Cardiovascular Flashcards
In what form does Hb carries about 15% of its respiratory carbon dioxide?
carbaminohaemoglobin
What percentage of respiratory carbon dioxide does Hb carry as carbaminohaemoglobin?
15%
Name three factors that can shift the O2 saturation curve to the right
Increased DPG Increased temperature Decreased pH
What effect does altitude adaptation have on the O2 saturation curve?
Shifts it to the right
What is a typical EDV?
110 to 120ml (Guyton and Hall, 1996)
What is a typical cardiac output?
5-5.25 L/min
What effects does parasympathetic stimulation of the heart have?
Decreased heart rate
What is APTT
Activated partial thrombin time
Identify these valve events


What are the 3 layers of a blood vessel?
Intima
Media
Adventitia
Which vessels contribute most to blood pressure?
Arterioles
Define embolus
Intravascular mass carried in the blood stream to a remote site. May be solid, liquid or gaseous
Define atherosclerosis
Accumulation of lipid and fibrous connective tissue (plaque) in the intima of medium and large arteries
Name 4 ways endothelium is implicated in atherosclerosis
- Endothelial damage increases permeability to LDL
- Damaged endothelium loses its normal anti-coagulant properties
- Endothelium recruits macrophages through expression of selectins, ICAM and VCAM
- Endothelial cells don’t produce as much prostacyclin or NO → impaired vasodilation
What is the ligamentum arteriosum a remnant of?
Ductous arteriosus
What condition is this?

Aortic regurgitation
What does concentric hypertrophy compensate for?
Increased afterload
What is the order of the cardio exam?
General inspection. Palmar creases. Capillary refill. Radial pulse. BP. Conjunctiva. Lips and tongue. JVP. Carotid pulse. Palpate apex beat. Auscultation. Lungs. Shin oedema. Dorsal pedis pulse. Posterior tibial pulse.
Define eccentric hypertrophy
Normal relative wall thickness
Increased LV mass
LV enlargement
Define concentric hypertrophy
Increased relative wall thickness
Increased LV mass
No LV enlargement
Define compliance
ability of any chamber to accept increased volume
What are the constitutive subunits of Hb in adults and foetuses?
Adults: 2 alpha and 2 beta Foetuses: 2 alpha and 2 gamma
What type of blood vessels are these?

Arterioles
What condition is this?

Mitral stenosis
What effects does sympathetic stimulation of the heart have?
Increased heart rate and force of contraction
What 2 forms may a true aneurysm take?
Sacular (unilateral outpouching) and fusiform (bilateral outpouching)
What is the molecular target of heparin?
Heparin enhances activity of antithrombin III, which inhibits factor Xa and thrombin
What percentage of red blood cell dry content does Hb make up?
97%
Name 4 outcomes of atherosclerosis that predispose to CV disease
- Stenosis
- Impaired vasodilation
- Unstable plaque
- Local prothrombotic environment
What makes up about 97% of red blood cell dry content?
Hb
What does eccentric hypertrophy compensate for?
Increased volume (preload)
What are the 4 main classes of drug used to treat hypertension?
ACE inhibitors
Angiotensin receptor antagonists
Beta blockers
Calciium channel blockers
What is a typical ejection fraction?
60% (Guyton and Hall, 1996)
List 5 acute signs of hypovolaemia
Tachycardia
Hypotension
Cold/clammy skin
Poor capillary refill (> 2 secs)
Tachypnea (if severe hypovolaemia)
What are 4 distinguishing features of the phrenic nerve course?
- Runs along scalenus anterior muscle
- Passes between subclavian artery and vein
- Passes anterior to lung root
- Pierce diaphragm
Why does Hb carry nitric oxide bound to a globin thiol group? And when does Hb release it?
It rrelaxes vascular walls and enhance gas diffusion. Hb releases NO at the same time as oxygen.
What type of blood vessel is this?

