✅NEUROLOGY Flashcards
Cerebral Salt Wasting etx
⬇︎Brain adrenergic output to Kidney –> ⬇︎PCT Na+ Reabsorption–> hypOvolemic hypONatremia
[Wernicke Korsakoff Syndrome] Clinical Presentation (3)
Wernicke problems come in a CAN of beer!
[Confusion & Confabulation]
Ataxia (Gait & Postural)
[Nystagmus + Oculomotor Dyf]
chronic alcoholism = most common cause
[Wernicke Korsakoff Syndrome] MOD
Wernicke Problems come in a CAN of beer!
[Thiamine B1 Deficiency] from (below) –> BL circuit dysfunction between mammillary bodies & ANT Thalamus:
- Chronic Alcoholism = MOST COMMON
- Giving [Glucose that doesn’t have B1] to a B1-deficient pt (i.e. homeless malnutrition pt)

Tx for [Wernicke Korsakoff Syndrome] (2)
[Thiamine B1 IV] ➜ Glucose
What’s the major complication of [SubArachnoid Hemorrhage] during recovery?
________________
How do you tx this?
Usually in the Suprasellar Cistern

Severe Cerebral Vasospasm 4-12 days post SAH onset
________________
Prevent with [Nimodipine CCB]
Other complications: Rebleeding, SIADH, Seizures

Describe the Demographic for the HA:
Migraine-2
Cluster
Tension
Migraine = Female and [Kids(will be bifrontal)]
Cluster = Male (100% O2 tx)
Tension = Female

Describe the Onset for the HA:
Migraine
Cluster
Tension
Migraine = Variable but possibly during menstruation
Cluster = During Sleep (100% O2 tx)
Tension = When Stressed “think tense”

Describe the Location for the HA:
Migraine
Cluster
Tension
Migraine = POUND = [Pounding/One-3 Day Duration /Unilateral/Nausea/Disabling] + photo vs. phonophobia & [flashing dots aura]
Cluster = Behind 1 eye (100% O2 tx)
Tension = [Bilateral & Band-like around the head]

Describe the Character for the HA:
Migraine
Cluster (3)
Tension (2)
Migraine = POUND = [Pounding/One Day-3 day Duration/Unilateral/Nausea/Disabling] + photo vs. phonophobia & [flashing dots aura]
Cluster = [Excruciating, sharp & steady] (100% O2 tx)
Tension = Dull & tight

Describe the Duration for the HA:
Migraine
Cluster
Tension
Migraine = POUND = [Pounding/One-3 Day Duration /Unilateral/Nausea/Disabling] + photo vs. phonophobia & [flashing dots aura]
Cluster = 15 - 90 MINUTES (100% O2 tx)
Tension = 30 min to 7 DAYS!!!! (Tammy’s Entire Work Week)

Describe the Associated Sx for the HA:
Migraine
Cluster - 4
Tension
“VTAP the migraine BEFORE it gets comes, and SEND it on its way when it does! “

Migraine = POUND = [Pounding/One-3 Day Duration /Unilateral/Nausea/Disabling] + photo vs. phonophobia & [flashing dots aura]
________________
Cluster = [Sweating/ Pupil Change / Lacrimation / Rhinorrhea]
Tension = [Muscle “Tension” in Head, Neck or Shoulders]
Which bone is associated with Epidural Hematoma?
Sphenoid

Violent Infant Shaking —> ⬜ . This is characterized by what 3 things?
________________
How is this differentiated from similar conditions?
[AHT- Abusive Head Trauma]! =
- Subdural Hemorrhage (from tearing bridging veins between Dura and Arachnoid)
- [BL Retinal Vein Hemorrhages]
- POSTERIOR rib fractures
- ________________*
- Usually* Accidental Fall is not sufficient for Subdural Hemorrhage OR [BL Retinal Vein Hemorrhage]
- AHT is formely known as Shaken Baby Syndrome*

What lab values differentiate seminomatous vs. NonSeminomatous Germ cell tumors?
seminomatous = ⬆︎bHCG
________________
NonSeminomatous(yolk sac/choriocarcinoma/embryonal) = [⬆︎bHCG AND AFP]

[Thiamine B1] deficiency causes ⬜ and BeriBeri
________________
Describe BeriBeri (2)
[Wernicke Korsakoff Syndrome] and [BeriBeri]
________________
BeriBeri (Wet vs. Dry vs. BOTH) is associated with…
- Heart involvement = WET
- Symmetrical Peripheral Neuropathy = DRY
[Thiamine B1] is needed to Decarboxylate a-ketoacids (carb metabolism)
Clinical Presentation for [Bells Palsy] (4)
Facial CN7 paralysis from inflammatory edema –> Loss of FACE

