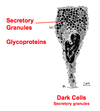
9-Histology brainscape Flashcards
(75 cards)





1= Stratum Basale 2= Stratum Spinosum 3= Stratum Granulosum 4= Stratum Lucidum 5= Stratum Corneum

Stratum Basale (note Desmosomes & Hemidesmosomes)







Left= Thin Skin Right= Thick Skin

Melanin granules of stratum spinosum with light coming from top down












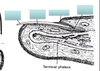
*Note underneath the nail plate is the hyponychium Matrix: part of epidermis responsible for nail formation Bed: Stratum basale & spinosum- physical support for nail plate Eponychium: cuticle, stratum corneum to protect underlying nail matrix from infection



paste-36597416329758.jpg

paste-36610301231663.jpg

paste-36644660969990.jpg

paste-36657545871878.jpg

paste-36713380446750.jpg

paste-36726265348696.jpg

paste-37344740639262.jpg

Sebaceous gland - simple branched acinar gland *Stem cells at bottom
paste-37379100377630.jpg

paste-37391985279518.jpg

paste-37417755083294.jpg

paste-37430639985182.jpg

paste-37464999723364.jpg
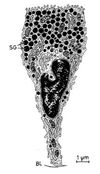
Screen Shot 2014-03-30 at 3.09.15 PM.png Eccrine Glands