Meningitis and Sub-arachnoid haemorrhage Flashcards
What are the 3 layers od the meninges?
Dura Mater
- Endosteal layer
- Meningeal layer
Arachnoid Mater
Pia Mater
- thin layer closesly adhered to brain
What makes up the leptomeninges?
The arachnoid + pia mater
What are the 4 important dural septa?
- Falx cerebri (between cerebral hemispheres)
- Falx cerebelli (between cerebellar hemispheres)
- Tentorium cerebelli
- Diaphragma sella

Between what layers do epidural bleeds (extradural) occur?
Between the endosteal layer of the dura and the skull
Between what layers do subdural bleeds occur?
Between the meningeal and arachnoid layer
Where is the subarachnoid space?
Between the arachnoid and pia
What are cisterns?
- Enlarged areas that occur in the subarachnoid space when the brain moves away from the skull
- Filled with CSF

What are the functions of CSF?
- Physical support of neural structures
- Excretion of brain metabolites
- Intracerebral transport (hormone releasing factors)
- Control of chemical environment
Describe the flow of CSF through the ventricles of the brain
- Formed in the choroid plexus
- Into lateral ventricles
- Through interventricular foramina to third ventricle
- Through cerebral aqueduct to 4th ventricle
- Through lateral and median aperture (Lushka and Megande) to subarachnoid space and small amount into spinal cord

How is CSF reabsorbed?
By arachnoid granulations that project into dural sinuses
How do spontaneous subarachnoid haemorrhages usually occur?
Rupture of saccular aneurysm (berry aneurysm) (80% of non traumatic)
Usully occur at bifurcation points of cerebral vasculature

In which demographics are subarachnoid haemorrhages more common?
- More likely in females (1.6: 1)
- More likely in black, Finnihs and Japanese populations
- Average age onset 50-55yrs
How will a subarachnoid haemorrhage present?
- Headache (48%) thunderclap- from nowhere
- Dizziness
- Orbital plan
- Diplopia
- Visual loss as aneurysms compress visual pathways
What is one of the most common sites for a berry aneurysm to occur?
The anterior communicating artery

Give some risk factors for develping saccular aneurysms?
- Same as cardiovascular- hypertension, smoking etc
- Alcohol +++
- Connective tissue disorders (dilate aneurysm)
What do you do with small aneurysms (<5mm)?
Unlikely to rupture
Manage with surveillance
What might you find on examination of someone with a subarachnoid haemorrhage?
History: sudden onset thundercalp heache, nausea and vomiting, may have LOC on onset
On examination:
- Normal mental state
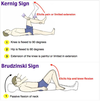
- Signs of meningism (due to bleeding irritating meninges) → neck stiffness, photophobia
- Right third nerve palsy if posterior communicating artery aneurysm (compresses 3rd nerve)
- No motor or sensory deficits
What can happen after a subarachnoid haemorrhage?
- Microtrhombi can occlude smaller distal arteries
- Vasoconstriction from CSF irritant
- Cerebral oedema in response to hypoxia
- Sympathetic activation → myocardial damage
- Early rebleeding is quite common
- Acute hydrocephalus
- Global cerebral ischaemia
What is the first line investigation for subarachnoid haemorrhage?
CT Scan
Detects 93% of bleeds if done within 24 hours of bleed

What should you do if you have a convincing history of subarachnoid haemorrhage, but the CT scan is negative?
Lumbar puncture
- wait 6 hrs (12+ preferable)
- Need time for lysis of red blood cells to take place and release bilirubin
- Gives CSF yellow tinge - xanthochromia

What will you see in the CSF results if there is a subarachnoid haemorrhage?
- High protein
- WCC not raised
- Glucose normal
What do you do once a diagnosis of subarachnoid haemorrhage is confirmed?
Angiography
Performed to confirm and locates the site of the aneurysm
How do you treat subarachnoid haemorrhage?
- Asses for airway support
- Monitor cardiovascular parameters
- Calcium channel blockers (Nimodipine → selective for cerebral vasculature) prevents vasopasm and secondary iscehmia
-
Operate on patients with good neurological stats within 72 hours to prevent re-bleeds
- clamping neck of aneurysm
- coiling (neuro-radiologists) inserting wire into aneurysm which causes thrombosis of blood

What is the prognosis for subarachnoid haemorrhage?
Poor prognosis - 40% mortality within the first month if you reach hospital
33% survivors hae major neurological haemorrhage