Week 3 - E - Respiratory and Cardiac Problems Flashcards
(33 cards)
What are some of the key features of sepsis?
Hot
Lethargy
Tachycardic
Low blood pressure
What is the sepsis 6 bundle?
Bloods
Urine
Fluids
Antibiotics
Lactate dehydrogenase
Oxygen - high flow
To rule out meningitis in sepsis, what is carried out?
A lumbar puncture is done to rule out meningitis
What type of bacteria causes meningitis with a rash?
Neisseria meningitidis - causes meningococcal meningitis
If you are in the community and a child has a purpuric rash, what test do you carry out? What do you give since no access to IV lines?
Tumbler’s test - hlds glass to arm to test for non blanching rast
Give IM benylpenicillin in the community
What is given to the child once reaching the hospital?
IV ceftriaxone
What must be carried out in the child before performing a lumbar puncture and why?
Child requires a clotting screen before carrying out a lumbar puncture
What abnormality of the fontanelles may occur in meningitis?
May have enlarged fontanelles
What is the cause of a respiratory distress in a premature child? Define premature child?
Child born earlier than 37 weeks grestatiion
Premature children do not have full pulmonary surfactant and therefore alveoli tend to collapse making it difficult to breathe
What cells produce pulmonary surfactant?
Type II alveolar cells aka type II pneumocyte
• Trouble in PE, feels quite short of breath inexercise, can have other atopy eg eczema and asthma What does this child have? How should you assess the child?
Child has asthma - assess using peak flow meter
What is laryngeotracheobronchitis more commonly known as? What organism mainly causes it?
More commonly known as croup
Caused by Parainfluenza Virus
What causes this condition?

Classic presentation of bronchioloitis
Caused by respiratory syncitial virus
Child complaining of flu like symptoms, usually gets cough and has difficulty sleeping due to obstructed airway What is this? What is the sign on xray?
This is croup
Steeple sign on Xray
What is the cough described as in croup? What causes the blockage of the airway? What is treatment of croup?
Barking cough
Virus causes inflammation and swelling of airway
Give steroids as treatment
• Can get prolonged bouts of violent coughing, children being unable to breathe and vomiting Vomtiing is so violent it causes vomiting What is this?
(had a stroke reading this <3)
This is pertussis - whooping cough
What causes pertussis? What is the treatment?
Bordatella pertussis
Like bronchiolitis it is self limiting and supportive care
Child with sternal recession, slight fever and high pitched bronchi with cough What is this?
Bronchiolitis
What is the difference between acyanotic and cyanotic breathlessness?
Acyanotic is the absence of cyanosis due to a left to right shunt
Cyanotic - cyanosed due to a right to left shunt of blood and therefore the blood is not being oxygenated in the lungs
Things like septal defects and patent ductus arteriosum tend to cause left to right shunts (acyanotic) What type of murmur does a ventricular septal defect sound like? What type of murmur is patent ductus arteriosus?
Harsh systolic murmur at left sternal edge
Continous machine like murmur
What is the ductus arteriosus knwon as after birth?
Ligamentum arteriosum
What are 3 of the causes of cyanotic heart disease?
Tetralogy of Fallot
Transposition of the great vessels
Truncus arteriosus
What is the tetralogy of Fallot?
- Right ventricular hypertrophy
- Ventricular septal defect
- Overriding aorta
- Pulmonary stenosis

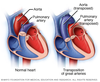
What ventricles does transposition of the great vessels cause attachment to?
Aorta attaches to the right ventricle causing deoxygenated blood to pass to the body
Pulmonary trunk attaches to the left ventricle therefore oxgenated blood goes to the lungs
Requires surgery