5.1 Microscopic anatomy of heart + contraction Flashcards
describe the microscopic features of cardiac muscles
comment on: what muscle looks like, connection, T tubule, and mitochondria
- cells are straited, short, branched and interconnected
- endomysium connects fibrous skeleton of heart
- each scaromere has a T tubule at the Z disc
- sarcoplasmic reticulum is simple than in skeletal muslce
- 25-35% of cell volume is mitochondira
-

heart has intercalated discs, what do they do
junctions between cells anchoring cardiac cells
heart has desmosomes, what do they do
prevents cells from separating durign contraction
*why muscle behaves as a functional syncytium
heart has gap junctions, what do they do
allow ions to pass; electrically couple adjacent cells -> connects cytoplasm of adjacent cells
*why muscle behaves as a functional syncytium
descirbe EC coupling in the cardiac muscle
*contractile cells
- AP from adjacent cell opens V gated Na channels
- Voltage gates Ca2+ channels open, Ca enters the cell
- Ca induces Ca2+ release through RyR (ryanodine receptor)
- local release causes Ca spark
- summed Ca sparks create a Ca signal
- Ca ions bind to troponin to initiate conraction
- relaxation occurs when Ca unbinds from troponin
- Ca pumped back into Sr for storage
- Ca si exchanges with Na by Na Ca exchanger
- Na gradient is maintained by na/K ATPase

what is the first step of cardiac muscle contraction
*contractile cells
- depolarization opens the Voltage gated fast Na channels in carcolemma
- Na enters, initiates postive feedback cucle (rising phase of AP)
- reveral of membrane potential from 90-30 mV
- Na channels quickly inactivate

what is the second step of cardiac muscle contraction
*contractile cells
depolarization wave in T tubules opens slow Ca2+ chanels (10-20% of Ca2+)
- Ca influx triggers opening of Ca sensitive channels in SR, liberates bursts of Ca (where 80% of Ca comes from)
- Ca surge prolongs depolarization phase (plateau)

what is the third step of cardiac muscle contraction
*contractile cells
repolarization resulting from inactivation of Ca channels and opening of voltage gated K channels
- long absolute refractory period

what is the last step of cardiac muscle contraction
*contractile cells
Resting Phase Na+-K+ ATPase & Na+-Ca+ exchanger restore resting membrane potential
why dont you get tatnus in heart
- short refractory period in skeletal muscle
0 in cardiac muslce the refractory period lasts almost as long as the entire muscle twitch

compare skeletal and cardiac muscle based on:
duration of AP
contraction time
Ca source
of mitochondira
respiration
presence of autorhythmic cells

what do conducting cells of heart do
*intrinsic cardiac conduction system
- network of noncontractile (autorhythmic) cells that initiate & distribtue impulses to coordinate depolarization & contraction of heart
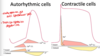
describe contraction in autorhythmic cells
- Pacemaker potential
- slow depolarization due to slow opening of Na channels and closing of K
- **membrane potential never a flat line
- Depolarization
- AP begins when pacemaker potential reaches threshold (~40 mV)
- depolarization is due to Ca2+ influx through Ca2+ channels
- NOTE in contractile cells this is accomplushed by sodium
- Repolariztion
- Ca channels inactiate and K+ chennls open allowing K efflux
- membrane potential returns and its most negatie voltage

compare the two types of cardiac cells
similarities and differences
autorhythmic vs contracile cells
- Autorhythmic
- depolarizes with Ca
- never flatlines
- sodium channels open slowly (slow sodium channel)
- BOTH repolarize with K+
- Contractile
- deloparize with Na
- quick spark of Na (fast sodium channel)
- BOTH repolarize with K+
what is the sequence of excitation
- Sinoatrial node
- atrioventicular node
- atrioventricular bunlde (bundle of his)
- right and left bundle branches
- purkinje fibers (Subendocardial conducting network)
describe the first sept of heart sequence excitation
- Sinoatrial (SA) node
- > right atrial wall inferior to SVC enterance
- generates impulses ~75 times/min (sinus rhythm)
*faster of pacemaker cells
*causes all contractile cells in atria to depolarize and contract
*If no PSNS, other extrinsic factors & hormones, SA node will fire 100 times/minute

describe step 2 in sequence excitation
@ atriventricular node
- inferior portion of interatrial septum (aboe tricuspid value)
- smaller diameter fibers; fewer gap junctions
- delays impulses approximately 0.1 second
- depolarizes 50x per min (absence of SA node input)

describe step 3 of the sequence of excitation
- atrioventricular Av bundle (bundle of His)
- superior interventriuclar septum
- only electrical connection between atria & ventricles
- > insulated by fibrous skeleton of heart

Describe step 4 of sequence of excitation
- right and left bundle branches (one of each ventricle)
- two pathways in interventricular septum carruing impulses toward heard apex

describe step 5 of sequence of excitation
purkinje fibers (subendocaridal conducting network)
- comeplte pathway into apex and ventricular walls
- AV bundle & purkinge fibers depolarize only 30x/ min in absence of AV node input

most firing action is the result of
neighbouring cells
*even tho cells are autorhythmic
*think: bunch of horses on a cart, ut the fastest ones at front to set the pace for others -> all AV node sets pace for all other cells
describe conduction delay
time between initiation of impulse by SA node and depolarization of ventricular muscles
~0.22 seconds
- ventricular contraction starts at apex & moves towards atria -> push blood up and out of pulmonary trunk & aorta

how is the heart innervated extrinsically
- vagus nerve will decrease HR acting in cardioinhibitory centre
- SNS inc HR & force of contraction acting on cardio aacceleratory center

if you innervate node you change the ____
if you innervate muscle you change the ____
node innervation changes rate
muscle innervation changes strength


