Anatomy-Facial & Trigeminal Nerves Flashcards
CN V Sensory functions
Face, Cornea, Dura, Ant. 2/3 tongue, nasal cavity & sinuses.

CN V motor functions
1st pharyngeal arch muscles: MM MATT: Mastication, mylohyoid, Ant. Digastric, tensor tympani, tensor veli palatini.
Nucleus for trigeminal nerve motor fibers location in the medulla.
Motor nucleus of V. It is located superior to the nucleus ambiguus (arches 3,4,6). Note that it is still in the column of nuclei that innervate the pharyngeal arches.

What autonomic fibers are associated with CN V?
No pre-ganglionic fibers are, but many post-ganglionic fibers hop on CN V to get to their target tissue.
Where do the initial branches off the trigeminal nerve pass through?
V1) Cavernous sinus -> Superior orbital fissure on its way to the orbit. V2) Foramen rotundum on its way to pterygopalatine fossa. V3) Foramen ovale on its way to the infra temporal fossa.

What type of nerve fibers from CN V innervate the regions shown below?

These regions are innervated by V1. V1 is solely sensory.
What branches arise from V1 in the orbit?
“NFL” Nasociliary. Frontal. Lacrimal.

What clinical correlations are associated with the nasociliary nerve?
It gives off the long ciliary nerve which pierces the back of the eyeball to innervate the cornea. This is involved in the sensory component of the cornea reflex. The sympathetic fibers from the superior cervical ganglion also course with the long ciliary nerve to innervate the dilator pupillae.
What type of nerve fibers from CN V innervate the regions shown below?

V2 sensory fibers.
Where does V2 go after it enters the pterygopalatine fossa? How else does V2 branch?
Some fibers pass through the pterygopalatine ganglion (they do not synapse, they just divide) -> greater & lesser palatine nerve. The other branches of V2 are the superior alveolar nerves, zygomatic nerve and infraorbital nerve.

When does the maxillary nerve become the infraorbital nerve?
At the point where the posterior superior alveolar nerve comes off the maxillary nerve.
What nerve innervates the regions shown below?

V3. Note that it has both sensory and motor innervation.
How does V3 branch after passing through the foramen ovale?
Anterior division: all motor nerves except buccal nerve (sensory to cheek). Posterior division: all sensory nerves except mylohyoid nerve (motor to digastric and mylohyoid).

A patient present with loss of sensation to the face, cornea, conjunctiva, mucosa of the nose, mouth & anterior 2/3 of tongue. Physical exam reveals loss of direct & indirect corneal reflex when they eye is touched. She also has mandible deviation to the right side. Where is the lesion in this patient?
Up near the brainstem where you can lesion all right CN V fibers. You know it is right because she has lost muscles of mastication and the jaw will deviate towards the side of weakness.
A patient presents to the clinic complaining of excruciating pain in his face every time he chews, laughs or blows his nose. The pain lasts 1-2 minutes every time he does this. What is your diagnosis?
Trigeminal neuralgia. This can be caused by displacement of a blood vessel that compresses the trigeminal nerve.
What could cause the lesion seen below to distribute in this manner?

Herpes zoster virus can get into the V1 trigeminal ganglion and cause damage to the region it innervates.
What are the 4 components of CN VII found in the lower pons?
Green = motor nucleus of VII (arch 2 muscles). Purple = superior salivatory nucleus (lacrimal & salivatory glands). Blue = solitary nucleus (taste). Orange = spinal Vth (ear sensation).

How are the components of CN VII divided between the two roots?
Motor root gets LMNs. Intermediate nerve gets somatosensory, parasympathetic and taste fibers.

Where does CN VII go after it goes through the internal acoustic meatus?

Motor root and intermediate roots join together at the end of the internal auditory meatus -> facial canal (lies on top of vestibule) -> geniculate ganglion -> gives off greater petrosal branch -> bends into posterior wall of middle ear cavity -> gives off nerve to stapedius and corda tympani -> rest of CN VII goes out stylomastoid foramen -> gives out terminal branches in parotid gland

CN VII’s course in tear production.
Branch of greater petrosal nerve carries the preganglionic parasympathetic fibers for lacrimation -> anterior face of petrous temporal bone -> groove for greater petrosal nerve -> foramen lacerum -> postganglionic sympathetic fibers hop off ICA to form deep petrosal nerve that joins w/ greater petrosal nerve -> nerve of pterygoid canal -> synapse in pterygopalatine ganglion -> postganglionic fibers hop on V2 -> then V1 -> lacrimal nerve!

What neurons are overactive when people have hay fever?
Post ganglionic fibers projecting from the pterygopalatine ganglion (CN VII).
What structure contains preganglionic parasympathetic fibers for the sublingual and submandibular glands. What other fibers does it contain?
Chorda tympani. It also contains taste fibers from the anterior 2/3 of the tongue. Note that it joins the lingual nerve (V3) on its way down. The parasympathetic fibers will synapse in the submandibular ganglion. Finally, note that the taste fibers will synapse in the geniculate ganglion.

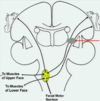
Which of these patients has a lower motor neuron lesion of the facial nerve (peripheral facial nerve palsy)? Which has an upper motor neuron lesion of the facial nerve?

A: LT UMN. Note that the forehead is spared and UMN lesions will show contralateral symptoms. B: RT LMN: Note that the forehead also is paralyzed. LMN lesions will affect the ipsilateral side.

What locations can be damaged to cause peripheral facial nerve palsy?
This is lower motor neuron damage. It can be damaged anywhere along its course to the muscle, at the motor nucleus of VII in the pons or where it exits the pons as the intermediate nerve and motor root.

Clinical symptoms patients present with peripheral facial nerve palsy?

Ipsilateral inability to smile, inability to close eye tightly, inability to raise eyebrow, difficulty chewing, blink reflex absent when cornea is touched and smoothed out appearance of the face. If you damage the nerve before the nerve to the stapedius, patients will complain that noises are louder than normal, decreased salivation (chorda tympani), dry eye (loss of lacrimation from greater petrosal nerve) and loss of taste to anterior 2/3 of tongue.

Which brainstem nuclei receive input from primary motor cortex corticobulbar fibers?
CN V, VII, IX, X, XI & XII because they are all involved in control of muscles of the face. CNs III, IV and VI receive separate input because they control muscles of the eye.

What is the big difference between corticobulbar fibers and corticospinal fibers?
They innervate brainstem nuclei bilaterally. This helps protect many of the lower motor neurons of the head from unilateral upper motor neuron lesions.
Why are the muscles of the upper face spared and lower face paralyzed in unilateral lesions of the corticobulbar tract?
The upper face has bilateral input from the corticobulbar tract. The lower face has unilateral input and will be paralyzed.