PREP TEST Flashcards
- When the edges of two pieces of metal are heated until they flow together, the process is called:
a. Oxygen welding
b. Braze welding
c. Fusion welding
d. Fission welding
- When the edges of two pieces of metal are heated until they flow together, the process is called:
c. Fusion welding
- The metal rod or wire that forms part of an electric welding circuit is called a/an:
a. Electrode
b. Weldment
c. Filler rod
d. TIG stick
- The metal rod or wire that forms part of an electric welding circuit is called a/an:
a. Electrode
- Which of the following welding processes uses electrical power?
a. Shielded Metal Arc
b. Gas Metal Arc
c. Gas Tungsten Arc
d. All of the above
- Which of the following welding processes uses electrical power?
D. All of the above
a. Shielded Metal Arc
b. Gas Metal Arc
c. Gas Tungsten Arc
- In which arc welding process is a non-consumable electrode used?
a. GMAW
b. GTAW
c. SMAW
d. OAW
- In which arc welding process is a non-consumable electrode used?
b. GTAW
- Short, temporary weld beads made to hold or align the metals to be joined are known as:
a. Tack welds
b. Boxing fillets
c. Single pass groove welds
d. Stringer beads
- Short, temporary weld beads made to hold or align the metals to be joined are known as:
a. Tack welds
- Which of the following action(s} is/are involved in joint fit up?
a. Spacing
b. Alignment
c. Edge preparation
d. All of the above
- Which of the following action(s} is/are involved in joint fit up?
D. All of the above
a. Spacing
b. Alignment
c. Edge preparation
- The voltage value across the welding arc depends on:
a. Open-circuit current
b. Arc length
c. Circuit polarity
d. Drooper characteristics
- The voltage value across the welding arc depends on:
b. Arc length
- What is the primary purpose of the inert gas used in the GTAW welding process?
a. Cool the torch
b. Reduce electrode consumption
c. Eliminate arc blow
d. Shield the weld area from contamination
- What is the primary purpose of the inert gas used in the GTAW welding process?
d. Shield the weld area from contamination
- What is the purpose of the coated electrodes for SMAW welding?
a. Forms gas shield
b. Produces slag covering
c. Supplies filler metal
d. All of the above
- What is the purpose of the coated electrodes for SMAW welding?
D. All of the above
a. Forms gas shield
b. Produces slag covering
c. Supplies filler metal
- In which arc welding process is a continuous consumable wire electrode used?
a. GMAW
b. GTAW
C. SMAW
d. All of the above
- In which arc welding process is a continuous consumable wire electrode used?
a. GMAW
- When it is possible to reposition the work, welds are easiest and simplest to make in the:
a. Flat position
b. Vertical position
c. Downhand position
d. Overhead position
- When it is possible to reposition the work, welds are easiest and simplest to make in the:
a. Flat position
- Which of the following are out-of-position welds?
a. Flat and horizontal
b. Flat and vertical
c. Vertical and overhead
d. All of the above
- Which of the following are out-of-position welds?
c. Vertical and overhead
- What causes arc blow?
a. Magnetic fields
b. Arc too short
c. Dirty base metal
d. All of the above
- What causes arc blow?
a. Magnetic fields
- Spatter is caused by arc blow, current set too high, excessive arc length or:
a. Using the wrong polarity
b. Welding without a flux
c. Welding in wide gap joints
d. Improper joint grooving
- Spatter is caused by arc blow, current set too high, excessive arc length or:
a. Using the wrong polarity
- Which of the following oxyacetylene flames is recommended when gas welding mild steels?
a. Neutral to slightly carburizing
b. Carburizing
c. Slightly oxidizing
d. Oxidizing, two-to-one gas ratio
- Which of the following oxyacetylene flames is recommended when gas welding mild steels?
a. Neutral to slightly carburizing
- Which of the following characteristics must be considered when welding aluminum?
a. Low melting point
b. High thermal conductivity
c. Oxide coating
d. All of the above
- Which of the following characteristics must be considered when welding aluminum?
d. All of the above
- How many preheat flame inner cones will appear if the cutting tip has seven orifices?
a. 6
b. 5
c. 4
d. 3
- How many preheat flame inner cones will appear if the cutting tip has seven orifices?
a. 6
- In any oxygen cutting operation, one of the major safety hazards is the danger of:
a. Falling objects
b. Sparks and hot metal
c. Electrical shock
d. Burning flux flames
- In any oxygen cutting operation, one of the major safety hazards is the danger of:
b. Sparks and hot metal
- Which of the following metal cutting operations can be achieved with oxygen cutting equipment?
a. Square cuts
b. Bevel cuts
