Chapter 16: Dermatologic Diseases II Flashcards
mucous membrane pemphigoid may also be termed ___, and is twice as common as ___
- cicatricial pemphigoid (cicatrix means “scar”)
- twice as common as pemphigus
what is the average age and gender predilection for someone with mucous membrane pemphigoid?
- 55
- F:M 2:1
mucous membrane pemphigoid oral lesions begin as ___ or ___ which eventually rupture and leave ___
- vesicles or bullae
- ulcerated mucosa
describe the oral lesions in mucous membrane pemphigoid
- intraoral blisters may be seen clinically (unlike with pemphigus)
- an intraoral blood blister is virtually pathognomonic
- unlike other lesions in this disease, oral lesions usually don’t scar
what is the most significant complication of mucous membrane pemphigoid?
ocular involvement (up to 25%)
the earliest ocular change in mucous membrane pemphigoid can be detected via ___ examination by an ophthalmologist
slit-lamp
as mucous membrane pemphigoid progresses, what can happen with the eyes?
- conjunctiva become inflamed and eroded, and attempts at healing lead to scarring
- adhesions, called symblepharons, result

describe symblepharons associated with mucous membrane pemphigoid
- scarring can turn the eyelids inward (entropion), which causes the eyelashes to rub against the cornea
- scarring can close opening of lacrimal glands
- after all this happens, the cornea produces keratin as a protective mechanism
- keratin is opaque, so this leads to blindness
- blindness can also occur by the upper and lower eyelids scarring together

what are the histopathologic features of mucous membrane pemphigoid?
autoantibodies are directed against the basement membrane, leading to a subepithelial split (interepithelial)

direct immunofluorescence of mucous membrane memphigoid shows ___ and ___ along the basement membrane
C3 and IgG
what is the treatment for mucous membrane pemphigoid?
- first part of treatment is to refer to an ophthalmologist, regardless of if the patient has symptoms
- topical corticosteroids are used first; if they are unsuccessful, systemic agents may be used

mucous membrane pemphigoid
___ is a blistering, ulcerative mucocutaneous condition of uncertain etiopathogenesis, which is likely immunologically mediated
erythema multiforme
in 50% of erythema multiforme cases, the clinician can identify a preceding infection or exposure to a medication. what is the infection? what are the medications?
- infection is usually herpes simplex or mycoplasma pneumoniae
- medications are usually antibiotics or analgesics
describe the disease spectrum of erythema multiforme
- erythema multiforme minor
- erythema multiforme major - aka stevens-johnson syndrome
- toxic epidermal necrolysis - aka lyells disease
is the onset of erythema multiforme acute or chronic? describe mild vs severe cases
- acute
- in mild cases, ulcerations affecting the oral mucosa develop
- in severe cases, the entire skin and mucosal surfaces may slough
what patients are usually affected by erythema multiforme?
young adults in their 20s-30s, M>F
what are the prodromal symptoms of erythema multiforme? how long before onset do they occur?
fever, headache, cough, sore throat occur 1 week before onset
how long does erythema multiforme last? what % of cases have recurrent episodes?
- 2-6 weeks
- 20%
what percent of patients with erythema multiforme develop skin lesions?
50%
describe the skin lesions associated with erythema multiforme
- early lesions are typically flat, round, and red
- lesions become elevated and evolve into bulla with necrotic centers
- a highly characteristic skin lesion that develops is a target lesion
- concentric circular erythematous rings resembling a target or bulls-eye

describe the oral lesions associated with erythema multiforme
- erythematous patches that undergo epithelial necrosis and ulcerate
- entire oral cavity can be involved except the gingiva and hard palate

what is a common presentation of the lips with someone who has erythema multiforme?
hemorrhagic crusting of the vermillion zone

erythema multiforme lesions emerge quickly and are painful. what is a potential problems this poses for patients?
patients may become dehydrated due to an inability to ingest liquids
stevens-johnson syndrome is also known as ___
erythema multiforme major
which form of erythema multiforme is usually triggered by a drug and must have skin, oral mucosa, and either ocular or genital mucosa involvement to be diagnosed?
steven-johnson syndrome (EM major)
which form of erythema multiforme is the most severe form, is almost always triggered by a drug, and involves diffuse sloughing of the skin and mucosa?
toxic epidermal necrolysis
toxic epidermal necrolysis tends to occur in what age patient, and what gender more commonly?
- older people (EM minor and major are younger people)
- F>M (unlike EM minor)
if a patient with toxic epidermal necrolysis survives, what happens to the cutaneous process?
typically resolves in 2-4 weeks
describe the management of erythema multiforme
- discontinuation of the causative drug is paramount
- if due to herpes, daily antivirals are indicated
- patient is usually admitted to hospital for IV fluids
- steroids are used in EM minor and major but are contraindicated in toxid epidermal necrolysis
- TEN patients are treated in the burn unit
what is the mortality rate for patients with erythema multiforme major?
up to 10%
what is the mortality rate for patients with toxic epidermal necrolysis?
about 35%

