Thorax 1: Thoracic wall Flashcards
What are the contents of the thorax? (big structures)

What are the 3 layers of intercostals and their functions?
External, internal and innermost.




What are the different superficial layers?

What are the anterior shoulder girdle muscles?
Pectoralis major and minor

The lower thorax is covered by _______ _______ and __________ muscles.

Why is a posteiror thoracotomy ideal?
It is a muscle sparing procedure bc there is no muscle over the fatty triangle. This allows you to get to the posterior thoracic wall.

What makes up the posterior thoracic wall?
What makes up the lateral thoracic wall?
What makes up the anteiror thoracic wall?

What borders the superior and inferior thoracic apertures?

What are the neurovascular structures in the intercostal space?

What muscles inparticular are these membranes continuous with?


The posterior intercostal arteries arise from -__________.
It enters into the intercostal space at the ______ boarder of the ______ muscle.
Thoracic aorta.
posterior boarder of the innermost intercostal muscle.

Where do the intercostal arteries run?
Where does the anterior and the posterior intercostal arteries arise from?
What do these arteries supply?
In the intercostal grove.
Thoracic aorta and internal thoracic artery (branch of subclavian).
The muscles, bone, subcutaneous tissue and skin.
Where do the intercostal veins drain into?
What do they drain?
Posteriorly the azygous system, anteiorly the internal thoracic vein.
They drain the structures supplied by the arteries (bone, muscle, subcutaneous tissue and skin).
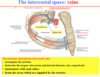


What is the function of the endothoracic fascia? Which two structures sit on either side of it?
Bone or muscle superficially, and the parietal pleura deep.

Which two structures does the neurovascular bundle sit between?
The innermost and internal intercostal muscles.

If you are trying to enter the thoracic cavity by an intercostal approach which structures would you need to go through in which order?
Skin, subcutaneous tissue, deep fascia, shoulder girdle muscles, external intercostal, internal, neurovascular bundle, innermost, endothoracic fascia, parietal pleura.

What is a thoracocentesis?
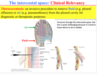
Where are the 4 common sites for intercostal catheter insertion?

Where is the triangle of safety?
Triangle of safety.
Is safe cause anteriorly there is pec etc.
Posteriorly there is the long thoracic nerve which innervates serratus anterior (cant lift arm).
Inferiorly there is the diaphragm which is bad because there are organs below that.