c. Piercing holes
d. All of the above
- Which of the following metal cutting operations can be achieved with oxygen cutting equipment?
D. All of the above
a. Square cuts
b. Bevel cuts
c. Piercing holes
- The primary purpose of a brazing flux is to:
a. Roughen joint surfaces
b. Wash away dirt and oil
c. Remove oxides
d. Provide chemical bonding
- The primary purpose of a brazing flux is to:
c. Remove oxides
- What is the correct name for the metal joining process commonly called silver soldering?
a. Brazing
b. Silver fusion welding
c. Stainless brazing
d. Hard soldering
- What is the correct name for the metal joining process commonly called silver soldering?
a. Brazing
- Which of the following represents a potential hazard while brazing?
a. Fumes
b. Fluxes
c. Bright light
d. All of the above
- Which of the following represents a potential hazard while brazing?
D. All of the above
a. Fumes
b. Fluxes
c. Bright light
- The process of hardening, tempering, and annealing ferrous metals is called:
a. Heat treating
b. Machining
c. Refining
d. Forging
- The process of hardening, tempering, and annealing ferrous metals is called:
a. Heat treating
- Steel is tempered for the purpose of:
a. Making it machinable
b. Aging the steel
c. Reducing brittleness and relieving internal stresses
d. Improving its corrosion resistance and increasing ferrite refinement
- Steel is tempered for the purpose of:
c. Reducing brittleness and relieving internal stresses
- How does an increase in the carbon content affecl the properties of steel?
a. It increases tensile strength
b. It increases hardness
c. It decreases malleability
d. All of the above
- How does an increase in the carbon content affecl the properties of steel?
D. All of the above
a. It increases tensile strength
b. It increases hardness
c. It decreases malleability
- Which of !he following factors determine(s) how the mechanical properties change in the heat-affected zone?
a. How hot the metal gets
b. How long the metal stays hot
c. How fast the metal cools
d. All of the above
- Which of !he following factors determine(s) how the mechanical properties change in the heat-affected zone?
D. All of the above
a. How hot the metal gets
b. How long the metal stays hot
c. How fast the metal cools
- The need to preheat a ferrous metal depends primarily on which of the following?
a. Iron content
b. Aluminum content
c. Carbon content
d. All of the above
- The need to preheat a ferrous metal depends primarily on which of the following?
c. Carbon content
- A low alloy electrode with the designation of E8018-B3L indicates the following:
a. 80,000 psi tensile
b. All position welding
c. Carbon molybdenum alloy
d. Chromium molybdenum alloy
e. “a” and “d”
f. “a” , “b” and “d”
- A low alloy electrode with the designation of E8018-B3L indicates the following:
f. “a” , “b” and “d”
- If you preheated a part but the part does not require post heating, you should cool the part:
a. Slowly under insulating material
b. In a tub of water
c. Using a fan
d. Using shielding gas
- If you preheated a part but the part does not require post heating, you should cool the part:
a. Slowly under insulating material
- Which of the following metals will not attract a magnet?
a. White cast iron
b. Austenitic stainless steel
c. Plain carbon steel
d. Low alloy steel
- Which of the following metals will not attract a magnet?
b. Austenitic stainless steel
- If you get underbead cracking with an E6010 or E6011 electrode, switch to:
a. An E6013 electrode
b. Argon shielding gas
c. A low-hydrogen electrode
d. DCSP current
- If you get underbead cracking with an E6010 or E6011 electrode, switch to:
c. A low-hydrogen electrode
- Which process is best for thin gage carbon steel when you need a fast process with low distortion?
a. GMAW
b. GTAW
C. SMAW
d. SAW
- Which process is best for thin gage carbon steel when you need a fast process with low distortion?
a. GMAW
- The best source of information on how to weld Q & T steels is the manufacturer of the:
a. Welding equipment
b. Steel
c. Electrode
d. Shielding gas
- The best source of information on how to weld Q & T steels is the manufacturer of the:
b. Steel
- Which of the following groups of electrodes are low-hydmgen electmdes?
a. EXX15,EXX16,EXX18
b. EC1, ELH, ENi-C1
c. E70S-1, E70S-G, E700-1
d. EWP, EWTh-1, EWTh-2
- Which of the following groups of electrodes are low-hydmgen electmdes?
a. EXX15,EXX16,EXX18
- The science and technology of extracting metal from their ores, refining them and preparing them for use is a definition of:
a. Atomic Fusion Welding
b. Metallurgy
c. Alloy Properties
d. All of the above
e. None of the above
- The science and technology of extracting metal from their ores, refining them and preparing them for use is a definition of:
