Blood Vessels of the Body Flashcards
Aortic Arch Branches

Brachiocephalic trunk àsplits into R Subclavian and R Common Carotid
- R Subclavian aheads to right arm
- R Common Carotid aheads to head
- L Common Carotid aheads to head
- L Subclavian aheads to left arm

Subclavian Artery will travel underneath the clavical
Axillary Artery (first rib to attached of tres major attaches to the interubercular groove) betwn section is same blood vessel just changing the name - axilla means armpit
Brachial Artery - where tres major inserts against the humerus running over upper arm
- Deep brachial artery (posterior and lateral) - help supply deeper muscles - triceps, bachialiis reconnects at the elbow also an example of an anatomosis. Can feel brachilla plus
- Radial artery (lateral) and ulnar artery (medial) at the elbow
- At the wrist you can palpate the radial artery (can feel radial pulse)
- Sidenote: pulses get us to know how to heart’s doing, pattern or skip beats, check for pufusion in body, tissues will die not getting enough oxygen. By palpating the the pulse is important on what the heart is doing.
Hand Deep Palmar Arches right against the metacarpals
Superficial Palmar Arch - superficial and distal on the metacarpals, muscles between.
Give rise to the digital arteries and then supply the digits of the hand
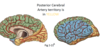
Ateries Supplying the Brain
In the neck top of larynx (top of throat) split into the internal (which is going up to head up through the carotid canal)/external (heads outside the skull) carotid artery. Pulses are taken distal to the split on the external carotid artery.
Different branches , temporal brand, maxillary and branch of that goes to the foramen spinosum (tiny pinhole)
Internal carotid artery goes throught carotid canal and enter into the cerebrum
2nd artery supplies the brain - Vertebral artery supplies brain stem one on each side
The Blood Supply of the Brain

Internal carotid gives supply to the different blood vessels
WE have anastomoses (Circle of Willis) - ensuring different blood supply in the brain and important if there is a blockage it can find another direction and supply the tissues
90 degree turn is midbrain
2 vertabral artereries on left and right and come together to create the Basilar Artery and continue up over the pons and midbrain then split to
Posterior Cerebral Artery - parahippocampus gyrus, fusiform gyrus, occiptial lobe
- Posterior Communicating Artery - more of connectors to the posterior carotoid artery and internal carotid
Internal Carotid Artery - will split
- Middle cerbral artery head laterally and out to the Sylivian Fissure and supply the whole lateral aspect of the brain
- Anterior Cerebral Artery - come forward to the frontal pole of brain then goes up and loop backwards within the longitudinal fissure over the Corpus Collsum
Anterior Communicating Artery - small, and most of time no blood flowing through it bc the pressure is high enough to push blood through the anterior cerebral arteries. the only time we see blood is if there’s a blockage
Anterior Cerebral Artery (ACA)

- Branches anteriorly off the internal carotid and loops over the corpus collsum
- Left/Right ACA
- Supplies the anterior pole of the brain as well as most of the brain regions within the longitudinal fissure
- What would be the deficits if there was a stroke in the ACA? (most proximal spot)
- medial frontal gyrus - math problems think abstractly
- working memory, memory recall
- homongulus longitudinal fissure - lower extremidities and gentials (right hemisphere have difficulty moving left lower extremities)
Middle Cerebral Artery (MCA)
- Branches off the internal carotid
- Passes through the Sylvian Fissure and supplies most of the lateral hemispheres of the brain
• What would be the effect of a stroke in the MCA?
- Superior central gyrus - Wernike’s aphasia - can’t process incoming sound
- audip and visual processing
- middle front gyrus (memory recall) and inferior frontal gyrus Broca’s
- from homuclus - upper extremities and face
- Left hemisphere, sensation and motor function on right side of the face and right upper extremities

Posterior Cerebral Artery (PCA)
- Formed from Basilar Artery
- Supplies the midbrain and ventral surface/occipital lobe
- What would be the effect of a stroke in the PCA?
- Vision on Occiptal lobe
- Fusiform gyrus in the middle
- Inferior temporal gyrus
- Parahippocampal gyrus
- Uncus - smell
- Parkinson Disease
Cerebrovascular Accidents (CVAs) - Strokes

Similar to effects of a blockage of a coronary artery, but this time brain tissue dies
- Section of the brain loses oxygen and those neurons die
- Due to plaque build up or thrombus occuldes
• Can also be hemorrhagic if an aneurysm bursts
- Embolism a piece of thrombus breaks off and travels to the blood supply and gets into a small. atery and blocks flood flow
- hermorrhage when the blood vessel burst opens
- aneugysms when blood vessels swell but doesn’t break. we have some in our brain that doesn’t cause problems but for some individuals they burst and problem could cause problems with nuerons and blood can fill in the subarachnoid space where the blood vessels are
- Due to lack of oxygen lack of blood supply
*
Venous System of the Brain Cerebral