erythema multiforme
what are two other names for erythema migrans?
geographic tongue and benign migratory glossitis
erythema migrans is a common condition that primarily affects the ___, affects ___% of the population, and is two times more common in which gender?
- tongue
- 3%
- F:M 2:1
erythema migrans may be related to what condition?
psoriasis
erythema migrans lesions characteristically appear where on the tongue?
- anterior 2/3 of the dorsal tongue
- concentrated on the tip and lateral borders
erythema migrans may occur in places other than the tongue. what helps with identifying these lesions as erythema migrans?
they will have a serpentine border

how do erythema migrans lesions develop?
- begin as multiple, small white patches which develop central erythematous atrophic zones and enlarge into well-demarcated zones of erythema
- these areas are surrounded at least partially by a slightly elevated, yellow-white, serpentine or scalloped border
- the lesions will heal in one area and then develop in a different area
what other feature is associated with erythema migrans?
fissured tongue
is erythema migrans symptomatic or asymptomatic?
asymptomatic, but some patients may experience burning when eating spicy foods
what is the treatment for erythema migrans? is a biopsy required?
- no treatment necessary for asymptomatic erythema migrans
- symptomatic patients should use topical corticosteroids
- no biopsy required - it is a clinical diagnosis
- patients should be assured they have a benign condition

erythema migrans
___ is a common, chronic dermatologic disease that can affect the oral mucosa, and may be due to medications, amalgam, etc
- lichen planus
- form that results from medications or amalgam is better known as “lichenoid mucositis”
what age and gender is most common in patients affected by lichen planus? approximately what percent of the population is affected?
- middle-aged adults
- F>M
- 1%
describe lichen planus skin lesions (4 Ps)
- purple
- pruritis
- polygonal
- papules
do lichen planus skin lesions itch?
yes, but the patient doens’t usually scratch because the lesions are painful
lichen planus skin papules have a thin, lacelike network of white lines termed ___
wickham’s striae
what are the two forms of oral lichen planus?
reticular and erosive
which form of lichen planus oral lesions are much more common and are asymptomatic?
reticular
describe reticular oral lichen planus
- involves the posterior buccal mucosa bilaterally, seen as wickham’s striae
- if it occurs on the tongue, the lesions will be plaque-like
- lesions tend to wax and wane

which form of oral lichen planus is symptomatic?
erosive
describe erosive oral lichen planus
- lesions are atrophic, erythematous areas with a central ulceration
- periphery is usually bordered by fine, white, radiating striae
- if confined to the gingiva, it is termed desquamative gingivitis
- becomes indistinguishable from pemphigus and pemphigoid, which may also be limited to the gingiva

how do drug-induced lichen planus lesions typically present?
found on the lower lip as non-healing ulcers
what are the histopathologic features of lichen planus?
- pointed, “saw-toothed” rete ridges
- destruction of the basal layer
- band-like infiltrate of lymphocytes subjacent to the epithelium
- degenerating keratinocytes within the epithelium (termed civatte bodies)
- deposition of fibrinogen at the basement membrane via DIF

is a biopsy needed for oral lichen planus lesions?
- not if lesions are bilateral AND asymptomatic
- this is consistent with a clinical diagnosis of reticular oral lichen planus
- biopsy is indicated if the lesions are symptomatic OR asymmetric
what is the treatment for oral lichen planus?
- no treatment is necessary for bilateral AND asymptomatic lesions
- if lesions are symptomatic OR asymmetric, oral topical steroids are used for treatment
28% of women with erosive oral lichen planus also have ___ lesions
vaginal
what 4 things can oral lichen planus lesions be induced by?
- stress
- trauma
- advil (any NSAID, acetaminophen is ok)
- yeast

reticular oral lichen planus

erosive oral lichen planus

lichen planus

lichen planus

lichen planus

lichen planus
wickham’s striae
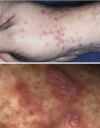
lichen planus skin lesions