b. Metallurgy
- Which of these metals will attract a magnet?
a. Aluminum
b. Copper
c. Magnesium
d. Nickel
- Which of these metals will attract a magnet?
d. Nickel
- The system of numbers which indicates pipe wall thickness is called:
a. Pipe wall thickness numbers
b. The OD system
c. The ID system
d. Pipe schedule numbers
- The system of numbers which indicates pipe wall thickness is called:
d. Pipe schedule numbers
- After welding, a fusible backup ring:
a. Is removed
b. Is peened
c. Becomes part of the weld
d. Is thrown away
- After welding, a fusible backup ring:
c. Becomes part of the weld
- The flux in shielded metal arc welding:
a. Protects your eyes against the arc flash
b. Contains spatter and sparks
c. Prevents contamination of molten metal
d. All of the above
- The flux in shielded metal arc welding:
c. Prevents contamination of molten metal
- In SMAW, the arc voltage while welding normally ranges between:
a. 0 and 15 V
b. 15 and 40 V
c. 50 and 100 V
d. 100 and 200 V
- In SMAW, the arc voltage while welding normally ranges between:
b. 15 and 40 V
- A welding machine with a duty cycle rating of eighty percent (80%) can deliver its rated maximum welding current for a total of:
a. 8 min. before idling 2 min. lo cool
b. 16 min. before idling 4 min. to cool
c. 48 min. before idling 12 min. to cool
d. 80 min. before idling 20 min. to cool
- A welding machine with a duty cycle rating of eighty percent (80%) can deliver its rated maximum welding current for a total of:
a. 8 min. before idling 2 min. lo cool
- The work piece lead is always connected to the:
a. · Bare end of the electrode
b. Base metal
c. Negative terminal
d. Positive terminal
- The work piece lead is always connected to the:
b. Base metal
- An E6013 covered electrode provides a weld deposit that has a minimum tensile strength of:
a. 1300 psi
b. 13,000 psi
c. 6000 psi
d. 60,000 psi
- An E6013 covered electrode provides a weld deposit that has a minimum tensile strength of:
d. 60,000 psi
- The current range for a given covered electrode depends mainly on:
a. Its diameter
b. Its length
c. The base metal to be welded
d. How long it was in storage
- The current range for a given covered electrode depends mainly on:
a. Its diameter
- Because of their high deposition rate, you should use iron powder electrodes primarily for:
a. Vertical welds
b. Flat or horizontal fillet welds
c. Overhead welds
d. All of the above
- Because of their high deposition rate, you should use iron powder electrodes primarily for:
b. Flat or horizontal fillet welds
- Unlike the low hydrogen covered electrodes, those with cellulose coverings need a certain amount of:
a. Moisture
b. Filler metal
c. Static suppressors
d. Oil and flux
- Unlike the low hydrogen covered electrodes, those with cellulose coverings need a certain amount of:
a. Moisture
- Unlike SMAW, the GMAW process:
a. Is less expensive
b. Produces no slag
c. Uses non-consumable electrodes
d. Uses no shielding gas
- Unlike SMAW, the GMAW process:
b. Produces no slag
- A disadvantage of GMAW is that strong drafts or winds can:
a. Blow out the arc
b. Change the electrode feed rate
c. Blow the shielding gas away
d. Make the gun hard to handle
- A disadvantage of GMAW is that strong drafts or winds can:
c. Blow the shielding gas away
- Your choice of shielding gas for GMAW depends upon:
a. Desired arc and metal transfer
b. Required penetration and fusion
c. Shape of the finished weld
d. All of the above
- Your choice of shielding gas for GMAW depends upon:
D. All of the above
a. Desired arc and metal transfer
b. Required penetration and fusion
c. Shape of the finished weld
- Your main concern when selecting electrode wire for GMAW is that the wire has the same:
a. Diameter as the feeder
b. Composition as the base metal
c. Length as the gun
d. All of the above
- Your main concern when selecting electrode wire for GMAW is that the wire has the same:
b. Composition as the base metal
- When you press the trigger on a GMAW gun, shielding gas flows out of the nozzle and:
a. Water circulates for cooling on water cooled torches
b. The electrode wire is energized
c. The electrode wire starts feeding
d. All of the above
- When you press the trigger on a GMAW gun, shielding gas flows out of the nozzle and:
D. All of the above
a. Water circulates for cooling on water cooled torches
b. The electrode wire is energized
c. The electrode wire starts feeding
- In GTAW, the electrode is:
a. Tungsten
b. Non-consumable
c. Held in the torch by a collet
d. All of the above
- In GTAW, the electrode is:
D. All of the above
a. Tungsten
b. Non-consumable
c. Held in the torch by a collet
- DCSP welding current for GTAW produces a narrow bead with:
a. Heavy slag
b. Shallow penetration
