Chapter 15: Odontogenic Cysts and Tumors Part III Flashcards
___ is a painless, nonulcerated, sessile gingival lesion, that is clinically determined to be one of the 3Ps (bump on the gum)
peripheral ameloblastoma
what is the average age of someone with a peripheral ameloblastoma?
50
where are peripheral ameloblastomas most commonly found?
mandibular posterior gingival mucosa
unlike intraosseous ameloblastomas, ___ have innocuous clinical behavior
peripheral ameloblastomas
what is the recurrence of peripehral ameloblastomas?
15%, and further excision has close to 0% recurrence

peripheral ameloblastoma
keep in mind that although this is in the anterior maxilla, most peripheral ameloblastomas are found in the posterior mandible
malignant ameloblastomas have histologic features of a ___, but shows metastatic deposits (what is the most common site for metastatic deposits?)
- conventional ameloblastoma
- lung most common site
ameloblastic carcinoma has ___ features and follows a markedly aggressive course
cytologic malignant
___ develops later in life than conventional ameloblastomas and malignant ameloblastomas
ameloblastic carcinoma
are ameloblastic carcinomas aggressive? what are the radiographic features?
- yes
- ill-defined margins and cortical destruction

ameloblastic carcinoma
adenomatoid odontogenic tumors occur in what age patient?
ages 10-20 (very uncommon in patients over the age of 30)
what are the common locations of adenomatoid odontogenic tumors? gender predilection?
- anterior maxilla
- F>M
most adenomatoid odontogenic tumors are what size? they may also rarely occur ___
- small
- peripherally
are adenomatoid odontogenic tumors symptomatic or asymptomatic? how are they discovered?
asymptomatic and discovered during xray to determine why a tooth hasn’t erupted
describe the radiographic features of adenomatoid odontogenic tumors
- 75% - tumor is circumscribed, unilocular RL involving the crown of an unerupted tooth
- most often canine
- RL often extends apically past the CEJ (helps differentiate from dentigerous cyst)
- lesion may contain fine, snowflake calcifications (can also help differentiate from dentigerous cyst)
- lesion may develop well-defined, unilocular RL between roots

what is the treatment of adenomatoid odontogenic tumors?
tumor has a thick, fibrous capsule that makes enucleation easy
what is the recurrence and prognosis for adenomatoid odontogenic tumors?
- recurrence doens’t occur - lesion is completely benign, and aggressive behavior ahs not been documented
- prognosis is good

adenomatoid odontogenic tumor

adenomatoid odontogenic tumor
(you can see the snowflake calcifications)

adenomatoid odontogenic tumor
calcifying epithelial odontogenic tumors are also called ___
pindborg tumors
calcifying epithelial odontogenic tumors occur around age ___
40
what is the common location of calcifying epithelial odontogenic tumors? genetic predilection?
- posterior mandible
- M=F
what is the most common presenting sign of calcifying epithelial odontogenic tumors?
painless, slow-growing swelling
what are the radiographic features of calcifying epithelial odontogenic tumors?
- unilocular or multilocular - unilocular more common in maxilla
- margins are typically scalloped and well-defined; may be corticated or ill-defined
- contains calcified structures of varying size and density
- some believe the calcifications are prominent around the crown in a “driven-snow” pattern
- occurs in 10%

calcifying epithelial odontogenic tumors are frequently associated with a ___
impacted tooth (most often a mandibular molar)
what are the histopathologic features of calcified epithelial odontogenic tumors?
- nuclear pleomorphism and atypia
- amyloid-like extracellular materia; positive for congo red, which exhibits an apple-green birefringence when viewed under polarized light
- calcifications with concentric rings form in the amyloid-like areas (Liesegang rings)


adenomatoid odontogenic tumor
what is the treatment of calcifying epithelial odontogenic tumors? what is the recurrence and prognosis?
- local resection with a narrow rim of bone is the treatment of choice
- 15% recurrence; highest with curettage as treatment
- prognosis is typically good, but rare lesions can exhibit aggressive or malignant behavior

calcifying epithelial odontogenic tumor

calcifying epithelial odontogenic tumor

calcifying epithelial odontogenic tumor
___ is a true mixed tumor - both epithelial and mesenchymal tissues are neoplastic
ameloblastic fibroma
ameloblastic fibromas typically occur in what age patient?
occurs in younger patients - usually before age 20
are ameloblastic fibromas symptomatic or asymptomatic?
- small tumors are asymptomatic
- largers ones cause painless swelling
70% of ameloblastic fibromas are located in the ___
posterior mandible
what are the radiographic features of ameloblastic fibromas?
- can be unilocular or multilocular
- margins are well-defined and sclerotic
- 75% are associated with an unerupted tooth

