Somatosensory system Flashcards
Which 2 tracts are ascending, somatosensory tracts?
- Dorsal column medial lemniscus pathway
- Spinothalamic pathway

What modalities does the dorsal column system carry?
- Fine touch
- 2 point discrimination
- Proprioception
- Vibration
What modalities does the spinothalamic tract carry?
- Pain
- Temperature
- Crude Touch
What are modalities?
Basic units of sensation
What type of signal do first order neurones carry?
Signals are analogue
Converted to digital as information moves along the neurone
How are signals transmited in low stimulation vs high stimulation of receptors on first order neurones?
Low stimulation = low frequency of action potentials
High stimulation = high frequenc of action potentials

What are rapidly adapting receptors? Give an example
Receptors where the initial stimulus is high, sending lots of action potential but then you lose sensation as action potentials become less frequent over time.
e.g. mechanoreceptors in bum cheeks on sitting

What are slowly adapting receptors? Give an example
Receptors where frequency of action potential remains high until you stop/ doing something about the stimulus
e.g. nociceptors

What is a receptive field?
A region of skin that is supplied by a sensory neurone
Explain why there is some overlap between the boundaries of different dermatomes
Receptive fields for different dermatomes can over lap

What is an autonomous region (with regards to receptive fields)?
An area where there is minimal overlap of the receptive fields of different dermatomes
What is the relationship between acuity and receptive fields?
High acuity = small receptive field

What is the relationship between acuity and number of neurones?
High acuity = high number of neurones

What are first order neurones?
Neurones that carry sensory information from the peripheral nerves to the medulla oblongata
Project into the spinal cord ipsilaterally

Where is the cell body for first order neurones?
In the dorsal root ganglion
What are second order neurones?
Fibres that transmit information from first order neurones to third order nuerones
2nd order neurones decussate within the medulla oblongata

What are third order neurones?
Neurones that recieve information from 2nd order neurones, transmitting sensory information from the thalamus to the primary sensory cortex of the brain
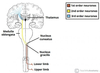
Where is the cell body for second order neurones?
In the medulla or the dorsal horn
Where is the cell body for third order neurones?
In the thalamus
What are the 2 different paths, first order neurones can take in the dorsal column medial lamniscus pathway?
From the upper limb (T6 and above): travel in fasciculus cuneatus and synpase in the cuneate nucleus in the medulla oblongata
From the lower limb (T6 and below): travel in the fasciculus gracilis and synpase in the gracile nucleus in the medulla oblongata

How do first order neurones from the upper limb and lower limb in the dorsal column medial lamniscus pathway travel in relation to each other?
Neurones from the lower limb are medial
Neurones from the upper limb are lateral

How do third order neurones travel from the thalmus to the primary sensory cortex?
They travel through the internal capsule
Lower limb neurones project medially
Upper limb neurones project laterally

How do signs appear in isolated lesions of the DCML pathway?
Signs will be ipsilateral (to the same side of the lesion) from below the lesion
How do signs appear in isolated esions of the spinothalmic tract?
Signs appear on the contralateral side to the lesion, and below the lesion