c. Deep penetration
d. Oxide-Cleaning action
- DCSP welding current for GTAW produces a narrow bead with:
c. Deep penetration
- The flux in the core of FCAW electrodes:
a. Forms slag
b. Provides a gas shield
c. Stabilizes the arc
d. All of the above
- The flux in the core of FCAW electrodes:
D. All of the above
a. Forms slag
b. Provides a gas shield
c. Stabilizes the arc
- Submerged arc welding (SAW) is usually:
a. Used under water
b. Most often automated
c. Used for vertical welding
d. A very smoky process
- Submerged arc welding (SAW) is usually:
b. Most often automated
- Which of the following is considered non-destructive testing?
a. Fillet weld shear testing
b. Hardness test
c. Visual inspection
d. Tensile test
- Which of the following is considered non-destructive testing?
c. Visual inspection
- Which of the following is considered duties of an inspector?
a. Selection of production test samples
b. Verification of procedure qualifications
c. Interpretation of test results
d. All of the above
- Which of the following is considered duties of an inspector?
D. All of the above
a. Selection of production test samples
b. Verification of procedure qualifications
c. Interpretation of test results
- Which of the following is/are essential elemenl(s) of a welding procedure?
a. Joint design
b. Base metal type
c. Welding position
d. All of the above
- Which of the following is/are essential elemenl(s) of a welding procedure?
D. All of the above
a. Joint design
b. Base metal type
c. Welding position
- Which of the following terms is not applicable to postweld heat treating?
a. Quench
b. Crystallize
c. Hardening
d. Normalize
- Which of the following terms is not applicable to postweld heat treating?
b. Crystallize
- Gaseous inclusions in welds are called:
a. Slag
b. Tungsten
c. Porosity
d. Undercut
- Gaseous inclusions in welds are called:
c. Porosity
- Which NOT process can best determine the presence of tungsten inclusions?
a. Magnetic Particle
b. Liquid Penetrant
c. Ultrasonic
d. Radiographic
- Which NOT process can best determine the presence of tungsten inclusions?
c. Ultrasonic
- Which testing method cannot determine ductility?
a. Nick break test
b. Free bend test
c. Guided bend test
d. Tensile test
- Which testing method cannot determine ductility?
a. Nick break test
- Metallographic examination can be used to determine:
a. Number of weld passes
b. Location and depth of weld penetration
c. Soundness of weld
d. All of the above
- Metallographic examination can be used to determine:
D. All of the above
a. Number of weld passes
b. Location and depth of weld penetration
c. Soundness of weld
- Which of the following is not a hardness measuring process?
a. Rockwell
b. Charpy
c. Vickers
d. Brine/I
- Which of the following is not a hardness measuring process?
b. Charpy
- Which of the following terms best describes the maximum load carrying capability of a material?
a. Yield strength
b. Ultimate tensile strength
c. Elongation
d. Reduction in area
- Which of the following terms best describes the maximum load carrying capability of a material?
b. Ultimate tensile strength
- What is the cross sectional area of a round tensile specimen with a diameter of .500 inches?
a. .2 sq. in.
b. 2 sq. in.
c. .1 sq. in.
d. 1 sq. in.
- What is the cross sectional area of a round tensile specimen with a diameter of .500 inches?
a. .2 sq. in.
- Which of the following destructive tests contains a swinging pendulum?
a. Drop weight test
b. Tensile test
c. Charpy impact test
d. Explosion bulge test
- Which of the following destructive tests contains a swinging pendulum?
c. Charpy impact test
- It is essential that welding attributes be visually inspected:
a. During welding
b. After welding
c. Prior to welding
d. All of the above
- It is essential that welding attributes be visually inspected:
D. All of the above
a. During welding
b. After welding
c. Prior to welding
- A single fillet weld gage can:
a. Determine undercut in butt welds
b. Measure all size fillet weld dimensions
c. Determine presence of cracking
d. None of the above
- A single fillet weld gage can:
D. None of the above
a. Determine undercut in butt welds
b. Measure all size fillet weld dimensions
c. Determine presence of cracking
- Liquid penetrant inspection is limited to:
a. Magnetic materials
b. Non-magnetic materials
c. Surface flaws
d. Large size defects
- Liquid penetrant inspection is limited to:
c. Surface flaws
- Magnetic particle inspection is limited to:
a. Magnetic materials
b. Non-magnetic materials
c. Surface flaws
d. Large size defects
- Magnetic particle inspection is limited to:
a. Magnetic materials
- A magnetic particle indication can be found if the indication is perpendicular to the:
a. Current
b. Magnetic flux-lines
