimic ___, except the margins are ___ and ___
- odontogenic cysts
- irregular and ragged

what is the histology of carcinomas arising in odontogenic cysts?
usually shows well-differentiated SCCA
what is the treatment for carcinomas arising in odontogenic cysts?
varies from local block excision to radical resection, +/- radiation and chemo
approximately ___% of patients treated for carcinoma arising in odontogenic cysts survive
50%
when diagnosing carcinomas arising in odontogenic cysts, you must rule out ___ before calling it a true primary intraosseous carcinoma
metastatic spread from another area

carcinoma arising in odontogenic cysts
what is the differential for a cyst that crosses the midline?
- glandular odontogenic cyst
- odontogenic keratocyst
- central giant cell granuloma
- traumatic bone cyst - not a true cyst, no expansion
___ is the most common clinically significant odontogenic tumor
ameloblastoma
ameloblastomas are tumors of ___ origin
odontogenic epithelial
what are the 3 different types of ameloblastomas and their relative prevalences?
- conventional solid or multicystic - 85%
- unicystic - 15%
- peripheral - 1%
what age are ameloblastomas most common?
equal prevalence from 3rd-7th decade of life
what is the gender predileciton of ameloblastomas?
none
85% of ameloblastomas occur where?
in the mandible, usually the molar-ascending ramus area
are ameloblastomas symptomatic or asymptomatic?
asymptomatic, smaller ones are usually detected during routine xrays
what is the clinical sign of ameloblastoma?
if there is on, it’s most often a painless swelling
what can happen if ameloblastomas are untreated?
they can grow to grotesque portions - even then, pain and parasthesia are uncommon
what are the radiographic features of ameloblastomas?
- typical features is a multilocular radiolucency
- “soap bubble” - when RL loculations are large
- “honeycombed” - when the loculations are small
- buccal and lingual cortical expansion is frequently present

is there root resorption associated with ameloblastomas?
yes
a ___ may be associated with an ameloblastoma
unerupted tooth
which pattern of ameloblastomas does not share features with the other forms, has a predilection for the anterior maxilla, and may be mixed RL-RO (due to osseous metaplasia)?
desmoplastic ameloblastoma
what is the histopathology of ameloblastomas?
- palisading, hyperchromatic basal layer
- reverse polarity
- apical vacuolization

what is the treatment for patients with conventional solid or multicystic ameloblastomas?
variety of treatment, from simple enucleation and curettage to en bloc resection
ameloblasts infiltrate between ___ at the lesion periphery
cancellous bone
in early stages of ameloblastoma, ___ cannot be seen via radiographs
bone resorption
what are the recurrence rates when ameloblastomas are curettaged?
50-90%
recurrence takes years
what is the most widely used treatment for ameloblastomas, and what is the recurrence rate?
- marginal resection - 1.5cm margins beyond what is visible radiographically
- recurrence is 15%
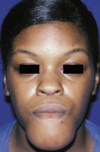
ameloblastoma

ameloblastoma

ameloblastoma

ameloblastoma
notice the soap bubble appearance

ameloblastoma
notice the honeycombed appearance

ameloblastoma

ameloblastoma
this is multilocular, so it can’t be a lateral periodontal cyst

ameloblastoma

ameloblastoma