Arteriole
How is bradykinin degraded?
By angiotension converting enzyme
Define thrombus
Clotted mass of blood that forms within the cardiovascular system during life
Define afterload
Load encountered by ventricle at the beginning of systole.
The amount of work the heart needs to do to eject blood
What effect does beta adrenoceptor stimulation have on the heart?
Increased heart rate and cardiac contractility
What is it called when there is an infection of heart valves?
Endocarditis
What effect does shifting the O2 saturation curve to the right have on Hb affinity for O2?
Decrease
Where does the parasympathetic nervous system innervate the heart?
SA node and AV node
What is the function of lipoproteins?
liporoteins transport fats such as cholesterol in the blood
When CO increases, what happens to venous pressure?
Decreases
Name two mechanisms Hb uses to achieve variable sigmoid binding character for oxygen association
Subunit cooperativity and allosteric effectors
What are 4 important things to ask about when taking a syncope history?
Before. What were you doing before it happened? Did you noticing anything else just before it happened?
During. How long were you unconscious for? Did anyone see it happen…what did they say?
After. How long did it take you to recover? How did you feel afterwards?
PMHx previous episodes? Heart problems?
What is the main risk factor for aortic disection?
Hypertension


What is the characteristic histological feature of elastic arteries?
Up to 50 layers of elastin in the media
How do beta blockers treat arrythymias?
Reduce sympathetic drive to SA node
What are the braches off the arch of the aorta from right to left?
Brachiocephalic a (branches into right subclavian a and right common carotid a)
Left common carotid a
Left subclavian a
What type of blood vessel is this?