c. Weld
d. Plate edge
- A magnetic particle indication can be found if the indication is perpendicular to the:
b. Magnetic flux-lines
- Which of the following types of current has the least ability to discover magnetic particle indications below the surface?
a. Alternating Current
b. Half-wave Rectified Direct Current
c. Full-wave Rectified Direct Current
d. Direct Current
- Which of the following types of current has the least ability to discover magnetic particle indications below the surface?
a. Alternating Current
- During magnetic particle inspection, an elongated, fuzzy indication is found. This probably indicates:
a. Surface crack
b. Subsurface crack or slag
c. Crater crack
d. All of the above
- During magnetic particle inspection, an elongated, fuzzy indication is found. This probably indicates:
b. Subsurface crack or slag
- Which of the following could cause irrelevant magnetic particle indications?
a. Physical contour
b. Change in magnetic characteristics
c. Magnetic to non-magnetic metal
d. All of the above
- Which of the following could cause irrelevant magnetic particle indications?
D. All of the above
a. Physical contour
b. Change in magnetic characteristics
c. Magnetic to non-magnetic metal
- Which of the following terms does not apply to “Radiography”?
a. Half-life
b. Density
c. Iridium 192
d. Couplant
- Which of the following terms does not apply to “Radiography”?
d. Couplant
- Which of the following devices indicates radiographic film sensitivity?
a. Image quality indicator
b. Screens
c. Lead Markers
d. Shim
- Which of the following devices indicates radiographic film sensitivity?
a. Image quality indicator
- Radiography:
a. Is the best method for finding cracks
b. Does not depend on material size or shape
c. Provides a permanent record of weld defects
d. Can be used to pin point subsurface flaws
- Radiography:
c. Provides a permanent record of weld defects
- Which of the following terms does not apply to Ultrasonic Inspection?
a. Couplant
b. Transducer
c. Clock
d. Electromagnetic
- Which of the following terms does not apply to Ultrasonic Inspection?
d. Electromagnetic
- Ultrasonic waves are:
a. X-ray waves
b. Light waves
c. Sound waves
d. Electric currents
- Ultrasonic waves are:
c. Sound waves
- Ultrasonics can:
a. Determine wall thickness
b. Determine general size of defect
c. All of the other choices
d. Determine general shape of defect
- Ultrasonics can:
c. All of the other choices
- A metallic structure of ultra-hard, needle-like crystals that are a super-saturated solid solution of carbon in iron is a definition of:
a. Austenite
b. Martensite
c. Ferrite
d. Pearlite
- A metallic structure of ultra-hard, needle-like crystals that are a super-saturated solid solution of carbon in iron is a definition of:
b. Martensite
- The reason a “shim” is used in radiographic set-up is to:
a. Improve the penetrameter image
b. Reduce diffraction
c. Simulate weld reinforcement
d. Intensify the image
- The reason a “shim” is used in radiographic set-up is to:
c. Simulate weld reinforcement
- The image of the required image quality indicator and hole on the radiograph indicates that the radiograph has the required:
a. Contrast
b. Definition
c. Sensitivity
d. Latitude
- The image of the required image quality indicator and hole on the radiograph indicates that the radiograph has the required:
c. Sensitivity
- In ultrasonic testing, moving a search unit over a test surface either manually or automatically is referred to as:
a. Scanning
b. Attenuating
c. Angulating
d. Resonating
- In ultrasonic testing, moving a search unit over a test surface either manually or automatically is referred to as:
a. Scanning
- An ultrasonic test using a straight beam contact search unit is being conducted through the thickness of a flat part such as a plate. This test should detect:
a. Laminar-type flaws with major dimensions parallel to the rolled surface
b. Transverse-type flaws with major dimensions at right angles to the rolled surface
c. Radial flaws with major dimensions along length but radially oriented to the rolled surface
d. None of the above
- An ultrasonic test using a straight beam contact search unit is being conducted through the thickness of a flat part such as a plate. This test should detect:
a. Laminar-type flaws with major dimensions parallel to the rolled surface
- The rate of gas flow with GMAW is determined by:
a. Speed of travel
b. Position of welding
c. Air movement
d. Climatic conditions
e. All of the above
- The rate of gas flow with GMAW is determined by:
E. All of the above
a. Speed of travel
b. Position of welding
c. Air movement
d. Climatic conditions
- The proper root opening between two pieces of V-grooved plate is determined by:
