2.1 Anatomy of Respiratory system Flashcards
What are the 4 processes of Respiration
-
Respiratory system
- Pulmonary ventilation (breathing): movement of air into and out of lung
- External respiration: exchange of O2 and CO2 between lungs and blood
-
Circulatroy System
- Transport of O2 and CO2 in blood
- Internal respiration: exchange of O2 and CO2 between systemic blood vessels and tissues
what are the amjor rogans of the upper respiratory system
- Nose and nasal cavity
– Paranasal sinuses
-pharynx
what are the major organs of the lwoer respiratory system
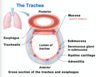
- larynx
– Trachea
– Bronchi and branches
– Lungs and alveoli

What is the function of the nose
- produces mucus, fitlers, warms and mositens incoming air; resonance chamber for speech
– Provides an airway for respiration
– Moistens and warms entering air
– Filters and cleans inspired air
– Serves as resonating chamber for speech – Houses olfactory receptors
*divided into two regions: external nose and nasal cavity
what is the function of the paranasal sinuses
- lightens skull
- may warm, moisten and filter incoming air
trachea and gas exchange
has no direct role in gas exchange
what are the areas of the external nose
- Root (area between eyebrows)
- Bridge,
- Dorsum nasi (anterior margin)
- Apex (tip of nose)
*Nostrils (nares): bounded laterally by alae

what is part of the external nose
formed by: Nasal bone forms bridge of nose, frontal bone forms root and maxillary bone laterally
- Plates of hylain cartilage inferiorly
Decribe the structure of the ansal cavity
- Divided by midline nasal septum
- formed anteriorly by septal cartilage, and posteriorly by vomer bone and perpendicular plate of ethmoid bone
- Posterior nasal apertures (chonanae): opening where naso cavity turns into nasopharynx
- Roof: formed by Ethmoid and sphenoid bones
- Floor: formed by hard palate (bone) and soft palate (muscle)

where is the nasal vestibule
what is it lined with
nasal cavity superior to nostrils (near nostrils)
• Lined with vibrissae (hairs) that filter coarse particles from inspired air
what muscus membranes line the nasal cavity
- Olfactory mucosa:
- lines superior region of nasal cavity and contains olfactory epithelium
- Respiratory mucosa:
- pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium
- contains goblet cells and many seromucous nasal glands
- Seromucous nasal glands
- contain mucus-secreting mucous cells and serous cells (mucus and serous secretions contain lysozyme and defensins)
what is the Nasal conchae
what are the sections
- scroll line, mucosa covered projections that protrude medially from each alteral wall of nasal cavity
sections are: sueprior, middle and inferior conchae (shape of them hels to increase contact with air)
what does the nasal conchae do during inhalation and exhalation
During inhalation they filter, heat, and moisten air
During exhalation they reclaim heat and moisture
what is teh nasal meatus
groove inferior to each concha

paranasal sinuses
what is their form, location and function
Form: ring around the nasal cavities
Location: frontal, sphenoid, ethmoid and maxillary bones
Function: lighten skull, secrete mucus, help watm and moisten air


What is rhinitis
- form of homeostatic imbalance
- Inflammation of nasal mucosa
– Nasal mucosa is continuous w/ mucosa of respiratory tract -> infections spread from nose to throat to chest
– Can spread to tear ducts and paranasal sinuses, causing blockage of sinus passageways
*Can lead to absorption of air, producing a vacuum, resulting in sinus headache
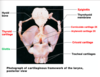
describe the shape, location, compostion and regions of the pharynx
shape: funnel muscular tube
location: runs from base of skull to Certevra C6, connects nasal cavity and mouth to larynx and esophagus
composition: skeletal muscle
Regions: nasopharynx, oropharynx, laryngopharynx
describe the nasopharynx
lining?
tonsil?
any other tube thing?
– Air passageway posterior to nasal cavity
– Lined w/ pseudostratified columnar epithelium
– Soft palate and uvula close nasopharynx during swallowing
– Pharyngeal tonsils (adenoids) located on posterior wall
– Pharyngotympanic tubes (auditory tubes) drain and equalize pressure in middle ear and open into lateral walls

describe the Oropharynx
lining?
tonsils?
– Passageway for food and air from level of soft palate to epiglottis
– Lining consists of stratified squamous epithelium
– Isthmus of fauces: opening to oral cavity
– Palatine tonsils located in lateral walls of fauces
– Lingual tonsil located on posterior surface of tongue

describe the laryngopharynx
– Passageway for food and air
– Posterior to upright epiglottis
– Extends to larynx, where it is continuous with esophagus
– Lined with stratified squamous epithelium

waldeyer’s Tonsillar ring
Nasal tonsils are: 2x tubal tonsils and pharyndeal tonsil
Oral tonsil: 2x palatine tonsil and a ligual tonsil
*tonsils are used to detect pathogens

what happens if adenoids are ifnected and swollen
(same type of function as tonsils but are a bit diff)
Infected and swollen adenoids can block air passage in nasopharynx, making it necessary to breathe through the mouth
As a result, air is not properly moistened, warmed, or filtered before reaching lungs
When adenoids are chronically enlarged, both speech and sleep may be disturbed