Medium vein
What cardiac phase does S2 correspond to?
Isovolumetric relaxation
At the level of which thoracic vertebrae does the heart sit?
T5 to T8
The names of angiotensin receptor antagonists end with what?
-sartan
Define compliance
Ability of a chamber to accept a volume of fluid
Mitral regurgitaiton would typically cause which type of hypertrophy?
Eccentric hypertrophy
Where is the sternal angle?
Horizontal line between manubriosternal joint and T4/T5
Describe 5 steps in secondary haemostasis
1 vessel damage releases tissue factor 2 extrinsic pathway: parathrombin → thrombin, 3 fibrinogen to fibrin, 4 fibrin crosslinks under factor XIIIa control 5 meshwork
What are the contraindications to treatment with ACE inhibitors?
Bilateral renal stenosis
Pregnancy
Angioneurotic oedema
What does the vascular funciton curve describe?
Describes what happens to venous pressure when CO varies
What is cardiac remodeling?
Increase of relative wall thickness without increase in left ventricle mass
What are the 3 components of Virchow’s triad of thrombosis?
Vessel wall Blood composition Blood flow
What is the descending order of WBC concentrations in the blood?
NLMEB
What are the 3 critical intermediates of cholesterol synthesis?
HMG-CoA (hdroxymethyglutaryl-CoA),
isoprene
squalene
What do the names of ACE inhibitors end in?
-pril
What is a typical SV?
70ml (Guyton and Hall, 1996)
What is the molecular target of warfarin?
Vitamin K reductase
Inhibition of this prevents reduced VitK acting as a cofactor for activation of factors 2, 7, 9 and 10
What are the 3 main components of the coagulation system?
Vasoconstriction, platelet plug and fibrin mesh
What type of noradrinergic receptors are found on the heart?
Beta 1 (because you have 1 heart)
Name 3 vasoactive agents that endothelium releases and describe their effect on vasculature
Vasoconstrictor: endothelin
Vasodilator: NO and prostacyclin (PGI2)
How do K+ channel blockers affect arrhythmias?
Prolong cardiac AP by slowing repolarisation
What percentage of the blood is in the arteries?
13%
List 5 factors that may affect the effects of warfarin
Diet (VitK)
Hepatic disease
Hypermetabolic state
Pregnancy
Drug interactions, eg NSAIDs, EtOH
What are the 3 general complications of atherosclerosis?
Infarct
Ischaemia
Aneurysm
Volume overload would typically cause which type of LV hypertrophy?
Eccentric
During which cardiac phase is ventricular volume greatest?
Isovolumetirc contraction
Define preload
The amount of stretch on cardiac myocyte fibres at the end of diastole.
Name 3 substances that have cholesterol as a precursor in their synthesis
Bile acids
VitD
Steroid hormones
The names of beta blockers end in what?
-olol
Define diaphoresis
Profuse sweating
Where are cholinergic receptors on the heart found?
SA node and AV node
What is the upper limit for recommended cholesterol levels?
5.5 mmol/L
A new drug called dozatapril is on the market. What class of drug is this likely to be?
ACE inhibitor
Aortic stenosis would typically cause what kind of LV hypertrophy?
Concentric
Where does ligamentum arteriosum attach?
Bifurcation of pulmonary trunk to inferior aspect of aortic arch
What is the most common cause of LV hypertrophy?
Myocardial infarction
What is the mechanism of action of statins?
All statins are competitive inhibitors of HMG-CoA reductase
What effect do Na+ channel blockers have on the cardiac action potential?
Reduce phase 0 (up phase) slope and peak of ventricular AP as well as shorten repolarisation
What is the average heart mass of a healthy young adult?
159g
Name three factors that can shift the O2 saturation curve to the left
Decreased DPG Decreased temperature Increased pH
How do Ca2+ channel blockers improve arrhythmias?
Reduce heart rate and conduction through SA and AV node
Name 7 modifiable risk factors for atherosclerosis
- Hypertension
- Smoking
- Diabetes mellitus
- Obesity
- High LDL:HDL ratio
- Physical inactivity
- Proteinuria
What are the ‘big 5’ risk factors for atherosclerosis?
Hypertension
Diabetes
Hypercholesterolaemia
Smoking
Family history
How is ejection fraction calculated?
EF = (SV/EDV) * 100
Where does the sympathetic nervous system innervate the heart?
SA node, AV node and ventricles
Which factors does warfarin inhibit?
2, 7, 9, 10
Which 3 things will affect SV?
Preload
Cardiac contractility
Afterload
Describe 4 steps in primary haemostasis
1 Vessel damage exposes von Willibrand factor on basement membrane and collagen 2 vWF binds to Gp1b on platelets 3 Platelet: adhere, flatten, recruit, degranulate (ADP and thromboxin A2) 4 platelet plug
Hypertension would typically cause which type of LV hypertrophy?
Concentric
Which ventricle is less compliant?
Left (because has thicker wall)
What percentage of the blood is in the heart?
7%
What percentage of the blood is in the capillaries?
5%
During which cardiac phase is ventricular volume least?
Isovolumetric relaxation
A new drug called buprolol is on the market. What class of drug is this likely to be?
Beta blocker
How is hypertension Dx?
Chronic BP greater than 140/90 mmHg
Branches of the descending aorta supply which 4 structures?
Intercostal aas
Pericardium
Esophagus
Bronchial aas
What cardiac phase does S1 correspond to?
Isovolumetirc contraction
What are the 4 major classes of drugs used for arrhythmias?
Beta blockers
Calcium channel blockers
Sodium channel blockers
Potassium channel blockers
Fluid in the pericardial cavity is called what?
Pericardial effusion
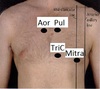
What are these areas?

What is INR and how is it calculated?
International normalised ratio INR = (patient PT/normal PT)^ISI INR = (Patient prothrombin time/mean normal prothrombin time)^international sensitivity index
What effect does shifting the O2 saturation curve to the left have on Hb affinity for O2?
Increase
What condition is this?