a. The welding procedure specification
b. The thickness of the plate
c. A fixed specification of 1/16” to 1/8”
d. The craftsman
e. None of the above
- The proper root opening between two pieces of V-grooved plate is determined by:
a. The welding procedure specification
- What are the three ingredients or conditions needed for combustion?
a. Fuel, heat and a source of ignition
b. Fuel, heat and oxygen
c. Vapors, dust and self-ignition
d. Ordinary combustibles, flammable liquids and combustible metals
- What are the three ingredients or conditions needed for combustion?
b. Fuel, heat and oxygen
- Cracks are less likely to occur when welding:
a. Thick sections
b. Thin sections
c. Thick sections to thin sections
d. All are equally susceptible to cracking
- Cracks are less likely to occur when welding:
b. Thin sections
- Laminations in beveled edges of plate can be inspected by:
a. Visual and Eddy Currents
b. Visual and Magnetic Particle
c. Visual and Radiography
d. Visual and Ultrasonics
e. “b and “d” above
- Laminations in beveled edges of plate can be inspected by:
b. Visual and Magnetic Particle
- In ultrasonic testing, a liquid coupling medium between the crystal surface and the part surface is necessary because:
a. Lubricant is required to minimize wear on the crystal surface
b. An air interface between the crystal surface and the part surface would almost completely reflect the ultrasonic vibrations
c. The crystal will not vibrate if placed directly in contact with the surface of the part being inspected
d. The liquid is necessary to complete the electrical circuit in the search unit
- In ultrasonic testing, a liquid coupling medium between the crystal surface and the part surface is necessary because:
b. An air interface between the crystal surface and the part surface would almost completely reflect the ultrasonic vibrations
- The penetrameter number shown on radiographic film is actual thickness of the penetrameter expressed in:
a. Millimeters
b. Centimeters
c. Hundredths of an inch
d. Thousandths of an inch
e. None of the above
- The penetrameter number shown on radiographic film is actual thickness of the penetrameter expressed in:
d. Thousandths of an inch
- Which of the following is an advantage of magnetic particle testing over penetrant testing?
a. It can detect surface discontinuities with foreign material imbedded in them
b. It is faster on individual parts
c. It can detect near-surface discontinuities using direct current
d. All of the above
- Which of the following is an advantage of magnetic particle testing over penetrant testing?
D. All of the above
a. It can detect surface discontinuities with foreign material imbedded in them
b. It is faster on individual parts
c. It can detect near-surface discontinuities using direct current
- A decision to postheat depends on which of the following factors:
a. Composition of the base metal
b. Part thickness
c. Part shape
d. All of the above
- A decision to postheat depends on which of the following factors:
D. All of the above
a. Composition of the base metal
b. Part thickness
c. Part shape
- Visible penetrant may be applied by:
a. Brushing
b. Spraying
c. Dipping
d. All of the above
- Visible penetrant may be applied by:
D. All of the above
a. Brushing
b. Spraying
c. Dipping
- The first step in conducting a liquid penetrant test on a surface that has been painted is to:
a. Carefully apply the penetrant over the surface
b. Completely remove the paint
c. Thoroughly wash the surface with a detergent
d. Wire brush the surface to roughen the smooth su1·face coating of paint
- The first step in conducting a liquid penetrant test on a surface that has been painted is to:
b. Completely remove the paint
- The black light lamp should not be used with a cracked filter or without the filter in place because of the harmful effects to the human eyes caused by the lamp’s emission of:
a. Black light
b. Ultraviolet light
c. Infrared light
d. None of the above
- The black light lamp should not be used with a cracked filter or without the filter in place because of the harmful effects to the human eyes caused by the lamp’s emission of:
b. Ultraviolet light
- SMAW is used as a standard terminology abbreviation for the following:
a. Shielded Metal Arc Welding
b. Shielded Metal After Welding
c. Shielded Manual Arc Welding
d. All of the above
e. None of the above
- SMAW is used as a standard terminology abbreviation for the following:
a. Shielded Metal Arc Welding
- Identify the welding symbol to the right:
a. Double 3/8” fillet weld
b. 3/8” fillet weld both sides
c. 3/8” groove weld each side
d. All of the above
e. None of the above
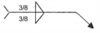
- Identify the welding symbol to the right:
b. 3/8” fillet weld both sides

