Reticular Formation and Conciousness Flashcards
(26 cards)
Define arousal
The emotional state associated with some kind of goal or avoidance of something noxious
Define conciousness
Difficult to define but something to do with awareness of both the external world and internal states
What two areas of the brain make up conciousness?
Cerebral cortex + reticular formation

What is the reticular formation?
A diffuse networks of neurones running the full legnth of the brainstem

Which 3 areas of the brain does the reticular formation project onto?
- Basal forebrain nuclei
- Hypothalamus
- Thalamus
What are the effects of stimulation by the reticular formation of the basal forebrain nuclei, hypothalamus and thalamus on the cerebral cortex?
Basal forebrain nuclei - realeases ACh → excitatory to the cerebral cortex
Hypothalamus - releases Histamine to cerebral cortex → drowsiness
Thalamus - releases Glutamate → excitatory to cerebral cortex

What inputs to the reticular formation regulate the level of arousal?
- Sensory system
- Cortex
What aspects are assessed in assessing conciousness in the Glasgow Coma Scale?

What does an EEG measure?
Electroencephalogram
Measure the combined activity of thousands of neurones in a given part of the cortex to a very high temporal resolution (but poor spatial resolution)
How many cycles of sleep do you go through in a night?
Typically 6 rounds of sleep
What are the different stages of sleep
Stage 1 -4 gets progressively deeper
Stage 4 rapidly switches to REM
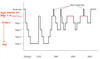
What type of waves are shown on an EEG when awake?
Beta waves
50 Hz - irregular pattern

What waves are seen on the EEG when the eyes are closed/ stage 1 sleep?
Alpha waves
10 Hz
reduced sensory input

What do you see on the EEG in stage 2/3 of sleep
Backgrounnd of alpha wabes with occasion spindles (thalamus burst) and K complexes

What is seen on the EEG during stage 4/ deep sleep
Delta waves
High amplitude, low frequency

Explain the neural mechanism of sleep
- Deactivation of the reticular activating system inhibits the thalamus
- Positive feedback loop between RAS and cortex is inhibited → decreased cortical activity
- Removed sensory inputs
Explain what happens in REM sleep
- Initiated by groups of neurones in the pons
- EEG acitivty beta waves (similar to arousal) but thalamus is strongly inhibited
- Most of the muscle tone of the body is lost due to descending inhibition of lower motor neurones by glycinergic fibres (from the reticular formation)
- Eye movements preserved
- See autonomic effects: penile erection, loss of thermoregulation
What are the functions of sleep?
Not fully understood:
- Energy conservation and bodily repair
- Memory consolidation
- Clearance of extracellular debris
- Resetting of CNS
What is insomnia?
Inability to sleep
Often a manifestation of some other psychiatric cause
What is narcolepsy?
Suddently falling asleep at innapropriate times
rare thought to be due to orexin gene
What is sleep apnoea?
Periods of stopping sleeping / shallow breathing during sleep
What are risk factors for sleep apnoea
- Overweight
- Older
- Main
- Thicker neck
- Smoker
- Nasal Congestion
What happens in brain death, what do you see on the EEG?
Widespread cortical and brainstem damage
EEG completely flat
What is a coma?
Widespread brainstem and cortical damage with various patterns on the EEG
Unarousable and unresponsive to psycholical stimuli
No sleep- wake cycle detectable


