Pseudomonas Flashcards
(22 cards)
Pseudomonas is a gram ______ bacteria.
Negative
[rods, motile]

True/False. Pseudomonas is an obligate aerobe.
True
True/False. P. aeruginosa is facultative symbiotic and facultative pathogenic.
True
Facultative pathogenic usually secondary infection
If most of P. aeruginosa are saprophytic, where would you expect to find it?
Mainly in waters
Also soil and on plants
What odor does P. aeruginosa give off in culture?
Candy sweet odor
What chemicals are in Mueller-Hinton medium that P. aeurginosa react with?
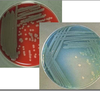
What does the bacteria look like on this culture?
Pycocyanins (is also an anti-bacterial)
Pyoverdins
Blue-greenish pigmentation on medium, large colonies
P. aeruginosa is oxidase ______.
Postive
Does P. aeruginosa react well to antibotic treatment?
No. It has a high natural resistance.
[can adapt to humid hospital envrionments - trach tubes, endoscopes]
What are the important virulence factors of pseudomonas?
Affinity for adhesion to mucoid surfaces
Biofilm (slime) - makes them more resistant to disinfectants
What kind of animals does pseudomonas as a genus typically infect? Warm or cold blooded?
Cold blooded animals - have mucus on their skin
[P. aeruginosa for mammals and birds]
What are the 3 predisposing factors for Pseudomonas infection?
High infection pressure (drinking water, environment)
Humidity
Reduced immunity (local and general)
What is the main infection you will with see P. aeruginosa in cats and dogs?
Otitis externa
[primary pathogens for otits externa: Staphylococcus pseudintermedius and Malassezia pachydermatis—plus pseudomonas get a treatment that covers gram + and - and fungus]

What secondary infections does P. aeruginosa cause in dogs and cats?
Skin infections: pyoderma
Cystitis (bladder inflammation)
Eye infections

You have a hamster, guinea pig, chinchilla, and mink farm. All of a sudden they all get pneumonia and specticemia and then they die. What killed them? How were they infected?
P. aeruginosa
Infected through drinking water
The rabbits in your rabbitry become infected with P. aeruginosa :(
What type of infection do you expect to see? Why is it hard to rid your rabbitry of pseudomonas?
Moist dermatitis - skin infection
Pseudomonas forms biofilms and is resistant to disinfectants
[sometimes rabbits will get pneumonia]
What secondary infections do you expect to see in a horse infected with P. aeruginosa?
Metritis-vaginitis - secondary to prolonged antimicrobial treatment
Keratitis conjunctivitis - following topical treatment with steroids
You have a farm. Your cows, sheep and goats all contract mastitis :( Also the beautiful fleece that your sheep grew this winter begins to rot. What bacteria is responsible?
P. aeruginosa

What conditions do you expect to see in reptiles kept in poor housing, infected with P. aeruginosa?
Necrotic stomatitis
Pneumonia
Septicemia
What is the rare skin infection caused in several animal species by P. aeruginosa (along with other bacteria) that resembles a fungal infection?
Botryomycosis
How do psittaciformes (parrots and parakeets) contract a secondary infection of P. aeruingosa?
Mainly through contaminated drinking water
[conjunctivitis, rhinitis pneumonia, air sacculitis, enteritis]
How do Galliformes (turkeys) become infected?
Origin is typically drinking water
In the oviduct of turkeys - contamination of eggs (exploding eggs!!)
What therapy is being experimented with because Pseudomonas is so resistant?
Phage therapy
[strain specific]


