3.3 Movements and muscles of the larynx Flashcards
Name the main muscle groups of the larynx and their function
intrinsic muscles: change position and tension of the vocal folds - adductors/abductors of folds, tensors/relaxers of vocal folds extrinsic muscles: move the whole larynx and hyoid bone - elevators and depressors of larynx and hyoid bone
Name the adductor muscles of the vocal folds and where they are attached to
lateral cricoarytenoid - attaches to lateral parts of cricoid andarytenoid cartilages transverse arytenoid - connects the two arytenoid cartilages in transverse orientation oblique arytenoid - connect the arytenoid cartilage in oblique orientation they close the vocal folds, intrinsic muscles
Name the abductor muscles of the vocal folds and name where they are attached to:

Posterior cricoarytenoid muscles -attached to posterior surface of cricoid cartilage and arytenoid cartilage. Moves the vocal folds out of the airstream.
Name the tensors and relaxors of the vocal folds:
Cricothyroid muscle is the primary tensor of the vocal folds, it pulls thyroid cartilage antero-inferiorly, which tenses the vocal folds.
Thyroarytenoid muscle is made of 2 parts - thryrovocalis(medial) tensor thryomuscularis (lateral) relaxer
Explain the function and position of the extrinsic laryngeal muscles.
Most attach to the hyoid bone. They move the whole hyoid bone and larynx. Suprahyoid muscles cause elevation and infrahyoid muscles cause depression of the hyoid bone and larynx.
Name the 4 suprahyoid muscles and their function:
geniohyoid, sytlohyoid, mylohyoid, digastric
Elevation of hyoid and larynx

Name the 4 infrahyoid muscles and their function:
Thyrohyoid, sternohyoid, sternothyroid omohyoid.
Depressors of hyoid bone and larynx.

Identify the muscles indicated at A, B and C:

A - Digastric
B - Mylohyoid
C- Stylohyoid

Identify these muscles:

Geniohyoid

Identify the following:

Mylohyoid
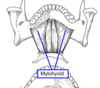
Identify D, E, F:

D - Thyrohyoid
E - Omohyoid
F - Sternohyoid
Explain the function movements of the cricoarytenoid joints:

The cricoarytenoid joints start and stop phonation. They move vocal folds in and out of airstream.
Their movements are:
sliding arytenoid cartilages together,
rotating on axis.
These both lead to adduction/abduction of the vocal folds.
What laryngeal muscle is this?
What does it do?

This is the lateral cricoarytenoid.
It adducts the vocal folds by causing the arytenoid cartilages to rotate laterally.
Name the two muscles indicated:
Describe what they do:

The transverse and oblique cricoarytenoid muscles slide the arytenoid cartliges towards one another, which adducts the vocal folds.
The thyroarytenoid muslce is made of two parts, shown here. Name them.

A- Thyrovocalis. Tensor of vocal folds.
B. Thyromuscularis. Relaxes vocal folds.


