Thyroid Anatomy and Pathology II Flashcards
(20 cards)
Too much thyroid hormone causes:
- ___/malingering, for example from a hamburger
- thyroid gland overproducing hormone.
- immune cause: ___
- Autonomous nodules: ___ ___ - Thyroid gland is releasing stored hormone:
ex: _____: Leakage of previously stored hormone) - Ectopic production of thyroxin:
ex/ ___ ___
- HCG stimulation seen in a ___ pregnancy

- IATROGENIC/malingering, for example from a hamburger
- thyroid gland overproducing hormone.
- immune cause: GRAVES
- Autonomous nodules: BENIGN ADENOMA - Thyroid gland is releasing stored hormone:
ex: THYROIDITIS: Leakage of previously stored hormone) - Ectopic production of thyroxin:
ex/ OVARY TERATOMA
- HCG stimulation seen in a MOLAR pregnancy

outline the pathomechanism of Graves disease
normally, pituitary gland releases TSH and the it binds to the TSH receptor on the thyroid cell to increase the regulated production of thyroid hormones.
in graves, there is an AUTO-ANTIBODY to the receptor, promoting unregulated overproduction of thyroid hormones

microscopic/histological findings of graves disease
you would see infoldings of hyperplastic epihelium.
YOU HAVE A LARGE VASCULAR OVERWORKING GLAND
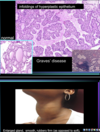
Nodular hyperthyroid Approach:
single nodule; think ___ ___ __. What is this?
if multinodular gland; think a __ ___ disorder
single nodule: BENIGN FOLLICULAR ADENOMA. Autonomous functioning nodule. suppresses rest of thyroid gland (atrophic)
Multinodular gland: - one or more autonomous areas in overal large gland. Long-standing disorder (usually older individuals)

Outline findings

thyroid follocular adenoma. Causing hyperfunctioning

dietary causes of multinodular goiters
dieteary goitrogens. Cassava, peanuts, etc.

outline the natural history of a multinodular goiter
TSH and T4s are normal to begin with, but hormone secretion starts to increase by autonomous follicles that are not well regulated. will result in lower levels of TSH (since you have enough thyroxin), and sky high thyroxin levels, possibly leading to THYROTOXICOSIS

which thyroid nuclear scan shows graves disease, toxic adenoma and toxic nodular goiter?


Which scan shows thyroiditis

THYROIDITIS: Leakage of previously stored hormone). there is a loss of thyroid hormone trapping

In thyroiditis, there is ___ uptake of radioiosine
very low uptake.

talk through this table


in subacute thyroidisits, the inflammatory process causes a ___ gland that is painful and tender. usually occurs after a viral infection, causing release of pre-fromed and stored thyroid hormone.

hard galnd

compare subacute thyroiditis vs graves disease pathomechanism
ST: release of pre-formed and stored thyroid hormone from the colloid. its a SELF LIMITED DISEASE since when the stores are empty, things normalize.
in GRAVES: antibody stimulates new thyroid hormone synthesis and release. hthis is a PROLONGED DISEASE.


Note

underactive thyroid gland:
in adults, most common cause of hypothyroidism is an __ disease called __. Hypopituitary causes 1% of hypothyroidism.
in adults, most common cause of hypothyroidism is an immunological disease called hashmotos. Hypopituitary causes 1% of hypothyroidism.

note; for both hyper and hypothyroid disorders, genetics give a predisposition vs environment

In Hashimoto’s thyroiditis:
Gland may be __ early in course, __ late in the course, __ to palpation
Gland may be enlarged early in course, atrophic late in the course Firm to palpation


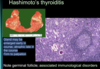
Ultrasound Key finding that may indicate hashimoto’s

tend to have moth eaten appaeance to lobes



