(5) HTN, Cardiac valve disease, Cardiomyopathy, Tumors, Transplantation Flashcards
What is the most common cause of arrhythmias?
Ischemic injury
What is sick sinus syndrome?
SA node damaged which leads to bradycardia
What is atrial fibrillation?
Myocytes depolarize independently and sporadically with variable transmission thru AV node –> irregular heart rate = atrial fibrillation
What is a heart block?
Describe the three types
Dysfunctional AV node
1st degree = prolonged PR interval
2nd degree = intermittent transmission
3rd degree = complete failure
What is the most common inherited arrhythmogenic disease?
Long QT syndrome
What is sudden cardiac death?
Unexpected death from cardiac cause
Either: without symptoms or within 1-24 hrs of symptom onset
What is hypertensive heart disease?
Left-sided systemic hypertensive disease occurs when pressure overload results in left ventricular hypertrophy
What typically occurs with right-sided hypertensive disease?
Isolated right-sided hypertensive heart disease arises in the setting of pulmonary hypertension
*remember: most common cause of pulmonary hypertension is left-sided heart disease
What are the 3 main types of pathologic change seen in cardiac valves?
- Damage to collagen that weakens the leaflets –> mitral valve prolapse
- Nodular calcification beginning in interstitial cells –> calcific aortic stenosis
- Fibrotic thickening –> rheumatic heart disease
What is valvular stenosis?
Valve doesn’t open completely, occurs chronically
This impedes forward flow
Chronic stenosis may cause pressure overload hypertrophy –> CHF
What is valvular insufficiency?
Valve doesn’t close completely
Allows reversed flow
Chronic insufficiency may cause volume overload hypertrophy –> CHF
What is (pretty much) the ONLY cause of mitral stenosis?
Postinflammatory scarring (rheumatic heart disease)
What are causes of aortic stenosis?
Postinflammatory scarring (rheumatic heart disease)
Calcification of congenitally deformed valve
What causes mitral regurgitation?
Abnormalities of leaflets and commissures
Mitral valve prolapse
What causes aortic regurgitation?
Postinflammatory scarring (rheumatic heart disease)
Aortic insufficiency
Syphilitic aortitis
Marfan syndrome
What is the most common valve abnormality?
Calcific aortic stenosis
What is commonly seen with calcific aortic stenosis?
Increased prevalence with increased age (60-80years)
Bicuspid valves show an accelerated course due to increased mechanical stress
Mounded calcifications in cusps prevent complete opening of the valve
What are the symptoms of calcific aortic stenosis?
Angina
CHF
Syncope
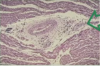
Identify
A:
B:
C:
D:

A: Calcific aortic stenosis
B: Bicuspid aortic valve
C: Mitral annular calcification
D: Mitral annular calcification

What is this an example of?

Aortic stenosis
*Remember: an aortic valve doesn’t NEED to be bicuspid to calcify. Sometimes in older adults, a normal aortic valve (three cusps) will undergo calcification, a so-called “senile calcific aortic stenosis”

Describe mitral annular calcification
Calcific deposits occur in the fibrous annulus
Normally does not affect valve function
Typically mitral annular calcification causes –> ARRHYTHMIAS
What are doctors referring to when they say, “floppy valve”?
Mitral valve prolapse
What is occuring anatomically with mitral valve prolapse?
Valve leaflets prolapse back into left atrium during systole
How do the leaflets in mitral valve prolapse (MVP) become thickened and rubbery?
Proteoglycan deposits (myxomatous degeneration)
&
Elastic fiber disruption