2.2 Lungs anatomy Flashcards
how many orders of branching are there for bronchi
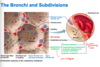
air passage undergoes 23 orders of branching (bronchial tree)
- tips of bronchial tree -> conducting zone structures give rise to respiratroy zone structures
how does the bronchi branch off?
* part of conducting zone
- trachea divides right from left main (primary) bronchi
main bronchus -> hilum of one lung and branches into lobar (secondary) bronchi
-lobar->segmental (teritary) bronchi
- teritary divde repeatedly, beocming smaller and smaller (called bronchiole when less than 1 mm in diameter)
- terminal bronchioles: smallest of all branches (< 0.5mm in diameter)

left vs right bronchi
Right main bronchus wider, shorter, more vertical than left
- secondary bronchi: 3 on right and 2 on left
*each lobar bronchus supplied one lobe

what changes occur in the conducting zoe of the lungs
- changes in support structures
- cartilage rings become irregular paltes
- in bronchioles, elastic fibers replace cartilage altogether
- Epithelium types changes
- Pseudostratified columnar -> cuboidal
- Cilia and gobelt cells ebcome more sparse
- Amount fo smoother msucle increases as go farther into lugns
- allows bronchioles to provide substantial resistance to air passage
- where does the respiratory zone begin?
what does it lead to?
- respiratory zone begins where terminal bronchioles feed into respiratory bronchioles
- lead into alveolar ducts and then alverolar sacs (saccules)
*Alveolar sacs contain clusters of alveoli (~300 million alveoli make up most of lung volume)

role of alveolar pores
communciation between alveoli

what is the respiratory membrane and its function
- blood air barrier that consists of alveolar and capillary walls along with their fused basement membranes
*very thin ~0.5 um); allows gas exchange across membrane by simple diffusion
featuers of alveoli
- Walls:
- single layer of squamous epithelium (type 1 alveolar cells)
- scattered cuboidal (type II alveolar cells) secrete surfactant and antimicrobial proteins
- Surroudned by fine elastic fibers and pulmonary capillaries
- alveolar pores connect adjacent alveoli
- equalize air pressue throughout lung
- provide alternate routes in case of blockages
- Alveolar macrophages
- keep alveolar surfaces sterile

lobes of lung
rights: superior, (horizonal fissure) middle (oblique fissue) inferior
left: superior (oblique fissure) inferior

what are bronchopulmonary segments
lung lobes are further divded into bronchopulmonary segments
- 10 on right and 8-10 on left
- separated by tissue septa
- each segment is served by its wn artery, vein and bronchus (if one segment is diseased can be individualy removed)

what are the lobules of the lung
smallest subdivisions visible to naked eye; hexagonal segments served by bronchioles and their branches
lungs are mostly composed of ____ the rest consists of __________
Lungs are mostly composed of alveoli; the rest consists of stroma, elastic connective tissue (makes lungs very elastic and spongy)
what are two circulations that perfuse the lungs
pulmonary and bronchial
describe pulmonary ciruclation innervation of lung
- Pulmonary arteries deliver systemic venous blood from heart to lungs for oxygenation
- branch profusely to beed into pulmonary capillary networks
- pulmonary veins carry oxygenated blood from respiratory zones bakc to heart
*low pressure high voluem system
- lung capillary endothelium cotnains many enzymes that act on diff substanced in blood
ex: angiotensin converting enzyme
describe bronchial ciruclation innervation of lung
- bronchial arteries provide oxygenated blood to lung tissue
- arise from aorta and enter lungs at hilum
- part of systemic circulatoin so are high pressue low volume
- supply all lung tissue except alveioli (get O2 from diffusion)
- Bronchial veins anastomose with pulmonary veins (create holes to connect with pulmonary veins)
vernve innervation of lungs
– Nerves enter through pulmonary plexus on lung root
-> Run along bronchial tubes and blood vessels
Parasympathetic fibers cause bronchoconstriction
Sympathetic fibers cause bronchodilation
visceral sensory fibers
what are Pleurae
thin double layered serosal memrbane that divides thoracic cavity into two pleural compartments and mediastinum
Parietal pleura: membrane on thoracic wall, superior face of diaphragm, around heart, and between lungs
Visceral pleura: membrane on external lung surface
Pleural fluid: fills slit like pleural cavity between two pleurae (provides lubrication and surface tension that assists in expansion and recoil of lungs)

what is Pleurisy
- inflammation of pleurae that often resutls in pneumonia
- inflammed pleurae ebocme rough, resulting in friction and stabbing pain with each breath
- pleurae may product excesive amounts of fluid which may exert pressue on lungs -> hindering breathing
hat fluids can accumulate in fleural cavity
what can it cause
– Blood: leaked from damaged blood vessels
– Blood filtrate: watery fluid that oozes from lung capillaries when left-sided heart failure occurs
*can cause pleural effusion: fluid accumucaltion in pleural cavivty


