auditory function and balance Flashcards
anatomy: summarise the anatomy of the ear, cochlea and labyrinth (23 cards)
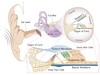
diagram of ear

diagram of external ear canal, middle ear, cochlea and labyrinth

diagram of anatomy of labyrinth

superior projection of right bony labyrinth on base of skull: diagram and angles of canals
as stimulus is movement, important to have correct orientation; anterior canal 45 degrees forward, posterior canal 45 degrees back, lateral canal 30 degrees (in between)

2 components of outer ear
pinna (auricle) and external acoustic meatus (external auditory meatus/auditory canal)
function of outer ear
collects and conduct sound waves towards tympanic membrane
location of middle ear
air-filled chamber in bone, lying between tympanic membrane laterally and oval and round windows medially
2 components of inner ear
cochlea and organs of balance; inner ear in petrous part of temporal bone (well protected); ampulla on one end of canal, not on other end
function of inner ear
hair cells transduce mechanical energy of sound into electrical signal in cochlear nerve
diagram of auditory pathway

diagram of middle ear

anatomical features of cochlear
hollow tube in bone, curled into spiral; divided longitudinally into 3 compartments, separated by 2 membranes; cochlear hair cells attached to basillar membrane
2 membranes of cochlear which vibrate with sound waves
vestibular (Reissner’s) and basillar membranes
diagram of cochlea

anatomical features of organ of corti
hair cells surrounded by support cells; tectorial membrane; spiral ganglion embedded in modiolus; stria vascularis secretes endolymph (high in K+ and low in Na+)
feature of tectorial membrane
gelatinous so doesn’t vibrate with sound
what does spiral ganglion innervate
hair cells
diagram of organ of corti (spiral organ)
how many otolith organs in each ear, and what are the two components
5 otolith organs (saccule and utricle)
what is the saccule connected to
cochlear
what is the utricle connected to
saccule
what connect to utricle
semicircular canals (anterior, posterior, lateral)
why is there fluid in vesitbular part of labyrinth as well as auditory part
help move hair cells to make transduction due to movement of head