- Which crack will cause the clearest indication?
a. “A”
b. “B”
c. “C”
d. Both Band C

- Which crack will cause the clearest indication?
a. “A”

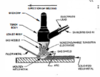
- The diagram to the right shows:
a. Shielded Metal Arc Welding
b. Gas Metal Arc Welding
c. Gas Tungsten Arc Welding
d. Submerged Arc Welding
e. Stud Arc Welding
f. Flux Cored Arc Welding
g. None of the above

- The diagram to the right shows:
c. Gas Tungsten Arc Welding
- A reduced-section tensile has a width of .750” and a thickness of .375”. The closest cross sectional square area is:
a: 2.00” SQUARED
b. 1.130” SQUARED
c. .281” SQUARED
d. None of the above
- A reduced-section tensile has a width of .750” and a thickness of .375”. The closest cross sectional square area is:
c. .281” SQUARED
- The reduced-section tensile (in #103 above), when tested, broke al a load of 20,350 pounds. Its ultimate tensile strength was rounded off to be:
a. 70,246 psi
b. 72,420 psi
c. 72,678 psi
d. None of the above
- The reduced-section tensile (in #103 above), when tested, broke al a load of 20,350 pounds. Its ultimate tensile strength was rounded off to be:
b. 72,420 psi
- Using the divided method for attaining the elongation of the above reduced-section tensile in a 2” span indicated that the specimen had stretched .510”. The percentage of elongation was (rounded to lhe next higher number):
a. 42%
b. 26%
c. 25%
d. None of the above
- Using the divided method for attaining the elongation of the above reduced-section tensile in a 2” span indicated that the specimen had stretched .510”. The percentage of elongation was (rounded to lhe next higher number):
b. 26%
- The _________ test is used to determine the notch toughness of steel at variations in temperature, such as at extremely low temperatures.
a. Tensile
b. Impact
c. Bend
d. None of the above
- The _________ test is used to determine the notch toughness of steel at variations in temperature, such as at extremely low temperatures.
b. Impact
- Identify the welding symbol to the right:
a. Square butt groove weld with melt-thru
b. Flush square butt joint
c. Square butt joint with backing
d. None of the above

