Bones: Neurocranium Flashcards
(167 cards)
16

Arterial Grooves
11, 12, 13

External Table
Diplöe - spongy inner portion analogous to the trabecula in long bones
Internal Table

Superior sagittal sulcus
the groove for the superior sagittal sinus is a depression formed on the internal surface of the frontal, parietal, and occipital bones in the midline.
It courses from the frontoethmoid junction to the internal occipital protuberance.
32

petro-occipital fissure

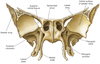
Frontal Bone
- know: frontal sinus, frontal orbits, supraorbital margin

Frontal crest
the union of the superior sagittal sinus sulcus margins
the entire ridge!

1

Fossa for lacrimal gland
houses lacrimal gland

glabella
slightly depressed area of frontal bone that joins the two superciliary ridges.

Frontal or Metopic suture
only the part of the highlighted bone within the eye socket

Frontal Orbits
What is this area (not anterior cranial fossa, but part of a single bone)?
What are the special markings to note on it?

Orbital Plate of the Frontal Bone
- could consider it the “roof” of the orbits
- its impressiones digitataes (“finger impressions”) correspond to the convolutions of the brain
1, not the bone but the portion of it

Squamous Portion of Frontal Bone
2

Frontal Sinus
area defined in red

supraorbital margin of frontal bone
tiny blue-marked area at top of eye socket

supraorbital notch, or foramen if it is more hole-like
2

Trochlear pit or fossa

Supraciliary arch
2

Frontal tuber or eminence
Tiny green area in anterior of skull here:
What bones make it up?

Foramen Caecum
- made up of alae of crista galli (of ethmoid) and frontal bone
- transmits emissary vein from nose to sup. sagittal sinus but is frequently closed
What is this hole and what does it connect?

Jugular Foramen
- connects external base of skull to posterior cranial fossa

blue

piri form aperature
“pear shaped”

Occipital Bone
know: Foramen Magnum, Occipital Condyles, Superior/ Inferior Nuchal Lines

Cerebellar fossa

Cerebral fossa