Loss of Facial m –> Unilateral Paralysis to ENTIRE HALF of face
Loss of Afferent somatics from Ear –> Hyperacusis
Loss of Crying 2/2 Loss of Parasympathetics to [Lacrimal/Salivary/Sublingual/Submandibular] glands
Loss of [Eating with Taste] 2/2 Loss of Taste to ANTERIOR 2/3 TONGUE
Clinical Criteria for diagnosing Alzheimer’s -5
CLAV –> HANDU
- GOE 2 Cognitive deficits
- Worsening Memory
- Consciousness intact
- Onsets after 60 yo
- No other Systemic/Neuro DO to cause cognitive defects

Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus Sx (3)
________________
Which is earliest to present?
⬇︎CSF absorption –> Wacky, Wobbly & Wet!

Wacky (memory loss)
Wet (Urinary Incontinence from compressing periventricular cortico-cortical white fibers traveling to sacral micturition center)
What causes [Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus]? -2
________________
what does [Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus] do to overall [subarachnoid space volume]?
[Idiopathic episodic ⬇︎Arachnoid villi CSF absorption] vs obstruction
________________
NOTHING
[NPH does NOT ⬆︎ subArachnoid space volume]
________________
Wacky, Wobbly & Wet!

ANY Clinical Suspicion of Stroke warrants _____. Why?-2
NonContrast Head CT; Ischemic stroke benefits from Thrombolytics vs ICH requires neurosurgery
How do ICH (IntraCranial Hemorrhage) stroke appear on NonContrast Head CT?
________________
How long does this take?
[HYPERdense White]; IMMEDIATELY!

Ischemic Stroke = [hypOdense dark] and takes >24 hrs to appear
Ethosuximide Indication
Sux to have Silent Seizures
Silent (Absent) Seizures
Features of Absence Seizures -4
- Staring spells that pauses a pt mid-activity
- < 20 seconds
- Not responsive to external stimulation
- NO recollection
________________
- Provoked by Hyperventilation or photic stimulation / Dx = 3 Hz EEG spike*
- ADHD staring spells occur only DURING BOREDOM!*
Name the 2 common triggers of Absence Seizures-2
________________
Dx?
- Hyperventilation
- photic stimulation
________________
3 Hz EEG spike
Why is it so important to recognize ⬜ in childen with epilepsy?
ADHD
________________
⬆︎ quality of life
Newborn Galactosemia etx
[ABSENCE OF {GALT}] prevents conversion of [Galactose1P ➜ UDP Galactose] ➜ accumulation of [Galactose 1P] ➜ accumulation of [Galactose] ➜ [Aldose reductase alternatively converts excess Galactose ➜ GALACTITOL] ➜
GALACTITOL accumulates in [Brain/Eye/Liver/Kidney]
________________
(GALT) = [Galactose 1 Phosphate Uridyl Transferase]

newborn Galactosemia affects (⬜#) major organs
________________
Describe how it affects each
4
________________
Galactitol accumulation in
[Brain ➜ convulsions & irritability]
[Eye ➜ BL cataracts]
[Liver ➜ hepatomegaly, jaundice, (E.Coli Sepsis), failure to Thrive, vomiting]
[Kidney ➜ urine with (reducing substance unmetabolized sugar)]

[Cavernous Sinus Thrombosis] etx
Infection of face vs teeth spreads thru facial veins –> cavernous sinus

Lacunar Stroke etx

lenticulostriate vessels perfuse [Be TIC] (not Pons)
Lacunar Stroke= [Thrombotic HTN Arteriolosclerosis & Thrombotic microatheromas] of lenticulostriate vessels –> [cystic infarcts < 15 mm] –> Lacunar Syndrome

Describe the Lacunar Syndrome CP

lenticulostriate vessels perfuse [Be TIpC] (not Pons)
1A: Basal Ganglia–>HemiBallismus & involuntary writhing
1B: ThalamuS VPL –> Sensory Stroke CTL
1C: [Internal Capsule-POST limb/Corona Radiata]–> Motor stroke (ataxia vs. clumsy hand-dysarthria)
________________
- Lacunar Stroke= [Thrombotic HTN Arteriolosclerosis & Thrombotic microatheromas] of lenticulostriate vessels –> [cystic infarcts < 15 mm] –> Lacunar Syndrome*
- VPL=VentroPosteroLateral nc*

What is Dejerine Roussy Syndrome
lenticulostriate vessels perfuse [Be TIC]
S/p Lacunar Thalamus Sensory stroke eventually –> Severe Paroxysmal BURNING worst w/light touch = Allodynia

