Numbers of things topics 1-6 Flashcards
(51 cards)
Four extrinsic tongue muscles:
Genioglossus Hyoglossus Styloglossus Palatoglossus
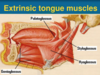
Four intrinsic tongue muscles
Superior longitudinal
Inferior longitudinal
transverse and vertical

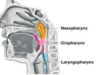
Three regions of the pharynx
nasopharynx
oropharynx
laryngopharynx
Seven mobile articulators:
larynx, pharynx, mandible, lips, tongue, cheeks, velum.
Three constrictor muscles of the pharynx:
superior
middle
inferior

Two faucial pillars (and their underlying muscles):
anterior faucial pillar = palatalglossus,
post faucial pillar = palatopharyngeus

Five muscles of the soft palate:
- Tensor veli palatini, which is involved in swallowing.
- Palatoglossus, involved in swallowing.
- Palatopharyngeus, involved in breathing.
- Levator veli palatini, involved in swallowing.
- Uvular, which moves the uvula.

Three common vocal registers:
modal (normal), fry (fake sick), falsetto (singing)
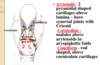
Three paired cartilages of the larynx.
Arytenoid, corniculate, cunieform.
Four if you include triticial.
One bone not attached to any other bone:
Hyoid
Three unpaired cartilages of the larynx:
thyroid, cricoid, epiglottus
Four suprahyoid muscles:
Digastric, Stylohyoid, Mylohyoid, Geniohyoid
Four infrahyoid muscles:
Sternothyroid, Sternohyoid, Omohyoid, Thyrohyoid
Five intrinsic laryngeal muscles (or six, depending on how you count them)
Cricothyroid muscle lengthen and tense the vocal folds.
Posterior cricoarytenoid muscles abduct and externally rotate the arytenoid cartilages, resulting in abducted vocal folds.
Lateral cricoarytenoid muscles adduct and internally rotate the arytenoid cartilages, increase medial compression.
Transverse arytenoid muscle adduct the arytenoid cartilages, resulting in adducted vocal folds.[2]
Oblique arytenoid muscles narrow the laryngeal inlet by constricting the distance between the arytenoid cartilages.
Thyroarytenoid muscles – sphincter of vestibule, narrowing the laryngeal inlet, shortening the vocal folds, and lowering voice pitch. The internal thyroarytenoid is the portion of the thyroarytenoid that vibrates to produce sound.
Two immobile articulators
Teeth, hard palate.
Two muscles involved in the control of vocal pitch
cricothyroid, thyroarytenoid
Eleven muscles of facial expression (listed in your module booklet)
Obicularis Oris,
Rissorius,
Buccinator,
Depressor anguli oris,
Depressor labii inferioris,
mentalis,
platysma,
Levator labii superioris alaeque nasi,
levitor labii superioris.
Zygomatic minor, Zygomatic major
(12 if you count levitor anguli oris)
Five major branches of the facial nerve (VII)
Temporal
Zygomatic
Buccal
Mandibular
Cervical

Four paranasal sinuses
frontal, maxillary, sphenoid, ethmoid
Three types of vocal attack
breathy, glottal, simultaneous
Five possible movements at the TMJ:
depression, elevation ,deviation ,protraction, retraction
Two branches of the vagus (X) nerve supplying the larynx:
Recurrant laryngeal nerve, superior laryngeal nerve

Three salivary glands
Parotid, submandibular, sublingual
Five cranial nerves involved in innervation of the tongue in some way:
V (5) Trigeminal (Facial muscles incl. chewing; Facial sensations)
VII (7) Facial (Taste, tears, saliva, facial expressions)
IX(9) Glossopharyngeal (Swallowing, saliva, taste)
XII (12) Hypoglossal (Tongue muscles - speech & swallowing)
plus pharyngeal plexus