Block 3: Basal ganglia Flashcards
Describe the general pathway/ flow of information between the primary motor cortex and basal ganglia
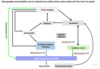
- Primary motor cortex activity sends excitatory output to the basal ganglia
- Basal ganglia main output is inhibitory to the thalamus
- The amount of activity in the basal ganglia can be modulated by different inputs to either increase thalamic inhibition or reduce it.
- If the thalamus is activated it sends excitatory impulses to primary motor cortex
- Motor cortex output to the muscles via the corticospinal and corticobulbar tracts –> movement
- Therefore activation of the basal ganglia reduces the activity of the thalamus which in turn reduces the activity of the primary motor cortex and restricts movement.

What structures form the striatum?
- Caudate nucleus and putamen= striatum

What structures form the lentiform nucleus?
- Lentiform nucleus = putamen + globus pallidus internus + globus pallidus externus

What structures form the pallidum?
- Globus pallidus internus and externus + substantia nigra pars reticula (SNPR).

What are some key components of the basal ganglia circuit?
- Primary motor cortex
- Thalamus and subthalamic nuclei
- Putamen
- Globus pallidus internus and externus
- Caudate nucleus
- Substantia nigra pars reticula (SNPR)
- Substantia nigra pars compacta (SNPC)

Label the image


Label the image


Label image


Label the image


What do the two thalami represent?
What is an immediate lateral relation to the thalamic lobes?
- The two thalami (L and R represent an organised collection of nuclei involved in following functions:
- sensory
- auditory
- visual
- limbic
- motor- associated
- Immediate relation = internal capsule

Label this Left sided lateral view of the thalamus.


What are each of the functions of the thalamic nuclei shown?


The caudate nucleus is large in size and connects anteriorly with the ________ and follows the curve of the _________ _________.
Label the image

The caudate nucleus is large in size and connects anteriorly to the putamen and follows the curve of the lateral ventricle.

Fill in the blanks

The basal ganglia and cerebellum modulate the output of the primary motor cortex, fine tuning its output
What is the main theory surrounding basal ganglia function?
- The main theory is that there is an indirect and direct pathway that operates in balance to basal ganglia output and therefore movement.
Describe the direct pathway
- Motor cortex initiates movement by sending excitatory input to the striatum.
- The striatum is now activated and inhibits the globus pallidus internus and SNPR.
- Inhibition of the globus pallidus internus/SNPR released the inhibition on the thalamus
- The thalamus is now disinhibited and able to excite the motor cortex
- The motor cortex sends excitatory inputs via the corticospinal and corticobulbar tracts to the muscles –> movement.
- This pathway is further stimulated by input from the substantia nigra pars compacta (SNPC) which sends dopaminergic excitatory input to the striatum and acts via D1 receptors.

What is parkinsons disease associated with?
- Parkinson’s disease is associated with loss of dopaminergic neurones in the substantia nigra pars compacta, which normally sends excitatory input to the striatum, relieving inhibition on the thalamus and enbaling voluntary movement.

Describe the indirect pathway
- Again the cortex excites the striatum, however now the striatum inhibits the Globus pallidus externus (GPe).
- Inhibition on the GPe prevents inhibition of the subthalamic nucleus
- The subthalamic nucleus can now activate the Globus pallidus internus/ SNPR which inhibits the thalamus
- Inhibition of the thalamus inhibits motor cortex output and therefore movement.
- The Substantia nigra pars compacata will act to inhibit this indirect pathway by sending inhibitory dopaminergic input to the striatum which prevents its inhibition of the globus pallidus externus. Globus pallidus externus can now inhibit the subthalamic nucleus, which releases the thalamus from inhibition by the GPi/ SNPR.

How does Huntington’s disease occur?
- Huntington’s disease occurs due to a loss of GABA-ergic neurons that project from the striatum to the Globus pallidus externus, inhibiting the GPe.
- Inhibition of GPe prevents its inhibition of the subthalamic nucleus.
- Subthalamic nucleus now free to activate GPi/ SNPR which inhibits that thalamus and prevents unwanted movement.
- Loss of GPe inhibition leads to GPi hyperactivity and hyperkinetic disorder.
- Huntington’s characterised by choreoathetosis- involuntary movements with irregular migrating contractions (chorea) and athetosis (writhing and twisting movements).



