(8.1) Intro to Biotransformation, Pharmacogenomics and Clinical Drug Trials (Kruse) Flashcards
What is drug biotransformation?
Enzymatically driven process whereby a substance is changed from one chemical to another
What is the general method of eliminating compounds?
Biotransformation into more polar and sometimes larger derivatives
*Polar and water soluble products are more readily excreted by the kidneys
What is a prodrug?
An inactive drug that undergoes biotransformation to become an active drug
Where does biotransformation primarily occur?
Mostly the liver
What is the first pass effect?
The process by which oral drugs undergo extensive biotransformation after absorption prior to entering circulation
Drugs administered __________ do NOT undergo first-pass biotransformation
Paraenterally
As a general rule:
Phase I reactions….
Phase II reactions…
Phase I reactions = INACTIVATION of the drug
Phase II reactions = ENHANCES ELIMINATION
Describe the mechanism of a phase I reaction
Enzymes convert the parent drug to a more polar metabolite by introducing or unmasking a functional group
Oxidation, reduction and hydrolysis reactions
Describe the mechanism of phase II reactions
Enzymes form a conjugate of the substrate (phase I product)
Conjugation with endogenous substrates to improve water solubility and increase molecular weight
PHASE II REACTIONS ARE ANABOLIC
What are phase I reactions carried out by?
Mixed function oxidases (MFOs)
- Cytochrome P450s
- Flavin-containing monooxygenases (FMO)
- Epoxide hydrolases (mEH, sEH)
What is the MOST important of the cytochrome P450 enzymes?
CYP34A
What are examples of phase II enzymes?
UGT : UDP-glucuronosyltransferase
GST : glutathione-S-transferase
NAT : N-acetyltransferase
TPMT : Thiopurine methyltransferase
SULT : Sulfotransferase
What is the clinical relevance of biotransformation?
Individuals differ in drug distribution and in their rates of drug metabolism and elimination
Define:
Pharmacogenetics
The study of differences in drug response due to allelic variation in genes affecting drug metabolism, efficacy, and toxicity at the genomic level
Define:
Pharmacogenomics
The study of the entire genome to assess multigenic determinants of drug response
Define:
Polymorphism
A variation in the DNA sequence that is present at an allele frequency of 1% or greater in a population
What is the most common disease producing enzyme defect of humans?
Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency
Describe the basic timeline of drug development and clinical trials
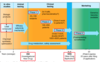
Define:
No-effect dose
The maximum dose at which a specified toxic effect is not seen
Define:
Minimum lethal dose (LDmin)
The smallest dose that is observed to kill any experimental animal under a defined set of conditions
Define:
Median lethal dose (LD50)
The dose that kills approximately 50% of the animals


