Week 4 - Kidney Failure Flashcards
What are the 2 types of nephrons?
Cortical nephrons
Juxtamedullary nephrons
What is the funciton of the renal corpuscle and tubular system of nephron?
Renal corpuscle = site of initial blood filtration
Tubular system = controls concentration and content of urine
What are the blood supplies to the nephron?
Glomerulus capillary bed - in Bowman’s capsule - high hydrostatic pressure - FILTRATION
Peritubular capillary bed - aroudn tubular system - low hydrostatic pressure - REABSORPTION AND SECRETION
What is GFR?
Volume of fluid entering Bowman’s capsule per unit time
What does the glomerular filter look like?
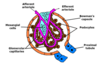
What is the organisatino of golumerular capillary membrane?


What are the effects of afferent arteriole constriction, efferent arteriole constriction and hypoproteinaemia on GFR?
Afferent constriction = - GFR
Efferent constriction = + GFR
Hypoproteinaemia = + GFR
What are the benefits of using inulin to estimate GFR?
- Freely filtered
- Not reabsorbed, secreted or metabolised by kidney
- No effect on renal function
- Easily measured in urine
What is RPF?
Renal plasma flow = amount of plasma that perufses kidney per unit time
How do you derive renal bloodflow using RPF?
RBF = RPF / 1 - haematocrit
What is the filtration fraction?
What does high FF indicate?
The proportion of plasma that forms filtrate
+ FF = + colloid osmotic pressure in peritubular capillaries
What are the ways autoregulation alters GFR?
Myogenic - afferent arteriole contraction
Tubuloglomerular feedback - NaCl concentration in filtrate sensed by macula densa of JGA and singal produced, contractin afferent arterioles
What is the juxtaglomerular apparatus?
What is its role?
Macula densa + granular cells
Autoregulation and renin release
What effect do vasodilators and NSAIDs have on RBF and GFR?
Vasodilators = increase RBF and GFR (prostaglandins)
NSAIDs = block prostaglandin synthesis = + vasoconstriction and ischaemia = actue renal tubular necrosis
What is glycosuria?
What causes it?
When renal glucose threshold (RTG) is exceeded, glucose excreted in urine
- Untreated diabetes
- Hyperthyroidism
- Pregnancy
- Familial
- Drugs
What happens in the proximal tubule?
- Bulk reabsorption of filtered ions and solutes
- Reabsorption of organic solutes, ions and water is coupled with sodium reabsorption
- water permeability means so significant osmotic gradient
- Tubular fluid = isosmotic with plasma
How is sodium trnasported in proximal tube?
Readily enters epithelial cells across apical membrane
How is bicarbonate transported in proximal tube?
Indirectly reabsorbed via carbonic anhydrase as apical membrane impermeable to bicarbonate
How is water transported and reabsorbed in proximal tubes?
+ permeability
Occurs paracellularly across tight junctions and transcellularly via water channels on apical and basolateral membranes
Reabsorption:
- Osmotic pressure gradient + low hydrostatic pressure = water passively moves down gradient
How is sodium, chloride, potassium and water processed in thick ascending limb of loop of Henle?
- Is impermeable to water
- 1 Na+, 1 K+ and 2 Cl- enter cell via symporter protein in apical membrane
- Cl- leaves via passive diffusion
- Most K+ leaks back into lumen
- Tubular lumen becomes + charged
- Sodium enters cell via Na+/H+ antiporter
- Sodium pumped out by sodium pump
- Low sodium = electrochemical gradient = drives Na movement into cell
What is the role of the thick ascending limb?
- Reduces tubular fluid osmolality
- Is diluting segment
- Makes interstitial fluid of medulla hyperosmotic
- role in creating medullary interstitium and regulating urine osmolality
What are the effects of aldosterone in the late distal tube?
- Enhances sodium reabsorption in principal cells
- Enhances K+ secretion in principal cells
- Enhances H+ secretion in intercalated cells
What happens in hyperaldosteronism and hypoaldosteronism?
Hyper = + aldosterone, metabolic alkalosis, hypokalaemia, hypertension, oedema
- DUE TO SODIUM AND WATER RETENTION
Hypo = type 4 renal tubular acidosis = hyperkalaemia
What are the effects of ADH on inner medullary collecting duct?
- urea permeability
- Water diffuses out of tubule lumen, into medullary interstitium
- Urea recycling occurs –> urea diffuses into ascending and descending limbs of loop of Henle
What happens to body during excess sodium and sodium defecit?
Excess:
- Weight gain
- Oedema
- Hypertension
- Nocturia
Defecit:
- Weight loss
- Change in skin tugour
- Syncope
- Orthostatic hypotension
What happens during chronic kidney disease?
- Slow function loss overtime
- Decreased ability to remove waste products
- Treat with dialysis, transplant or supportive care
- Clinically = < 60 ml/min
How does chronic kidney failure present?
- Asymptomatic serum biochemical abnormaility
- Asymptomatic proteinuria or haematuria
- Hypertension
- Oedema
- Primary renal disease symptoms
- Uraemia symptoms
- Complications of CKD
- Tiredness
- Salt and water retention
- Itching
How can you treat CKD?
- ACE inhibitors
- Lifestyle change
- Monitor BP, creatinine and GFR
- Haemodialysis
- Peritoneal dialysis
What is acute kidney injury?
- Rapid decline in kidney function
- serum creatinine conc.
- Fall in urine output
- Uraemia
- Due to haemodynamic, septic, immunological, nephrotoxic or obstructive insults
What are causes of pre-renal AKI?
Intravascular volume depletion
- cardiac output
Systemic vasodilatation
What are the causes of intrinsic AKI?
Diseases or toxins damaging small renal vessels and glomeruli
Acute tubular necrosis
Miscallaneous renal diseases
Toxins
What causes post-renal AKI?
Acute obstruction of urine flow


