Physics 2 Flashcards
(71 cards)
1
Q
- Think of a “FIELD” as:
A
- an invisible influence capable of exerting a force on a MASS or CHARGE
2
Q
- Universal Law of Gravitation (formula)
A
Fg=Gm1m2/r2
3
Q
- The Universal Law of Gravitation is true everywhere, but NEAR EARTH’S SURFACE:
- What do we assume?
- What formula can we simplify to?
A
- Assume g= 10 m/s2
- Simplify to:
- F=mg
- Simplify to:
4
Q
- Give the PEgrav formula NEAR EARTH
For FLUIDS (which DON’T always move as a single uni), what change to the formula do we make?
A
PEgrav=mgh
- For fluids:
- use PEgrav=pgh
- p=density=m/v
- use PEgrav=pgh
5
Q
- Give the PEgravformula
- IN SPACE, or
-
NEAR EARTH’S SURFACE
- if we AREN’T assuming g=10 m/s2
A
PEgrav= - Gm1m2/r
Radius is NOT squared here!!!
6
Q
- Friction opposes ____, not ____
A
SLIDING!
- not motion
7
Q
- If theres SLIDING, it’s ___ friction
- If NOT, its ___ friction
A
- sliding= kinetic friction
- not sliding=static friction
8
Q
- Give the formulas for static & kinetic friction
A
STATIC FRICTION:
-
Ff=UsFn
- or Ff=Usmgcosθ
KINETIC FRICTION:
-
Ff=UkFn
- or Ff=Ukmgcosθ
Us / Uk = Coefficient of static/kinetic friction
Fs / Fk= Force of static/kinetic friction
n= “normal force”=mgcosθ
9
Q
- Define MAX static friction
A
- once this value is reached, OBJECT BEGINS TO SLIDE
- at this moment, we now have kinetic friction, NOT STATIC
Ex: no mvmt at 500 N (static) but starts moving at 501 N=kinetic
10
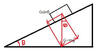
Q
- Inclined Planes
- Give the equation for:
- Force down an inclined plane
- parallel to the surface
- Force down an inclined plane
- Give the equation for:
A
F=mgsinθ
11
Q
- Inclined planes:
-
Normal force on an Inclined Plane
- Equation=?
-
Normal force on an Inclined Plane
A
Fn=mgcosθ
12
Q
- Inclined planes:
- Velocity of a particle at the base of an inclined plane
- Equation=?
A
Vf=√2gh
13
Q
- Inclined planes
- ACCELERATION down an inclined plane
- Equation=?
A
a=gsinθ
14
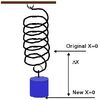
Q
Hooke’s Law formula
A
F=kΔx
15
Q
- How do you calculate k (spring constant) by hanging weights?
- Remember calculation is different for just doing ONE trial and doing TWO (+) trials
A
- Solve using Hooke’s Law
- F=kΔx
- for Δx, use:
- _Displacement from equilibrium p_oint
- for ONE trial
-
Difference in displacement
- between TWO trials
- _Displacement from equilibrium p_oint
- For F, use:
- Force applied in ONE trial, or
-
Difference in force
- between TWO trials
- Remember to convert mass of object to force
- using F=mg
16
Q
- PEelastic
- Definition
- Equation=?
A
PEelastic=½kΔx2
- PEelastic= PE stored in a compressed spring
17
Q
- PEelastic most likely used for what kinds of questions?
- How would you use PEelastic to find out how far a spring compresses when an object hits it?
A
Conservation of energy questions!
- When a mass of velocity V hits a spring:
- ALL of its KE is converted into PEelastic
- Setting KEinitial equal to final PEelastic
- …lets you find how far the spring will compress
18
Q
- Kinetic Energy equation=?
A
KE=½mv2
19
Q
- Finding how far a spring compresses
- What COMBINATION of formulas would you use?
A
Set KE equal to PEelastic
- ½mv2 = ½kΔx2
20
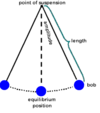
Q
-
ONE CYCLE of a pendulum is?
- (LOTR)
A
- “There and back again”
21
Q
- For a pendulum to exhibit Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM)…
- What value must be LOW?
A
- Angle of displacement