Clinical Presentation of Congenital Syphilis -7
- Frontal Bossing
- Deaf
- Saddle nose
- Rhinitis
- Hutchinson Mulberry Molars
- Liver/Spleen Dz
- Saber Shins

Clinical Presentation for Fetal Hydantoin Syndrome -9
p HHH HHH en (“PHEN”)

- [palate and Lip Cleft]
- Head small with neuro deficits
- HypOplastic face
- Heart defects
- HypOplastic digits
- HypOplastic nails
- Hirsutism
- [embryopathy 2/2 phenytoin or carbamazipine intrauterine exposure]
- [neonatal bleeding 2/2 phenytoin ⬇︎ neonatal Vitk]
Classic signs of Fetal Alcohol Syndrome - 4
- Microcephaly
- Small Palpebral fissures
- Long Smooth Philtrum
- Thin Upper Lip

Sturge Weber Syndrome Clinical Presentation -5

- SEIZURES
- Red Facial Lesion (Port Wine Stain vs Red Nevus along CN5 territory = congenital UL cavernous hemangioma)
- Glaucoma IPL
- Homonymous Hemianopsia CTL
- Hemiparesis

Tramline Gyriform Calcifications on CT
Sturge Weber Syndrome Dx

Tramline Gyriform Calcifications on CT

Sturge Weber Syndrome Tx -3

- Seizure control
- Glaucoma control (⬇︎Intraocular pressure)
- [Red Facial lesion] control with Argon laser
________________
- Tramline Gyriform Calcifications on CT*
- Red Facial Lesion = Port wine stain vs Red nevus along CN5 territory*

In [Neurofibromatosis Type 1], Fleshy cutaneous neurofibromas are made of ⬜, which embryologically come from ⬜.
_____________________
These pts may also have hyperpigmented spots known as ⬜
Schwann cells ; Neural Crest.
________________
[Cafe Au Lait Spots (image)]
Image: Cutaneous Neurofibromas & Cafe Au Lait Spots

Main features of Narcolepsy -4
- Paralysis upon Awakening
- [sudden REM entry > 3x/week & >3 mo]
- cataplexy
- hypnaGOgic/hypnopompic hallucinations
* hypnoGOgic = when GOing to sleep*
Cataplexy may be treated with ⬜-suppressing drugs
________________
Name 2 examples
REM Sleep
________________
[Sodium Oxybate] and Antidepressants
List the 3 main causes of HemipLegia in Kids
- Seizure w/Todds Paralysis
- Hemorrhagic Stroke 2/2 AVM
- HemipLegic Migraine (Teens w/Fam hx, self-resolving)
Describe Todds Paralysis
focal (ipsilateral UE and LE) paralysis after seizure that resolves naturally within 36 hours
What Dz occurs from [Tetrahydrobiopterin BH4] deficiency?
________________
Explain the etx
(PKU) Phenylketonuria
________________
Dihydropteridine Reductase becomes deficient w/out [Tetrahydrobiopterin BH4] cofactor –> Inability to convert Phenylalanine –> Tyrosine –> MESS sx
PKU smells a MESS!
Phenylketonuria tx (2)
________________
Why is Newborn screening important for these?
- low phenylALAnine diet
- [TetraHydroBiOpterin BH4] supplementation
NEWBORN SCREENING–> early dx –> early tx –> Normal lives!!
________________
PKU smells a MESS!
PKU-Phenylketonuria S/S (4)
PKU smells a MESS!
Musty Odor
Eczema
Seizures
Slow mentally (retard)
- Newborn screening is ESSENTIAL for early dx of PKU, which “smells a MESS”*
- ________________*
How do you diagnose PKU?
Tandem mass spectrometry of dried blood spots –> detects PKU products
Name the classic complaint pts with Presbycusis will give regarding conversations - 2
Can hear one-on-one BUT can not hear if there’s ANY background noise + BL tinnitus
Sensorineural hearing loss secondary to age
What conditions are associated with [Berry Saccular Aneurysm]? (5)
“Eating AppleBerries Can Sound Heavenly”
- ADPKD**
- [Ehlers Danlos Syndrome]
- HTN
- SAH (from Trauma > Berry Saccular Aneurysm)
- Coarctation of Aorta (associated w/HTN)
Image: Blood around Brainstem & Basal Cisterns

[Communicating Hydrocephalus] cause

[Meningitis vs SAH vs Intraventricular hemorrhage] ➜ disruption of [Arachnoid Villi granulation] CSF reabsorption

[SubArachnoid Hemorrhage]
Dx-3?
________________
Tx-2?
Usually in Suprasellar Cistern

Dx:
- NonContrast Head CT
- Lumbar Puncture revealing Xanthochromia (6 hrs after onset)
- Cerebral Angiography
________________
Tx: [Endovascular Coiling/Stenting to stabilize aneurysm] + Nimodipine
Xanthochromia comes from Blood breakdown products

What’s the major complication of [SubArachnoid Hemorrhage] 24 hrs post onset?

