Cerebellum Flashcards
tf Cerebellum give rise to descending motor pathways.
Cerebellum does not give rise to descending motor pathways. Ø
tf Damage to the cerebellum or its pathways DOES cause paralysis
Damage to the cerebellum or its pathways DOES NOT cause paralysis
Input to cerebellum is
sensory
Output of cerebllum
travels to motor structures
rate, range, direction or accuracy of motor movements.
is disturbed by damage to the cerebellum
cerebellum
modulates motor output
in addition to motor output cerebllum
modulates complex behavioral and cognitive functions
receives and processes vestibular information
flocculonodular lobe
nodulus is
medial flocculonodular
flocculus is
flocculus is lateral part of flocculonodular lobe
tf flocculonodular lobe is post to post lobe
f
ant to it

posterior lateral fissure
sep flocculonodular lobe and posterior lobe

Lateral Hemisphere
forms the bulk of the cerebellum
Paravermis:
Paravermis: R and L zones adjacent to the vermis

highly convoluted, forming the cerebellar folia
cerebellum
Molecular layer
contains local circuit neurons and abundant axons and dendrites.

.Purkinje cell layer (middle layer):
formed by a single layer of large neurons called Purkinje cells(PCs)

Granular layer (deep layer):
composed mainly of small granule cells, but also contains other cell types.
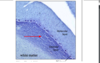
t The white matter core of the cerebellum is t
he location of the deep white matter cerebellar nuclei (DCN).

Buried within the white matter of the cerebellum
deep cerebellar nuclei (DCN)
most medial of deep cerebellar nuclei (DCN)
receives projections from vermis
Fastigial nucleus •

lateral to fastigial n.
receives projections from paravermis
Globose nucleus
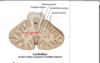
Emboliform nucleus
lateral to globose n
receives projections from paravermis
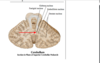
Dentate nucleus
• most lateral •
receives projections from lateral hemisphere

tf body parts are epresented continuously in the cerebllar cortex
body parts are not represented continuouslyin the cerebllar cortex
fractured somatotopy
body part is represented in several locations on cerebellar cortexx
trunk is represented in
the midline region (vermis) of cereblar cortex

Label wat is missing on cerebllar cortex



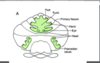
Inferior Cerebellar Peduncle
afferents to cerebellum from spinal cord & medulla.

Middle Cerebellar Peduncle
o Mainly afferents to cerebellum from pontine nuclei
Superior Cerebellar Peduncle
Mainly efferents from the cerebellum.

The cerebellum is attached to the brainstem by – pairs of —– bundles comprised of — and —- axons —– the cerebellum
The cerebellum is attached to the brainstem by 3 pairs of fiber bundles comprised of afferent and efferent axons to/from the cerebellum




(1.) cerebellar cortical region (2.) cerebellar nucleus/nuclei
Functional systems associated with the cerebellum

These regions are involved in processing vestibular information
Vestibulocerebellum
These regions are involved in processing cerebral cortical inputs
Cerebrocerebellum
These regions are involved in processing proprioceptive inputs
Spinocerebellum
lateral hemisphere and dentate nucleus
Cerebrocerebellum
flocculonodular lobe,
fastigial nucleus
vermis
Vestibulocerebellum
vermis, paravermis
globose and emboliform nuclei
Spinocerebellum
maintaining equilibrium, posture and head position
Vestibulocerebellar System
uses vestibulospinal tracts
Vestibulocerebellar System
primary vestibular afferents and axons of 2nd order neurons from the vestibular nucleus.
FN lobe and vermis

Purkinje cells in the FN lobe mainly project
directly to the vestibular nuclei

vermis project to the
fastigial nucleus (most) which serves as a relay to the vestibular nucleus.
Vestibulocerebellar System

primary vestibular afferents and axons of 2nd order neurons from the vestibular nucleus.
go thru Inferior cerebellar peduncle
Vestibulocerebellar System Assists in coordinating eye movements with head movements via
connections with the motor nuclei of CN-III, -IV and -VI
coordinating eye movements with head movements
of Vestibulocerebellar System
Vestibular apparatus (position of head in space) –>
vestibular nucleus –> cerebellum à vestibular nucleus
–> CN III, IV, VI via medial longitudinal fasiculus (MLF)