22
Q
Give 3 examples of Simple Harmonic Motion
A
- Pendulum
- mass on a string
- Things w/ circular motion when viewed from the side
- Ex: Something bobbing up & down in the water
- has a circular motion!
- Ex: Something bobbing up & down in the water
- Waves sloshing back & forth in a container
23
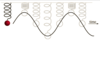
Q
-
Simple Harmonic Motion
- Give the Mass on a Spring formula
A
T=2π√m/k
24
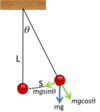
Q
-
Simple Harmonic Motion
- Give the pendulum formula
A
T=2π√L/g
25
* **Simple Harmonic Motion**
* What is **"T?"**
* What thing is its ***inverse***?
**T=period**
## Footnote
* inverse to ***frequency***
* *f=*1/T

26
* Objects **at rest** are in ___ equilibrium
***STATIC*** equilibrium
27
* Objects moving at **CONSTANT velocity** are in ___ equilibrium
***DYNAMIC*** equilibrium
28
* What do you do to solve **equilibrium** problems?
* Hint: make a T...
**_Make a T_**
* put **opposing** forces on **opposite** sides
* **balance** them out
* Ex: If 180 N in *downward* direction
* then 180N *upward*
29
* Give 3 examples of **equilibrium**
1. Terminal velocity
* mg=Fair
2. **Constant** velocity
3. Objects ***at rest***
30
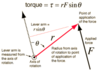
* **Torque** formulas3 variations)
* Break down what each part represents
1. **T=fl**
2. **T=mgl**
3. **T=Frsinθ**
* l=lever arm
* r=dist b/t force & point of rotation
31
* In Torque equation:
* ***r = l*** *only* when...?
* What is **always** equal to "l?"
**r = l only when θ=90°**
* **"rsinθ"** is *always* equal to l
32
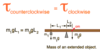
* To solve for:
* **fulcrum** and **boards on strings** problems
* Hint: these are in *equilibrium*
_Set:_
* **Tclockwise=Tcounterclockwise**
* include ***ALL*** torques!
33
* Torque
* In what scenario would you use ***T=Frsinθ?***
* When Force applied is ***NOT*** perpendicular to the surface
* i.e., when θ is _NOT_ 90°
34
* Define:
* systems ***NOT*** in equilibrium
* where the **object** has ***NON-ZERO ACCELERATION***
35
* When solving for systems NOT in equilibrium:
* How do you solve it ***differently*** than systems that **are** in equilibrium?
* What can you ***IGNORE*** when solving for systems that are not in equilibrium?
* Solve in **same** way as equilibrium problems (T method
* but **add "ma"** to the **"losing side"**
* This equals it out
You can ***IGNORE SIGNS (+/-)*** when you do this method!
36
* Equilibrium on an Inclined Plane
* How to solve?
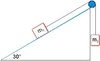
_Use T method_
* One side= ***UP*** forces
* Other side=***DOWN*** forces
* Down forces always equal to **F=mgsinθ**
* since force of friction is always **parallel** to the plane **opposite the direction of motion**

37
How to solve problems involving ***2D*** forces
_Use T method_
* Put **formula** that **predicts component of each force** into boxes
* Add "ma" onto the "losing side"
38
Define the **"right hand rule"** for **angular velocity (ω)**
* Curl fingers around axis of rotation, so that fingers are pointing in the direction of rotation
* Your **thumb** will then be pointing in the **direction of the vector** (ω)

