Quizzes - To Review Flashcards
Where (which segments of the spinal cord) does the sympathetic innervation of the kidney arise from?
T10 - L1
Embryologically, from which structure is X derived?

Ureteric B ud
Name a part of the nephron that you would find in the area of the kidney labelled X –

LoH
What is the predominant tissue type that makes up structure labelled X (be specific)?

Smc
!tissue type
Name the specific part of the organ that is labelled X

Trigone
Identify structure labelled A on the given image (be specific)

Left renal vein
Identify the structure B on the given image.

Abdo Aorta
Identify the part of the kidney that this histological image is taken from.

Cortex
(also the parietal layer, this specific structure is bowmans capsule)
Identify the layer labelled X

Bowmans Capsule
Name a structure that crosses X anteriorly in the female pelvis.

Uterne Artery
What congenital anomaly do you see in the given image?

Duplication of the left ureter
Name a horizontal surface marking plane that passes through the hilum of the kidneys at L1.
Transpyloric Plane
What is. the vertebral extent of the organ X?

C5 - T1
Name one muscle that lies anterior to X.

Any one of omohyoid, sternohyoid, sternothyroid
How do hormones from X reach the anterior pituitary gland?

Via the hypophysial portal veins
During surgical excision of a thyroid nodule, the superior thyroid artery is ligated at X. What structure lies in close proximity that the surgeon should be aware of?

Superior Laryngeal nerve
Identify A & B

A - pancreas
B - Splenic artery
Name two classes of hormones secreted by the adrenal cortex.
Any two of mineralocorticoids, glucocorticoids and androgens
Name three arteries from which organ A derives its blood supply.

Abdominal Aorta, Renal and Inferior phrenic arteries
What mbryological origins are the bladder and urethra
Endodermal origin
Embryological origin of medulla and cortex
Kidney parenchyma arise from metanephric mesoderm
Which muscles inferior border is used as a landmark to describe the termination of Axillary artery and the begining of Brachial artery?
T. mj.
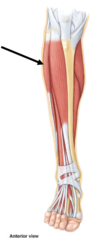
What is the main action of the muscle labelled X?

Rotates the scapula, allowing the arm to be raised over 90 degrees. It also holds the scapula against the ribcage.
A fracture at X could result in which of the following appearances at the distal extremity of the upper limb?

Claw hand dt dmg to ulnar n.