7.1 Urinary Flashcards
what is the funtion of the kidneys
- keys functoin is to maintain bodys internal environment
- > filters 200L plasma/day, allowing toxins, metabolic wastes and excess ions leave body in urine
- regulates total water volume and total solute concentration
- ensures long term acid-base balance
- produces erythropoietin (reg RBC production) and renin (reg blood pressure)
- activates vitamin D
- carries out gluconeogenesis
what are the main structures of the urinary system
- renal artery
- renal hilum
- renal vein
- kidney
- ureter
- urinary bladder
- urethra
where are kidneys located?
- retroperitoneal
- in superior lumbar region (btwn T12-L3)
- concave medial surface with renal hilum leading to internal kidney space (renal sinus)
- convex lateral surface
- ureters, renal BV, lymphatics and nerves enter and exit at the hilum

what are the 3 layers of tissue surrounding the kidney
renal fasia
perirenal fat capusle (fatty cushion)
fibrous capsule
describe the renal fasia
most external of 3 tissue layers supporting kidney
- anchors outer layer of dense fibrous connective tissue

describe the perirenal fat capsule
what is a potential complicaiton of it
aka fatty cushion
middle of 3 layers
- protects kidneys from moving in retroperitoneal cavity
- rapid weight loss can decrease the capsule causing renal ptosis -> kinking of ureters causing back up of urine called hydronephrosis -> can cause necrosis and renal failure

describe the fibrous capsule
most visceral layer of the 3 layers of supportive tissue surrounging kidney
- transparent capsule that prevents spead of infection to the kideny

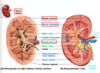
what are the 3 internal regions of the kidney
renal cortex
renal medulla
renal pelvis
describe the renal cortex
outermost layer of internal kideny
- granular-appearing superficial region

describe the renal medulla
- deep to cortex, composed of cone-shaped medullary renal pyramids
- broad base of pyramid faces the cortex, filters down to apex (papilla) which points internally
-
what separates renal pyramids
renal columns -> inward extensions of cortical tissue
describe the renal pelvis
- inside ther is a funnel shaped tube that is continuous with ureter
- has minor and major calyces
- minor: cup shaped areas that colelct urine draining from pyramidal papillae
- major: areas that collect urine from minor calyces -> empty urine into renal pelvis

how does urine flow
Renal pyramid -> minor calyx -> major calyx -> renal pelvis -> ureter
what is Pyelitis
Infection of renal pelvis and calyces
what is pyelonephritis
- infection or inflammation of entire kidney
- > infection in feales caused by fecal bacteria entering urinary tract
- severe cases can cause swelling of kidney and abscess formation, pus may fill renal pelvis
- if left untreated, kidney damage may result
- noramlly treatmed sucessfully with antibitoics
what percentage of cardiac output is delivered to kidneys
renal arteries deliver 1/4th cardiac output to kidneys each minute
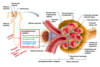
describe arterial flow in kidneys
aorta -> renal -> segmental -> interlobar -> arcuate -> cortical radiate
then goes ut afferent arterioles to glomerulus and back out by efferent arteriles feeding into pericubular capillaries or vase recta
Ryans, Stuck, In Amy’s Cat

venous blood flow through kidneys
cortical radiate -> arcuate -> interlobar -> renal veins
*no segmental veins

what are nephrons? what are the two main parts
nephrons = structural and functional units that form urine
- two main pats: renal corpuscle and renal tubule
what types of cells exist in the nerphon
- Parietal layer of glomerular capsule
- stratefied squamous
- Visceral alyer of glomerular capsule
- have fenestrated endotherlium of glomerulus, podocyte, basement membrane
- Proximal convoluted tubule
- cuboidal cells
- apical microvilli and lots mitochondira
- Distal convoluted tubule
- less microvilli
- simple sequamous in desending, mix of squamous, cuboidal and columnar in ascenind limb
- Colecting duct
- principal and intercalated cells

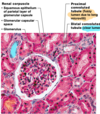
what are the two aprts of the renal corpuscle
glomerulus and glomerular capsule
descirbe the glomerulus
- tuft of capillaries composed of fenestrated endothelium
- highly porous capillaries that allow for efficient filtrate formation (plasma - protiens and - RBCs)
* filterate = plasma-derived fluid that renal tubules process to form urine

describe the glomerular capsule
- cup shaped, hollow structure with a two layers
- > Parietal layer: simple squamous epithelium
- > Visceral layer : clings to glomerular capillaries; branching epithelial podocytes, extensions terminalt in foot processes clings to basment membrane,

what is the renal tubule composed of?
what are the parts of the renal tubule
copmsed of single ayer of epithelial cells
- parts are
1. proximal convoluted tubule
2. Nephron loop
3. Distal convoluted tubule (farthest from renal corpuscle
* DCT drains into collecting duct