(21.1) Sleep and EEG, [includes DSA and Lecture] (Karius) Flashcards
(24 cards)
__________ in an EEG are often considered pathological
Clear “patterns” in an EEG are often considered pathological
When do alpha waves occur?
Quiet wakefulness (thinking) with eyes closed

When do beta waves occur?
Alert wakefulness with eyes open
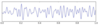
What is happening here?
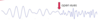
Alpha Block
Someone is having their EEG measured with eyes closed, then once eyes open, abrupt change in wave pattern
Where are these waves most prevalent?
Alpha waves =
Beta waves =
Alpha waves = Occipital lobe
Beta waves = Frontal and parietal cortex
When do gamma waves occur?
Individual is aroused or focused on something
***Especially prominent when planning a motor response

Gamma waves require the ____________
Hippocampus
When do Theta waves occur?
Normal in children
In adults, may occur with frustration or disappointment
Also occur in sleep

Theta waves originate from the…
Hippocampus
When do delta waves occur?
Deep sleep in adults
Infants
What would a delta wave during “wakefullness” indicate?
Serious organic brain disease

Reduced metabolism leads to ________________ that can be observed on en EEG
Reduced metabolism leads to reduced neuronal activity that can be observed on en EEG
What stage of sleep is associated with vivid dreams that you remember?
REM sleep
Dreams do occur during non-REM sleep, but that are generally _______________
Dreams do occur during non-REM sleep, but that are generally rehashing of day’s events
The __________ controls both the circadian rhythm and sleep induction/arousal separately
The hypothalamus controls both the circadian rhythm and sleep induction/arousal separately
What actiates the VPO neurons thus inducing sleep?
Adenosine
It is crucial to prevent muscle activation during dreams.
What is responsible for that?
Locus Ceruleus
Provides inhibitory input to alpha-motoneurons
What does the locus ceruleus“spare” during it’s inhibitory actions?
Spares the:
Diaphragm and Small muscle groups
_________ released from the locus ceruleus activates the LC neurons. These neurons release NE and suppress REM sleep and lead to arousal
HISTAMINE released from the locus ceruleus activates the LC neurons. These neurons release NE and suppress REM sleep and lead to arousal
What is the earliest stage of sleep?
Stage N1
low voltage EEG

What is the second stage of sleep?
Stage N2
Slowing of frequency with SLEEP SPINDLES

What is the third stage of sleep?
Stage N3
aka “Deep Sleep”
Theta and delta waves are prominent

What is the 4th stage of sleep?
REM Sleep
EEG similar to wake state