what is the treatment of ameloblastic fibroma?
- conservative initial therapy; recurrences requrie more aggressive surgery
- 50% of ameloblastic fibrosarcomas develop in the setting of a recurrent ameloblastic fibroma
50% of ___ develop in the setting of a recurrent ameloblastic fibroma
ameloblastic fibrosarcomas

ameloblastic fibroma
___ histologically appears similar to ameloblastic fibroma, except it also has enamel and dentin
ameloblastic fibro-odontoma
what is the average age patient with an ameloblastic fibro-odontoma?
10 years old
what is the most common locations of ameloblastic fibro-odontomas?
posterior jaws
are ameloblastic fibro-odontomas symptomatic or asymptomatic?
small tumors are asymptomatic; larger ones are associated with a painless swelling
what are the radiographic features of ameloblastic fibro-odontomas?
- well-circumscribed unilocular RL
- contains varying amounts of calcified material
- typicaly associated with an unerupted tooth

what is the treatment of ameloblastic fibro-odontomas? what is the recurrence?
conservative curettage with rare recurrence

ameloblastic fibro-odontoma

ameloblastic fibro-odontoma
___ is the malignant counterpart of the ameloblastic fibroma
ameloblastic fibrosarcoma
ameloblastic fibrosarcomas typically show features of malignancy on what portion of the lesion?
mesenchymal
what is the average age and gender predilection of ameloblastic fibrosarcomas?
- M>F
- average age is 25-30
80% of ameloblastic fibrosarcomas occur in the ___
mandible
patients with ameloblastic fibrosarcomas often complain of ___ and ___
pain and swelling
what is the radiographic presentation of ameloblastic fibrosarcoma?
ill-defined, destructive RL lesion

what is the treatment for ameloblastic fibrosarcoma? what % of patients will succomb to disease?
- radical surgical excision
- 20% will succomb to disease, usually due to uncontrolled local growth

ameloblastic fibrosarcoma
___ is the most common odontogenic tumor, and is considered to be a developmental anomaly (hamartoma) rather than a true neoplasm
odontoma
odontomas are divided into what two types?
compound and complex
which type of odontoma is composed of multiple, small, toothlike structures?
compound
which odontoma type is a conglomerate mass of enamel and dentin; bears no anatomic resemblance of a tooth
complex
what is the average age of someone with an odontoma?
15
are odontomas symptomatic or asymptomatic?
completely asymptomatic
how are odontomas typically discovered?
they are rarely small and discovered via xray when films are taken to determine the reason for failure of an unerupted tooth
odontomas are typically associated with a ___
unerupted tooth
compound odontomas are more common in what location? what about complex odontomas?
- compound - anterior maxilla
- complex - molar regions
how do compound odontomas appear radiographically?
- appears as a collection of toothlike structures of varying size and shape
- surrounded by a narrow RL zone
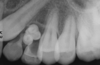
how do complex odontomas appear radiographically?
- calcified mass with the radiodensity of a tooth
- surrounded by a narrow RL rim

are radiographic findings usually diagnostic for compound and complex odontomas?
yes
what is the treatment of odontomas? what is the prognosis?
simple local excision with excellent prognosis

compound odontoma

compound odontoma

compound odontoma

complex odontoma

complex odontoma
what is the differential for a radiographic presentation of soemthign that is RL with calcifying RO?
- calcifying odontogenic cyst
- adenomatoid odontogenic tumor
- calcifying eptihelial odontogenic tumor
- ameloblastic fibro-odontoma
odontogenic myxomas only occur in ___
the jaws
odontogenic myxomas are commonly found in patients of what age? gender predilection?
ages 25-30
M=F
are odontogenic myxomas more common in the maxilla or mandible?
mandible
are odontogenic myxomas symptomatic or asymptomatic?
- small lesions are asymptomatic
- large lesions are associated with a painless expansion of bone
what is the radiographic presentation of odontogenic myxomas?
- unilocular or multilocular RL - may displace or cause resorption of teeth
- RL defect may contain thin, wispy trabeculae of residual bone, which are often arranged at right angles to one another

what is the treatment of odontogenic myxomas?
- small myxomas - curettage with careful periodic re-evaluation every 5 years
- larger lesions - more extensive resection because they tend to infiltrate the surrounding bone
what is the recurrence and prognosis of odontogenic myxomas?
- recurrence 25%
- prognosis is good

odontogenic myxoma

odontogenic myxoma

odontogenic myxoma

odontogenic myxoma


