Radiology [3] Flashcards
(16 cards)
Identify

calcification of GS
- Typicallly laminated due to forming over long periods of time and faceted due to being multiple and

Pancreatic calcification
- BUZZ for chronic pancreatitis
air can be seen above the diaphragm if the pt has a ____
Hiatal hernia
Small or large intestines?

Valvulae conniventes
In small bowel - folds go all way around bowel
- Sm bowerl should be in midddle
(look for haustra in colon)
Small or large intestines?

Haustral folds
interrupted by teniae coli
does not go all the way around
Large intestines
Small vs large intestine
Haustra vs Valvulae conniventes
Large vs Small Int
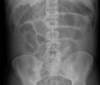
Bowel obstruction
rule
proximal bowel will distend –> dilatation of bowel
(3,6,9)
<3-Small bowel
<6cm transverse colon
<9cm cecum
What imaging is most sensitive for free air
upright PA CXR
- look underneath diaphragm
When looking for free air, it will be located in the most “non dependent space” so important to note the position of patient when x-ray was obtained.

reflux esophagitis
- “granular”

reflux esophagitis with ulcers and hiatal hernia

peptic stricture of esoph & hiatal hernia

Candida esophagitis
- Note how plaques have a linear configuration and are separated by normal intervening mucosa.

double-contrast esophagography:
shaggy esophagus of fulminant Candida esophagitis in a patient with AIDS.
This shaggy contour results from innumerable pseudomembranes and plaques, with trapping of barium between lesions.
Which part of the stomach is typically anterior
fundus
Types of barium enema+ indication
double contrast: rectal bleeding, poyps, cancer, IBD
Single contrast: fistula or sinus tract, pt unable to tolder double
Water soluble contrast: risk for intestinal perforation, therapeutic for disimpaction
BE: evaluates colon + rectum
When is CT without contrast useful?
When is CT with IV contrast useful?
detection of renal stone/hemorrhage
With contrast:
- ischemic, infectious, or inflammatory disease, trauma, tumor
- arterial, venous, portal venous