REBLEEDING WITHIN 6 HRS –> MAJOR CAUSE OF DEATH!

Other complications: SIADH, Seizures
Lumbar puncture with CSF pressure ⬜ = Intracranial HTN
> 250 mmH20
PCiiH [Pseudotumor Cerebri Idiopathic Intracranial HTN] Tx - 3
Big Girl with PCiiH just SAT on her problems
- Surgery (Shunt vs Optic N sheath fenestration)
- Acetazolamide (inhibits Choroid Plexus Carbonic Anhydrase)
- Topiramate (will also –> Wt loss :-) )
This HA will make you go Blind!

[Syringomyelia central cord syndrome] etx
________________
CP-2?
Formation of [CSF filled cavity = SYRINX] in C8-T1 region of spinal cord –> damage of STT [Ventral white commissure (crossing fibers)] –>
________________
- [BL Cape distribution Pain/Temp Loss in Arms & Hands]
- ***Eventually Ventral Horns are also destroyed –> [LMN (FAAW)] - Fasciculations / Atrophy / Areflexia / Weakness

Parkinsonism Clinical signs (8)
PARK & hamp
[Pill Rolling Resting 4-6 Hz unilateral Tremor] worst with Rest & Mental Task
[AReflexia posturally] –>Shuffling Gait/Fall when turning or stopping
[Rigidity Cogwheel]
BradyKinesia
+
- hypOphonic speech
- autonomic ⬇︎ (constipation / bladder problems / orthostatic hypOtension)
- micrographia
- poker masked face
- PARK = primary signs*

Name the Major UMN signs (5)
UMN signs = Weak MESH
Weakness
[Spastic Gait & Paralysis] (partially from disproportionate Extensor weakness)
[Exaggerated Reflexes (Babinski)]
Mental Status change
HemipLegia
Name the Lower Motor Neuron signs - 4
LMN signs (FAAW) - Fasciculations / Atrophy & Areflexia / Weakness
3 Main causes of Spinal Cord Compression

- DJD Disc Herniation (Smoking risk factor)
- [Epidural Staph a. Abscess (think IV drug user vs DM)]
- Tumor (Prostate/Renal/Lung/Breast/Multiple Myeloma mets)

Dx = MRI, Positive Straight Leg, Classic S/S
DJD=Degenerative Joint Disease
Causes of [Anterior Spinal Cord Syndrome] - 2
Thoracic AAA Repair vs Vertebra Burst Fracture

Describe the 3 main sx for [Brown Sequard Syndrome]
- Ipsilateral DCP Loss of 2TVP-2point/Touch/Vibration/[Position Proprioreception]
2. Ipsilateral CST Loss –> [UMN (Weak MESH)]
- Contralateral STT Loss of Pain/Temp 2 LEVELS BELOW ORIGINAL LESION

Causes of [Brown Sequard Syndrome] - 3
- [(Extramedullary Tumor]
- Trauma
- [DJD Disc Hernation (Smoking risk factor)]

[Cauda Equina Syndrome] etx
________________
Clinical Presentation - 5
(Compression of S2 - S4 n. roots) –>
- Saddle Anesthesia (image)
- ⬇︎ Anocutaneous Reflex (perianal pinpoint does NOT cause anal sphincter contraction)
- Incontinence (urinary AND fecal)
- uL Radiculopathy
- hypOreflexia (Conus Medullaris syndrome has HYPEReflexia)
Decompression required within 72 hours!!!

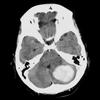
Where does Charcot Bouchard Aneurysms occur (4)

Charcot Bouchard Tears Pink
- Basal Ganglia
- Cerebellum
- Thalamus (shown in image below)
- Pons
Acute ICHH [Intraparenchymal CharcotBouchard HTN Hemorrhage] in image

What causes Hemiballismus
Lacunar Stroke damage to [Subthalamic nc. of the Basal Ganglia] (important in modulating basal ganglia output) –>
CTL Hemiballismus
Note: Basal Ganglia is in Subcortical nuclei

Huntington’s Dz Clinical Presentation (2)
- “Hunting 4 food is way too aggressive & dancey”*
1st: Aggressive Dementia w/ strange behavior
2nd: Dance-like Chorea mvmnts - AUTO DOM = Affects BOTH sexes equally!!*