39
How many **radians** per **1 revolution**
**~6**
## Footnote
* 6.28 exactly
40
How to **convert Radians** to **degrees**
* 2π radians/360°
or
* π radians/180°
41
* An object is in rotational equilibrium IF:
* 2 options...either one or the other
1. It is ***NOT rotating***, or
2. It is rotating with **constant** ω (angular velocity)
42
* **Momentum** formula=?
**p=mv**
43
* Think of ***momentum*** as?
* When is it ***always conserved***?
...as ***INERTIA INCREASED BY VELOCITY***
* p is always conserved **in an isolated system**
* is not conserved when not in an isolated system
44
* Define "Impulse"
* **change** in an object's **momentum**
* **"Δp"**
45
* **Impulse** formula
* 3 variations (in order of *how you should think of impulse*)
1. **I=Δp**
2. **I=mΔv**
3. **I=Favgt**
46
* What are **common impulse questions**?
* How are **velocity** and **impulse** related?
***CAR CRASHES!***
## Footnote
* **No** change in V= **No** impulse
* **High** change in V=**High** impulse
47
* Elastic vs Inelastic collisions
_Elastic Collisions_
* p ***AND*** KE conserved
_Inelastic Collisions_
* p conserved ***ONLY***
48
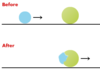
* If object is **deformed** during collision, it was a _____ collision
* **inelastic**
49
* Elastic collisions
* Equation=?
* Hint: What gets conserved during elastic collisions?
**½m1v12+ ½m2v22= ½m1v12+ ½m2v22**
* p and KE both conserved
50
* For ***PERFECTLY*** elastic collisions, what 2 weird things happen?
* What's a (albeit *imperfect*, but close enough) example of this?
1. ***Speed is conserved***
* before ***AND*** after collision
2. If mass of 2 objects is **equal** but they have **different velocities**:
* velocities get **exchanged**
* in order to **conserve momentum** (p=mv)
Think of: ***BILLIARD BALLS***
51
* **Inelastic** collisions formula
* What thing ***DO*** you need to remember to use here that you ***DON'T*** need to use for **elastic** collisions?
**m1v1+m2v2=m1v1+m2v2**
## Footnote
You need to remember to ***USE SIGNS!! (+/-)***
* Velocity has a *negative sign* when:
* going to the **LEFT** or
* **DOWN**
52
* "Perfectly ***IN***elastic" collisions
* definition & formula
* objects collide and **stick together**
* it's like MARRIAGE!
* if they move **after** collision, they do so **together**
**m1v1+m2v2=(m1+m2)v3**
53
* **Reverse Collisions** definition
* What is commonly use by the MCAT to test you on **reverse** collisions?
* Two objects **start out together** and **come apart**
* it's like DIVORCE
_Common examples:_
* Bomb exploding
* Also, RADIOACTIVE DECAY is frequently used
54
* **Thermal expansion** formula
ΔL=αLoΔT

55
* Heating solids leads to \_\_\_
* Cooling solids leads to \_\_\_
* expansion
* shrinkage
56
* What makes water ***unique*** when it comes to **thermal expansion?**
* When temperature of water gets close to zero, it ***EXPANDS (INSTEAD OF SHRINKING)***
* because of of *highly ordered lattice structure* of ice
* This is why the solid ice doesnt sink on liquid water
57
* PEelec
* formula=?
* 2 variations
* **PEelec=Kq1q2/r**
or
* **PEelec=qEd**
58
* PEcapacitor formula=?
* 3 variations
* **PEcapac=½QV**
* **PEcapacitor=½CV2**
* **PEcapacitor=½Q2/C**
59
* **Internal** energy
* definition
* Energy of:
* **Internal vibrations** &
* **Random motions** of:
* molecules and/or
* atoms w/
...in a system
60
* Heat energy
* Definition
* Where can Heat Energy **come from?** (2)
**=energy dissapated as heat**
## Footnote
* _Can come from:_
1. a collision
2. a current-carrying wire
(among other things)
61
* **Law** of **Conservation of Energy** says...?
* in an **isolated** system:
* energy is _***ALWAYS*** ***CONSERVED***_
* e.g., it can be **transferred**, but **never lost**
62
* Define an **"Open system"**
* both **mass *AND* energy**
* **...**can be **exchanged** with surroundings
63
Define a **"Closed system"**
* **Energy**, but ***NOT mass***
* ...can be exchanged with the surroundings
64
* Define an **"Isolated system"**
* ***Neither mass NOR energy***
* ***...***can be exchanged with the surroundings
65
* Think of "Work" in what order?
* ...when it comes to ***formulas***
1. **W=ΔE**
2. **W=Fdcosθ**
66
* When I see the following, Ill think "WORK"
* 7 things
1. Change in **velocity**
2. Change in **height**
3. Change in **positon of masses** (or planets in space)
4. Change in **position of a charge**
5. **Compression** of a spring (PE stored up)
6. Friction
7. Air resistance
67
* Give 2 examples of **W=Fdcosθ**
* aka...give 2 examples of **force** being applied **along a displacement**
1. Pushing a block along a table
2. An object falling from height
* height=displacement!
* Dont forget that!
68
* What are the **ONLY** 2 ways energy can be transferred in/out of a system?
1. Work
2. Heat (dissapated)
69
* 1st Law of Thermodynamics
* Equation=?
**ΔE= W + Q**
70
* Work-Energy theorem
* What should you focus on **instead**?
* If Fnet does work on a **rigid** object:
* the **work done** on that object is equal to:
* the **change in KE** of the object
* Focus on W=ΔE
* correct use of this **negates** need to use work-energy theorem
71