- Identify the welding symbol to the right:
a. Square butt groove weld with melt-thru

- Identify the welding symbol to the right:
a. Staggered intermittent groove weld
b. Staggered intermittent fillet weld with spacing 3” apart
c. Staggered intermittent fillet welds., both sides with increments 3” long, 8” apart
d. Intermittent ¼” fillet welds both sides with welding increments 3” long, 8” apart
e. Intermittent ¼” fillet welds, both sides with welding increments 3” long, 5” apart

- Identify the welding symbol to the right:Next
e. Intermittent ¼” fillet welds, both sides with welding increments 3” long, 5” apart

- a. b. c. d.

- a. b. c. d.
C.

- a. b. c. d.

- a. b. c. d.
B.

- A circle indicated at the apex of the reference line indicates:
a. Field weld
b. Weld all around
c. Weld only one side
d. All of the above
e. None of the above
- A circle indicated at the apex of the reference line indicates:
B.
- The muitipass weld seen in this sketch represents:
a. A vertical up weld
b. A 3-layered weld
c. A 3-bead weld
d. A fillet weld
e. All of the above
f. None of the above

- The muitipass weld seen in this sketch represents:
E. All of the above
a. A vertical up weld
b. A 3-layered weld
c. A 3-bead weld
d. A fillet weld

- The sketch below represents the measuring of a ______ fillet weld.
a. Convex
b. Concave
c. Flat
d. Unequal leg

- The sketch below represents the measuring of a ______ fillet weld.
b. Concave

- The sketch below represents the measuring of a ______ fillet weld.
a. Convex
b. Concave
c. Oversized
d. Undersized

- The sketch below represents the measuring of a ______ fillet weld.
a. Convex

- The test samples shown to the right represent a test for:
a. Transverse fillet weld shear test
b. Longitudinal fillet weld shear test
c. Fillet weld notch effect
d. None of the above

- The test samples shown to the right represent a test for:
a. Transverse fillet weld shear test

- The lest sample shown below represents a test called:
a. Microfracture lest
b. Fillet weld break test
c. Fillet weld tensile test
d. Macrofracture test

- The lest sample shown below represents a test called:
b. Fillet weld break test

- The test specimen shown below represents a test specimen used lo measure:
a. Tensile strength
b. Yield strength
c. Elongation
d. All of the above
e. None of the above

- The test specimen shown below represents a test specimen used lo measure:
D. All of the above
a. Tensile strength
b. Yield strength
c. Elongation

- The test set-up below is a method for making a
a. Tensile break test
b. Charpy notch test
c. Nick break test
d. Notch toughness test

- The test set-up below is a method for making a
c. Nick break test

- The photo below represents a type of destructive testing known as:
a. Photomacroetch
b. Photomicroetch
c. Photominietch
d. Photographic

- The photo below represents a type of destructive testing known as:
a. Photomacroetch

- The sketch below represents a type of testing known as:
a. Nick break test
b. Charpy impact test
c. lzod impact test
d. Drop weight test

- The sketch below represents a type of testing known as:
b. Charpy impact test

- Which sketch below is the proper measurement of the size of a convex fillet weld?

- Which sketch below is the proper measurement of the size of a convex fillet weld?
A.

- The portion of weld metal that is above the base metal is called:
a. Excess weld
b. Complete penetration
c. Reinforcement
d. None of the above
- The portion of weld metal that is above the base metal is called:
C.
- Using the formula below, what is the heat input for a weld made at 700A, 25V, and 4” per minute?
a. 15
b. 2,625
c. 262,500
d. 4,375

- Using the formula below, what is the heat input for a weld made at 700A, 25V, and 4” per minute?
D. 4,375

- AWS specifications for mild steel and low alloy steel electrodes (SMAW) respectively are:
a. 5.17 and 5.23
b. 5.23 and 5.17
c. 5.5 and 5.1
d. 5.1 and 5.5
- AWS specifications for mild steel and low alloy steel electrodes (SMAW) respectively are:
d. 5.1 and 5.5
- A tensile bar measures .375” thick and .780” wide. What is the approximate cross sectional area?
a. .293 sq. in.
b. 293 sq. in.
c. 2.93 sq. in.
d. 29.3 sq. in.
- A tensile bar measures .375” thick and .780” wide. What is the approximate cross sectional area?
a. .293 sq. in.
- A standard round tensile bar broke at a load of 22,400 lbs. What is the tensile strength?
a. 44,800 psi
b. 101,122 psi
c. 114,100 psi
d. 110,700 psi
- A standard round tensile bar broke at a load of 22,400 lbs. What is the tensile strength?
c. 114,100 psi
- Select the NDE method would be the most sensitive for detection of the following illustrated discontinuities. (NOTE: The testing will be performed from the top side.)

- Select the NDE method would be the most sensitive for detection of the following illustrated discontinuities. (NOTE: The testing will be performed from the top side.)
D.

- Select the NDE method would be the most sensitive for detection of the following illustrated discontinuities. (NOTE: The testing will be performed from the top side.)

- Select the NDE method would be the most sensitive for detection of the following illustrated discontinuities. (NOTE: The testing will be performed from the top side.)
B. PT

- Select the NDE method would be the most sensitive for detection of the following illustrated discontinuities. (NOTE: The testing will be performed from the top side.)

- Select the NDE method would be the most sensitive for detection of the following illustrated discontinuities. (NOTE: The testing will be performed from the top side.)
A. RT

ANSWER SHEET