When does Huntington’s Dz onset
30 - 50 y/o

AUTO DOM = Affects BOTH Sexes Equally!!
Parkinson’s Dz Tx - 6
“Eat SALADS after you Park”

- [Levodopa (Dopamine Precursor) + Carbidopa]
- Amantidine
- Anticholinergics
- [Dopamine PostSynaptic Agonist] (NonErgot: Ropinirole vs. Pramipexole) & (Ergot:Bromocriptine)
- Selegiline
-
Surgery
- Pallidotomy: Destructive of [Globus Pallidus:internal]
- SubThalamic nuc. inhibition with electrode
- ANT Choroidal a ligation
Lesch Nyhan etx
MALE DO in which HGPRT deficiency –> ⬆︎ Purine –> Uric Acid accumulation
–> CROUG ( UE Self-Injury (Biting) / Choreoathetosis / Retardation / Gout / Obstructive Nephropathy
Lesch Nyhan Clinical Presentation - 7
[6 mo old Male] with [hypOtonia + vomiting] eventually –> CROUG
Choreoathetosis
Retardation
[Obstructive nephropathy]
[UE SELF-INJURY (BITING)]
Gout
Dx for Multiple Sclerosis - 5
- Clinical (SLUM SiiiN)
- T2 MRI: [Periventricular white matter demyelinating plaques with lipid laden macrophages]
- T1 MRI Black holes
- CSF Oligoclonal IgG bands
- Visual conduction velocity test

Sx will be disseminated in time and space
CP for [MIOS-MLF Internuclear Ophthalmoplegia Syndrome] (3)
[MIOS-MLF Internuclear Ophthalmoplegia Syndrome]
*[Impaired ADDuction of affected eye]
+
[Normal ADDuction of affected eye during [near reflex convergence]
+
*[Nystagmus of UNaffected eye when attempting to ABduct]
Image: L MIOS

Clinical Manifestation of Multiple Sclerosis (9)

Charcot classic triad of MS is a [SLUM SiiiN] !
Sensory sx (think BL Trigeminal Neuralgia)
Lhermittes sign = “electric tingling” down spine into arm & legs when chin is touched to chest
Uhthoff phenomenon (sx ⬆︎ during heat)
Motor sx
Scanning Speech
[Internuclear Ophthalmoplegia (MIOS)] / Intention Tremor / Incontinence
Neuritis Optic - (uL eye pain + vision loss + Marcus Gunn afferent pupillary defect) = ALSO RISK FACTOR
Which drugs are used to treat Multiple Sclerosis Exacerbation?-2
1st: [Methylprednisolone IV High Dose]
2nd: [Plasmapharesis (Refractory)]

Which drugs are used to treat Multiple Sclerosis maintenance?-3
- β-interferon
- Glatiramer acetate
- Natalizumab

Myotonia Dystrophy Clinical Manifestation - 6
My Tonia, My Toupee, My TV Viewers, My Throat, My Ticker, My Testicles,
Tonia = MyoTonia = [⬇︎ relaxation after volitional muscle contraction with Weakness & Atrophy] (cant let go of doorknob)
Toupee = Frontal Balding
TV viewer = Cataracts
Throat = SEVERE DYSPHAGIA –> Aspiration PNA
Ticker = Arrhythmia
Testicle = Testicular Atrophy
[AUTO DOM CTG Repeat]

Main features of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy - 5
- [CALF PSEUDOHYPERTROPHY requiring gower manuever + teenage wheelchair]
- [Xp21 deletion] (X-link recessive deletion on Chromo Xp21)
- Scoliosis
- [peds onset at 2 yo]
- [cardiomyopathy ➜ 20-30 yo DEATH]

Main features of Becker Muscular Dystrophy - 4
- [Xp21 deletion] (X-link recessive deletion on Chromo Xp21)
- Scoliosis
- [peds onset at 5 yo]
- [cardiomyopathy ➜ 40-50 yo DEATH]

Frontotemporal Pick’s Dementia
Sx -2
Prounouced Frontal & Temporal lobe atrophy –>
[Socially inappropriate Behavior] + aphasia
OCCURS MORE IN FEMALES!!!
Dementia with Lewy Bodies (DLB) CP - 3
DLB at the DMV
- Dementia confusion periodically
- MichaelJFox Parkinsonism (PARK + hamp) tht does NOT respond to dopaminergic tx
- Visual Hallucinations
Lewy Body= [LABS (Lewy α-synuclein BodieS)] that are Eosinophilic intracytoplasmic accumulations
Tick Paralysis and Gullain Barre both present with ascending paralysis
What differentiates Tick Paralysis? - 3
Tick Paralysis has…
- NO Autonomic Dysfunction
- Normal CSF (GBS CSF=High Protein > 40)
- Can be Asymmetrical (GBS=Symmetrical)
CP of Cerebellar Damage - 7