Aortic stenosis
Which substance mediates endothelial vasoconstriction in coagulation?
Endothelin
Describe 5 steps in the feedback loop of short term regulation of low blood pressure
- Low blood pressure sensed by stretch receptors in carotid sinus in internal carotid artery
- Less stretch causes less firing of glossopharyngeal nerve to nucleus of solitary tract in medulla
- Sympathetic nervous system stimulated
- Sympathetic nervous system:
- Increases heart rate (chronotropic)
- Decreases AV conduction time
- Increases cardiac contractility (inotropic) (more Ca2+ released per contraction)
- Increases TPR (alpha adrenocetpors)
- Increase venous tone (don't want blood hanging around uselessly in the veins) - Blood pressure increased
Define left ventriuclar hypertrophy
Increase in lefr ventricle mass relative to body size
How do beta blockers lower blood pressure?
Reduce cardiac output and renin release through antagonism of beta 1 +/- beta 2 adrenocetpors
How is left ventrilce relative wall thickness calculated?
T/D
Thickness of wall / Diametre of chamber
What percentage of the blood is in the lungs?
10%
What are 3 important qualities to establish when taking a history of palpitations?
1 Rhythm. Regular or irregular? Can you tap out the rhythm?
- Rate. Faster or slower than normal?
- Strength. Stronger or more forceful than normal?
What percentage of the blood is in the veins?
65%
List 8 actions of thrombin
Fibrinogen → fibrin V -> Va VIII -> VIIIa IX -> IXa XI -> XIa XIII -> XIIIa Binds to thrombomodulin (inhibits Va and VIIIa) Platelet activation
Which factors is vitamin K a co-factor for?
2, 7, 9, 10
ie the same cofactors that warfarin affects
A raised INR indicates which 2 possible things?
There is a problem with Factor VII or the patient is on warfarin
Define anaemia and which two blood tests are used most often in diagnosis
A reduction of the total circulating red cell mass below normal limits.
Haematocrit and haemoglobin concentration
Dietary deficiences of which 3 substances may cause anaemia?
Iron, VitB12, folate
What is the molecular action of calcium channel blockers?
Inhibit voltage-gated L-type Ca2+ channels
What effect does adrenaline have on TPR and how?
What receptors are involved?
Increases TPR due to vasoconstriction.
Stimulation of alpha adrenoceptors.
A new drug called stortosartan is on the market. What class of drug is this likely to be?
Angiotensin receptor antagonist
Name 2 substances that may be elevated in blood after death of cardiac myocytes
Troponin I and T
Creatine kinase MB
What type of aneurysm is classically seen on the circle of Willis and what is this called?
Sacular aneurysm
Called a berry aneurysm
What is the most lateral structure in the mediastinum?
Phrenic nerves
At what vertebral level does the aorta pass behind the diaphragm?
T12
Identify these stages of the cardiac cycle


What is a typical ESV?
40-50ml (Guyton and Hall, 1996)
What type of blood vessel is this?

Small vein.
The wall of the vein consists of two to three layers of smooth muscle fibres. Note the wide diameter of the lumen relative to the thickness of the wall.
What type of blood vessel is this?

Capillary
At what vertebral level does the inferior vena cava pass through the diaphragm?
T8
Name these volumes or pressures


What is the molecular target of ACE inhibitors?
Block conversion of Angiotensin I to Angiotensin II by inhibiting angiotensin converting enzyme
Where does left anterior descending artery supply?
LAD supplies anterior surface and anterior 2/3 of interventricular septum
Where does circumflex artery supply?
lateral wall of LV
Where does posterior interventricular artery supply?
Inferior part of LV and posterior 1/3 of interventricular artery
How soon after an AMI will cardiac enzymes begin to possibly be elevated?
3 hours
How long after the event will cardiac enzymes be a sensitive measure of AMI?
6 hours
How soon after an AMI must repurfusion be to be effective?
6 hours
Which artery most commonly supplies the atrio-
ventricular node?
Right coronary artery
What is the most common inherited genetic disease of hypercoagulability of blood?
Factor V Leiden mutation
Which bacteria classically causes subacute bacterial endocarditis?
Viridans strep
Why is aspirin given in low doses as a blood thinner?
Low dose maintains selectivity for platelets because it will be at a low concentration by the time it reaches endothelium
Why do some NSAIDs increase bleeding time?
They impair thromboxane A2, thus impairing platelet aggregation
Where is the SA node?
In the right atrium, at the top of the crista terminalis and sweeps across in front of the SVC
Where is the AV node
In the right atrium, between tricuspid valve and coronary sinus


