Head and neck 5 Flashcards


Where is the apex of the orbit?
At the optical canal (medial to superior orbital fissure).
What is the name for the eye lid? What is the part of the eyelid which touches the eye ball?

What is this structure?
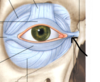

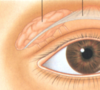
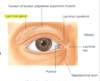


What does the levator palpebrae do and its innervation?
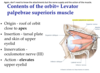


Function of superior rectus, lateral rectus, inferior rectus and medial rectus?
Function of superior oblique and inferior oblique muscles?
What are these nerves innervated by?
Remember that superior, inferior and medial rectus are involved in turning the eye in.

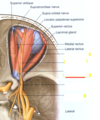

The nasocilliary nerve eventually becomes the ________ nerve.
Trochlear.
What are the long ciliary nerves? What nerve do they originate from?
What is their function?

What are these nerves and their function?



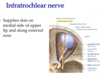
What is the ciliary ganglion?
Where is it and what is its function?

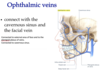
What are these two arteries?



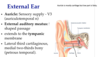
External acoustic meatus: The ______ _/_ is cartilagnous, the _______- _/_ is bone (_____ of the ___ bone).
Lateral 1/3, medial 2/3 (petrous part of temporal bone).



3 bones of the inner ear?


The ____ cavity contains auditory ____ (bones) which connect the __________ to the _________.
the tympanic cavity contains auditory ossicles which connect the tympanic membrane to the oval window of the inner ear.
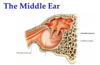
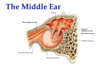
What are the two muscles of the inner ear which dampen noise?

Where does the auditory tube extend from and to?
tympanic cavity to the nasopharynx.

What is the vestibule of the ear?

The cochlear lies _____ to the vestibule.
The semicircular canals lie _____ to the vestibule (one in each plane).

What is the innervation of the internal ear?