Cere is def on GRINDRR
Gait Ataxia IPSILATERAL
Rapid alternating mvmnt impairment
Intention tremor/Dysmetria IPSILATERAL
Nystagmus IPSILATERAL (medial AND Lateral Vermis)
Dysarthria (Lateral Vermis only)
Rebound phenomenon (pt hits themself in face if flexing bicep and examiner releases arm-image)
Reflex Pendular (knee swings >4x after Deep tendon reflex is elicited)
Vermis is midline

Describe the “Clasp Knife” phenomenon
________________
What disease is this related to?
Rapid SPASTIC RESISTANCE to passive mvmnt of limb
________________
UMN (Weak MESH) Pyramidal Tract dz
- Pyramidal Tract = Corticospinal and Corticobulbar*
- Pronator Drift also indicates Pyramidal Tract Dz*
Dx for Creutzfeldt Jakob disease - 6
- [PRNP prion protein] genetic testing
- EEG Biphasic vs Triphasic sharp wave complexes
- Postmortem brain biopsy
- ⬆︎CSF 14-3-3 proteins
- MRI Cortical Ribbons
- MRI basal ganglia hyperintensity
[Creutzfeldt Jakob Dz] etx
PrP (prion protein), normally in neurons as [α -helical structure] converts–> [INFECTIOUS Beta pleated sheets] –> Protease resistance –>
Vacuoles in [Gray Matter Neurons & Neutrophils] develop –> Cyst = [Spongiform Gray Matter]
[Creutzfeldt Jakob Dz] CP - 2
[RAPIDLY Progressive Dementia] + [STARTLE Myoclonus] –> DEATH
Can be Acquired vs. Inherited
[Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis] (Lou Gehrig’s) etx - 2
- Rare = [Superoxide Dismutase gene mutation] –> copper-zinc dysfunction —>[Upper AND Lower Motor Neuron Disease!]
- Common = Idiopathic
UMN Dz includes loss of neurons in motor nc. 5/9/10/12
DDx of Neuromuscular Weakness has 5 origins
Describe Upper Motor Neuron causes of Neuromuscular weakness - 4

DDx of Neuromuscular Weakness has 5 origins
Describe Anterior Horn Cell causes of Neuromuscular weakness - 4

DDx of Neuromuscular Weakness has 5 origins
Describe Peripheral Nerves causes of Neuromuscular weakness - 5

DDx of Neuromuscular Weakness has 5 origins
Describe Neuromuscular JUNCTION causes of Neuromuscular weakness - 4

DDx of Neuromuscular Weakness has 5 origins
Describe Muscle Fibers causes of Neuromuscular weakness - 5

Guillain Barre Tx - 2
IVIG vs Plasmapheresis
Guillain Barre CSF = HIGHLY ELEVATED Protein > 40
Postconcussive syndrome can occur __(length of time)__ after any TBI (Traumatic Brain Injury).
Describe CP for Postconcussive Syndrome - 4
hours-days;
- Continued Confusion/Amnesia
- HA
- Mood changes
- Vertigo
This is Self-Resolving
In pts with Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI), what’s the major cause of morbidity?
Diffuse axonal injury at Gray-White matter junction (since this is where density difference is highest)
USE MRI FOR DX

How long does it take ketoralac to reach Max efficacy
3 hours
Dose = q4-6 hrs
You suspect a baby has ingested Botulinum spores
What’s the Clinical Presentation? - 4
- Descending Flaccid Paralysis (Floppy Baby)
- Ptosis
- Poor Suck & Gag Reflex w/drooling
- Constipation
Tx = IMMEDIATE Botulinum Ig
Spinal Muscular Atrophy etx and CP
[ANT Horn Cell degeneration] from [Chromo 5 SMN1 and 2 gene mutations]–> LMN signs of FAAW- Weakness/[atrophy & areflexia] /Fasciculations
Spinal Muscular Atrophy
What’s the difference between Infant type and Adult type
*Infantile onset = (Werdnig Hoffman) –> [Auto Recessive FATAL condition –> Floppy Baby from defuse [Distal muscle atrophy]
________________
*Milder childhood/adult onset types –> [Non-fatal Chronic Disability]
Why are Multiple Sclerosis pts at risk for BL Trigeminal Neuralgia

Demyelination may occur at Trigeminal nucleus –> BILATERAL neuralgia

Sx will be disseminated in space and time
After Getting Labs, NonContrast Head CT is next for dx unprovoked seizures
When would MRI be the better option?
elective NONemergent situations

