auditory function and balance Flashcards
middle ear function: explain the mechanisms for amplification and protection of the middle ear
how is amplification achieved
lever system of articulated ossicles and ratio of area of tympanic membrane to oval window protective mechanisms
what does the ear project the stimuli onto, how is this accomplished, and where are these
projects stimuli onto hair cells, via a series of mechanical coupling, which are the sensory receptor of the inner ear within the cochlea
structure of hair cells
have a hair bundle on projecting surface, which is a cluster of modified microvilli (stereocilia)
where do superior olivary complex neurones send feedback to
hair cells (mainly outer hair cells)
effect of activity in superior olivary complex neurone fibres
increases representation of signals in noise and protects it from damage by loud sounds
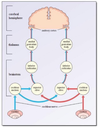
diagram of superior olivary complex neuronal feedback

2 functions of activity of superior olivary complex neurones
balance responses from the two ears; reduce cochlea sensitivity
what reduces amplitude of vibrations passing through ossicles
reflex contraction of tensor tympani and stapedius muscles
what does auditory tube allow
equilibration of air pressure on either side of tympanic membrane
2 types of hair cell
inner and outer hair cell
how are inner hair cells arranged and innervated
3500 in single row, densley innervated by 10 sensory axons per cell (provide info for brain)
how are outer hair cells arranged and innervated
20000 cells arranges in 3 rows, sparsely innervated, with 1 axon innervating several cells
function of outer hair cells
efferent nerve causes cells to change shape -> amplifies response to sound of adjacent inner hair cells at centre of vibration
diagram of auditory pathway from cochlea to brain