- Cerbral veins
- superficial set - all feed into the superior sagittal sinus - made of dura mater, also cerebrospinal fluid circulates through the subarchanoid space around brain, spinal cord and exit points one way valve whcih feed into the superior sagittal sinus to take the fluid back into circulation then new CSF will be formed by the choroid plexus
- Inferior Sagittal Sinus right above the Corpus Collosum, collecting blood from the veins deep within the brain feeds to the straight sinus and joins w/ the superior sagittal sinus at the posterior aspect of brain betwn occiptal lobes and cerebella hemispheres confluences of sinuses where superior saggital sinus and inferior sagittal sinus, straight sinus come together to bring deoxygenated blood
- Confluence of of sinuse we have transverse sinus runs horizontallly betwen occiptial lobes and the cerebellar hemispheres
- Heads inferiorly through the sigmoid sinus and down through the internal jugular vein - return the blood to the subclavian vein which will feed into our superior vena cava and bring deoxygenated blood back to heart
Arteries Supplying the Visceral Organs (Abdomen)

- Phrenic artery tarveling through the diaphragm to supply it with blood - first ones that brand off the aorta one on each side
• Celiac Trunk splits into the: thich stock - one truck
a. Splenic artery - head out towards the spleen filters old red blood cells and being a site where white blood cells can be produced, part of our immune system some branches to the pancreas, and then larger branch epiolic artery - supplies spleen and greater curvatrue of stomach
b. Common Hepatic artery - large artery supplies the liver and greater curvature of stomach some branches that supply the stomach or first part of the small intestine
c. Left Gastric artery - supplies the stomach lesser curvature
* Right gastic artery - lesser curvature of the stomach
Arteries Supplying the Visceral Organs
- Superior Mesenteric artery: supplies small intestine and first half of large instestine
- Renal arteries: one on each side Renal referes to kidneys - kidneys so filter so toxins don’t remain in our blood
- Gonadal arteries: Gonads (sex organs)
- ovarian arteries one on each side (female)
- testicular one on each side (male)
• Inferior Mesenteric artery: supply last half of colon and part of the rectum - only have one
Arteries Supplying the Visceral Organs
Level l4
- Internal Iliac Artery:
- Right common illiac artery
- right internal iliac
- left internal iliac
- Within our pelvis illum
- Supply blood to bladder, uterus sex organs (penis, clitouris, penis, rectum
- • External Iliac Artery:
- Down the legs and lead to blood supply down the legs
- Left external iliac
- Right external iliac
External Iliac Artery
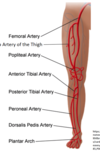
External Iliac Artery
- Femoral Artery main artery of the thigh - if you cut it you will bleed out quickly
- Deep Artery of the thigh - supplies all hamstring muscles, adductor muscles and some of the quadriceps
- Femoral through the adductor magnus and called
- Popliteal Artery - behind the knee
- Anterior Tibial Artery - head towards anterior side and deep to dorsiflexor muscle and lead to an artery
- Dorsalis pedis - occurs at about the ankle and sits close to the first and second metatarsals
- if you palate there and can’t feel a pulse and go back to the knee and feel the popliteal artery pulsing with diabeties there. is no perfusion with the tissues in the distal extremities and those tissues will die so our abilitiy to palate this artery can give us an idea if the toes are still supplied with blood. Lack of color looks kinda of chalky if coldness and pain - problem with purfision in lower extremities
- Posterior Tibial - run down the backside of lower leg and run to bottom foot and give rise to
- medial and plantar arteries ateries on each side
- come together to form the plantar arch and give rise to metatarsal arteries and then digital arteries
- Anterior Tibial Artery - head towards anterior side and deep to dorsiflexor muscle and lead to an artery
- Anastomoses at the knee bc how often our knees are bent and could be cutting off circulation in the arteries
Arcuate Artery Plantar Arch
Venous System
- Veins typically run next to arteries
- Veins are typically named the same as the arteries they run next to
- Where do veins from the lower extremity and thorax drain into?
- Inferior vena cava will return blood from the lower extremities and the thorax and then from the head and arms above the diaphram and go through the superior vena cava
• Where do veins from the head and arms drain into?
Veins of the thorax and right upper limb, anterior view
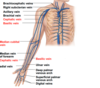
- Cephalic vein - lateral side of forearm and join up with the cephalic (head)
- Basilic vein - superficial vein that’s going to fun on the medial aspect of the forearm and the brachium and jon up to the subclavian vein - runs up base to arm
- Median cubital vein - onnecting vein between cephalic and basillic - important vein bc where we draw blood from
- with the venous system if there is a blockage or clot the blood will find another vein to run through
Veins in Lower Extremidities
Femoral Vein - Deep vein runs alongside the femoral artery. It’ll travel throuhg that adductor hiatus along with the femoral artery
Great Saphenous Vein (superficial) - branches off really high into the groin. Longest vein in body and pieces of it will be harvested when a cornoary artery bypass graft will need to be done on the heart.
Small Saphenous Vein - Posterior caft and lower leg (lateral) and join back up wih the popliteal vein which drains into the femoral vein