After Getting Labs, NonContrast Head CT is next for dx unprovoked seizures
Name structural causes of epilepsy-7
Temporal Sclerosis-shown in image
Cortical Dysplasia
TBI (Traumatic Brain Injury)
Vascular Malformation
Infection
Tumor
Infarction

[LEMS - Lambert Eaton Myasthenic Syndrome] etx
[Autoimmune attack against (Presynpatic Ca+ channel)–> No ACh release]
What other condition is [LEMS - Lambert Eaton Myasthenic Syndrome] associated with?
“LEMS has a good SOLC(soul)”
SOLC-Small Oat cell Lung Carcinoma
Name 4 Differentiating Factors for Myasthenia Gravis vs. [Lambert Eaton Myasthenic Syndrome]
- [LEMS] improves with exercise/exertion during the day!
- [LEMS] will show no imprvmnt with [Tensilon Edrophonium] injection OR ice pack
- [LEMS] nerve testing shows INC muscle responses
- [LEMS] has autonomic dysfunction (orthostasis, dry mouth, impotence)
What other condition is [Myasthenia Gravis] associated with?
May cause Thymoma (thymic hyperplasia)
[Myasthenia Gravis] etx
________________
Demographic?-2
Autoantibodies block and degrade [postsynpatic nicotinic ACh Receptors]] –> [⬇︎ motor end plate potential]
_____________________
Presents in [Women 20-30] and [Men 60-80]
[Myasthenia Gravis] Clinical Presentation (5)
“Give me Mya’s P DDD F”
[Ptosis
[Diplopia from Disconjugate gaze]
Dysarthria-bulbar dysfunction
Dysphagia w/nasal regurgitation-bulbar dysfunction
[FATIGABLE Weakness Muscularly (Extraocular/RESP/Proximal/limbs/worst w/repetition)]
Tx: Pyridostigmine AChesterase inhibitor

[LEMS - Lambert Eaton Myasthenic Syndrome] Clinical Presentation - 3
- Weakness of [Proximal limbs and trunk] mimicking myopathy, better with exercise
- Autonomic sx (Dry mouth /Orthostasis / Impotence)
- ⬇︎Deep Tendon Reflexes
You suspect a pt had an ischemic Stroke
After FIRST, ruling out Hemorrhagic stroke with ⬜ , what thrombolytic therapy should be given?
________________
When should you give it?
NonContrast Head CT; IV Alteplase
________________
WITHIN 4.5 HOURS OF SX ONSET!
How are HTN and DM mngmnt related to Acute CVA/TIA - 2
BP > 185/110 in setting of stroke can –> ICH - so Use Labetalol
&
Hyperglycemia augments brain injuries (so ONLY use NonDextrose IVF)
What is Therapeutic hypOthermia often used for?
________________
How low of temp can you go?
Prevents hypoxic Brain injury in pts with [out of hospital cardiac arrest]
________________
32C
Therapeutic hypOthermia prevents [hypoxic Brain injury] in pts with [out of hospital cardiac arrest]
________________
SE of this?-4
;
- HYPERKalemia
- ⬇︎Cardiac Output
- ⬆︎Coagulation
- Immunosuppression
Homocystinuria Clinical presentation-5
auto recessive [Cystathionine synthase] deficiency –> Thromboembolism–> Stroke
- Marfanoid habitus (elongated limbs, arachnodactyly, scoliosis) - MH
- Ectopia Lentis - MH
{3. Retarded -h}
{4. Fair Hair & Eyes -h}
{5. Stroke -h}
________________
- MH = MARFAN and HOMOCYSTINURIA*
- h = homocystinuria only*

Homocystinuria tx -2?
auto recessive [Cystathionine synthase] deficiency –> Thromboembolism–> Stroke
tx = [Pyridoxine B6] + AntiCoag

Homocystinuria dx-2
auto recessive [Cystathionine synthase] deficiency –> Thromboembolism–> Stroke
[Homocysteine⬆︎] and [Methionine⬆︎]

Name the Differences in cp between Marfan and Homocystinuria - 3
Marfan DO NOT HAVE
- Retardation
- Fair Complexion
- Strokes
Tay-Sachs etx ; CP-3
auto recessive B-hexosaminidase A deficiency –>
- Cherry Red Macula
- Seizures
- Retarded

Pronator Drift is a good indicator of what type of disease?
UMN Pyramidal Tract Dz (think stroke)
- Pyramidal Tract = Corticospinal and Corticobulbar*
- Clasp Knife phenomenon also indicates Pyramidal Tract Dz*

