PCTH - Burns Flashcards
Burns occur when
- heat or caustic materials come in contact with the skin and damage its chemical or cellular components
- in addition to actual tissue damage, the body’s inflammatory response can cause additional damage or increase the damage done by the initial burn
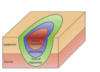
Burn Zones
1) Zone of Coagulation - the area that is directly affected by the burn (usually where the point of contact is) - where we see charring/necrosis
2) Zone of Stasis - standstill area (has compromised blood supply, inflammation, and tissue injury); where ischemia occurs
3) Zone of Hyperemia - sustains least damage; lots of swelling/inflammation
4 types of burns
Thermal
Electrical
Chemical
Radiation
Thermal Burns
- exposure to extreme heat
- can be sustained from temps 44ºC or greater for extended periods of time
- can be sustained from temps 80ºC or greater for short periods of time
Considerations for electrical burns
- find the source - is the current still live
- entry (where the direct contact was) and exit wounds (where they were grounded)
- SMR
Chemical Burn sources
- ANY KIND OF CHEMICAL
- car battery acid
- Bleach
- ammonia
- denture cleaners
- teeth whitening products
- pool chlorination products
Sources of radiation burns
sun, radiaton therapy (cancer tx)
Characteristics and causes of 1st degree burns
Characteristics: redness of skin, pain, no blisters
Causes: sunburn
Characteristics and causes of 2nd degree (partial thickness) burns
Characteristics: deep redness, mottled skin, extreme pain, blisters
Causes: contact with hot liquids, flash burns (intense light)
Characteristics and causes of 3rd degree (full thickness) burns.
Characteristics: dry and leathery; dry; charred appearance; very little to no pain due to nerve endings being burnt through)
Causes: fire, electricity or lightning, prolonged exposure to hot liquids/objects
Rule of 9’s (adult)

Rule of 9’s (Pediatric)
Head: 18% total (9% back, 9% front)
Front torso: 18%
Back torso: 18%
Arms: 9% (4.5% front, 4.5% back x2)
Legs: 14% (7% front, 7% back x2)

As per the Burns (Thermal) Standard in the BLS, the paramedic shall:
ASK FOR THE BURN KIT IN SCENARIOS!
1) If the patient is in a smoke/fume filled environment, request assistance from fire personnel and ensure that the patient is moved as quickly as possible to a fresh air zone when safe to do so;
2) consider life/limb/function threats, such as,
- airway burns
- asphyxia (smoke inhalation)
- carbon monoxide/cyanide poisoning, and
- shock
3) attempt to determine,
- source of burn
- if burn due to fire:
- whether the fire occurred in an enclosed space, and
- whether the patient was unconscious or lost consciousness during exposure to fire/fumes/smoke;
4) stop the burning process
5) when attempting to remove clothing from injury site, cut around clothing that is adherent to skin;
6) perform, at a minimum, a secondary survery burn assessments, as follows:
- estimate severity to include,
- area burned (eg. location, circumferential),
- burn depth (degree), and
- percentage of body surface area burned,
- assess distal neurovascular status in burned extremities,
- assess for signs of smoke inhalation and upper airway injury,
- if burns involve an eye, assess eye as per Visual Disturbance Standard, and
- however, if burns involve eye and eye is swollen shut, leave eye shut;
7) for burn sites <15% BSA, cool burns and limit cooling to <30 mins to avoid hypothermia - do no use ice/ice-cold water
8) cover all 1st degree burns with moist sterile dressing, then cover with dry sheet/blanket (burn sheets)
9) cover all 2nd degree burns estimate <15% BSA with moisr sterile dressing, and dry sheet/blanket
10) cover all 2nd degree burns ≧15% BSA with dry sterile dressing or sheet; (due to concern for hypothermia)
11) if remoistening dressing is needed to continue to cool burn, remove dry sheet or blanekt and remoisten previously applied sterile dressing;
12) if shivering or hypotension develops, discontinue cooling efforts;
13) cover all 3rd degree burns with dry, sterile dressing or sheet;
14) if dressing digits, dress digits individually;
15) leave blisters intact
16) keep patient warm
17) prepare for expected problems, including:
- airway obstruction
- if airway burns: bronchospasm, and orolingual/laryngeal edema (i.e. throat/mouth swelling);
- respiratory distress/arrest, and
- agitation or combativeness
As per Burns (Thermal) Standard, what are signs of smoke inhalation/upper airway injury?
- decreased air entry
- burns to lips/mouth
- carbon particles in saliva or sputum
- cough
- drooling
- stridor or hoarseness
- facial burns
- burned or singed nasal hair or eyebrows
- SOB, shallow respirations, auddible wheezes, or tachypnea
Considerations for burns and jeweltry/accessories.
Remove them to prevent swelling from cutting off circulation
Guidelines for applying oxygen to burn patients.
- in case of facial burns, gauze pads (soak 4x4’s) may be placed under edges of oxygen mask to decrease pain and irritation (or use NC)
- CO poisoning, cyanide toxicity are potential concerns for any incident involve combustible materials - HIGH FLOW O2
- upper airway burns - HIGH FLOW O2
True or False. There is a 4th degree burn category.
True - this is total destruction of tissue, burned down to the bone (slim chances these individuals will be alive)
treatment (if alive, not obviously dead): same as 3rd degree burns
As per Electrocution/Electrical Injury Standard, the paramedic shall:
1) make no attempt to touch a potential energized source or a patient who is still in contact with a potential energized source;
2) consider life/limb/function threats such as
- a) cardiopulmonary arrest
- b) dysrhythmias
- c) extremity neurovascular compromise
- d) multiple and/or severe trauma
- e) seizures
- f) significant inernal tissue damage
3) attempt to determine,
- a) type of current, and
- b) voltage
4) assess for signs of significant electrical injury, including,
- burns
- cold/mottled/pulseless extremities,
- dysrhythmias,
- entry/exist wounds,
- muscle spasms,
- neurologic impairment, and
- shallow/irregular respirations
5) re-assess distal neurovascular status in the affect extremity approximately every 10 minutes if status was compromised on initial assessment, and
6) prepare for potential problems, including,
- a) dysrhythmias
- b) extremity neurovascular compromise
As per Electrocution/Electrical Injury Standard, guidelines indicate that if there are multiple patients as a result of a lightning strike, the paramedic shall:
focus efforts on those who are VSA, due to his/her high potential for resuscitation
As per Hazardous Materials Injury Standard, what shall the paramedic do in respect to chemical burns?
- if an alkali burn is known or suspected, irrigate for a minimum of 20 minutes at scene if patient is stable, and attempt to continue irrigation en route;
- for a knwon acid burn, irrigate for a minumum of 10 minutes at scene if patient is stable;
- for unknown chemical exposure, irrigate for a minumum of 20 minutes at scene if patient is stable
- provide burn care as per Burns (Thermal) Standard


