Movement Disorders Flashcards
(20 cards)
What is the basal ganglia?
A group of structures found deep within the cerebral hemispheres, including;
- putamen
- caudate nucleus
- globus pallidus
- substantia nigra
Identify structures 1 and 2 of the tegmentum (ventral aspect of midbrain)

1= Red Nucleus
2= Substantia Nigra

What is the function of the substantia nigra?
Major source of dopamine
Identify structures 1 and 2 of the cerebellum


What is the normal function of the basal ganglia?
Takes an idea/ motor plan supplied by the primary motor cortex and determines the most appropriate set of movements
Direct and indirect pathways- direct is excitatory, indirect is inhibitory

What is the normal function of the cerebellum?
Cerebellum looks at the position of the limbs (needs input from sensory proprioceptors) and determines the most appropriate sequence of movements to conduct the motor plan

Using the pathway, explain why the direct pathway has and excitatory effect on the cortex facilitating appropriate movement

Starting at the putamen (ignoring Dopamine)
- The direct pathway inhibits the internal globus pallidus segment which inhibits the inhibitory effect of GABA on the Thalamus
- Inhibiting the inhibitor = excites the thalamus to release gluatmate and stimulate the cortex
Using the pathway, explain why the indirect pathway inhibits inappropriate movement

Stating at the putamen (ignoring dopamine)
- The indirect pathway inhibits, the inhibition of the substantia nigra nucleus i.e. it ACTIVATES it to release Glutamate
- Glutamate release activates the substantia nigra reticulata which has an inhibitory effect on movement
- Activation of an inhibitory pathway = net inhibition
What is major defect in Parkinson’s Disease?
Loss of Dopamine from the substantia nigra

What type of dopamine receptors exist in the direct pathway?
D1 receptors
What type of dopamine receptors exist in the indirect pathway?
D2 receptors
Using the pathway, explain what the overall effect on movement is in Huntington’s Chorea

Huntington’s is an autosomal dominant disorder
There is degeneration of the inhibitory pathway on the GPe
Loss of inhibition of inhibitory neurones = GPe is inhibitory on the STN, you therefore get less Glutamate release and less inhibition of movement
Overall effect= loss of inhibition → hyperkinetic disorder
Using the pathway, explain what the overall effect on movement is with Hemiballismus

Hemiballismus involves a defect at the STN
You therefore have less excitation of the inhibitory pathway i.e. less inhibition of the thalamus
Hemiballismus is a hyperkinetic disorder
Using the pathway, explain why Parkinson’s is a disease of decreased movement

Parkinsons is a disease of less dopamine
Normally: dopamine excites the direct pathway (excitatory) and inhibitis the indirect pathway causing net excitation of the cortex
Parkinsons: less dopamine = less excitment of the direct pathway and less inhibition of the indirect pathway causing a net effect of less cortex excitation
What are the classic signs of Parkinson’s Disease
- Pill Rolling Tremor
- Lead Pipe Rigity
- Bradykinesia
- Psychiatric features
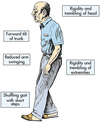
What is lead pipe rigidity?
Ridigity throughout the course of limb movement
What are the classic features of cerebellar lesions
- Dysdiadochokinesis
- Ataxia
- Nystagmus (flickering eye movement)
- Intention tremor
- Slurred Speech
- Hypotonia
Mneumonic ‘DANISH’
Which regions of the body do the different regions of the cerebellum control?
Vermis controls the trunk
Cerebral hemispheres deal with distal limbs
Do cerebellar lesions affect the ipsialateral or contralateral sides of the body?
Ipsilateral