Etx of Parkinsons Disease
[LAB (Lewy α-synucleinBodies)] accumulate in [substantia nigra pars compacta] –>degeneration –> of [substantia nigra pars compacta] –> ⬇︎Dopamine to stimulate the [Striatum blocker] which –> unblocked [Globus pallidus internal] continuously inhibiting [VA/VL Thalamus] from stimulating motor cortex

Alzheimer’s Dz etx (3)
Alzheimers etx = CHA
**Cleavage, Hemorrhage, (ACh⬇︎) **
- Cleavage of [chromo 21 transmembrane amyloid precursor glycoprotein] –> [β-amyloid] which accumulates–> [Neuritic Senile plaques] in temporal lobe early on.
________________
- Hemorrhages Spontaneously occur in Occipital/Parietal lobes (image) from [β-amyloid] deposition in cerebral vessels
________________
- ACh ⬇︎ in the [Basal nc. of Meynert & Hippocampus] 2/2 [β-amyloid] accumulation causing defective [Choline Acetyltransferase] in those areas –> Alzheimer Sx (CLAV–>HANDU)

What type of Hemorrhage is shown in image ; What is this typically associated with?

Lobar Hemorrhage (parietal) ; Amyloid Angiopathy 2/2 Alzheimers

Hypokalemic periodic paralysis CP-2
Occurs right after vigorous activity
- SUDDEN generalized muscle weakness +
- ⬇︎ Deep Tendon Reflexes
Occurs right after vigorous activity
Benzos can cause an uncommon SE known as Paradoxical Agitation. Describe this
[⬆︎Agitation, confusion and disinhibition] within a hour of benzo admin. GIVING MORE BENZOS WILL WORSEN THIS!
What is a Cephalohematoma? Tx?
Neonatal SubPeriosteal Hemorrhage limited to 1 cranial bone (i.e. does NOT cross suture lines) that onsets hours after birth and presents as scalp swelling +/- ⬆︎jaundice;
Tx = Nothing, since it self-resorbs within 2 weeks-3 mo.

Cerebellar infarction of medial vermis presents as _____-2
- Nystagmus
- Vertigo

Cerebellar infarction of Lateral vermis presents as _____-6
Cere is def on GRINDRR
Gait & Coordination Ataxia - IPSILATERAL
Rapid alternating mvmnt impairment
Intention tremor/Dysmetria - IPSILATERAL
Nystagmus (medial AND Lateral Vermis infarcts)
Dysarthria (Lateral Vermis only)
Rebound phenomenon
Reflex Pendular (knee swings >4x after Deep tendon reflex is elicited)
Intention tremor = worst as finger moves closer to target

Describe Features of BENA (Brocas Expressive NonFluent Aphasia) -4
- Right Hemiparesis
- Nonfluent speech
- Impaired Repetition
- Impaired Naming
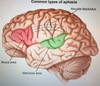
BENA = Dominant Inferior Frontal
Describe Features of Wernickes Aphasia - 3
- R SUP homonymous quadrantanopia
- Comprehension problems
- Impaired Repetition

Conductive AND Wernicke Area = Dominant SUP Temporal
Describe Features of CONDUCTION Aphasia
VERY POOR Repetition

This is in addition to Fluent but many phonemic errors
Status Epilepticus clinical criteria?-2
- Single seizure > 5 min OR
- Cluster of Seizures w/ no return to baseline in between episodes

Image showing Cortical Laminar Necrosis s/p Status Epilepticus
What is the long term outcome of status epilepticus on the brain? ; Dx for this?
Cortical laminar necrosis ; MRI w/cortical hyperintensity

What is the most common cause of ICH in kids?
ArterioVenous Malformation
Tx for Cluster HA - 1st, 2nd and 3rd choice
1st = 100% O2 Nasal Canula
2nd = Sumatriptan
3rd = NSAIDs
Px = Verapamil

Px for Cluster HA
Verapamil

Also Px for Migraines
Neonatal Intraventricular Hemorrhage occurs in premies less than ⬜ weeks gestation or less than ⬜ grams
________________
Px?
< 30 weeks vs 1500g
________________
Antenatal Maternal Corticosteroids
- Normal Gestation = 37-42 WG*
- Image: BL IVH & Dilated Vt*

What is the Etx of Intraventricular Hemorrhage in premature babies less than ⬜ weeks or less than ⬜ grams
< 30 weeks vs 1500g
________________
Subependymal germinal matrix contains thin-walled vessels that easily rupture. Normally, these migrate before birth, but in premies they never have the chance which –> IVH –> ⬇︎Arachnoid CSF absorption –> Communicating Hydrocephalus
- Normal Gestation = 37-42 WG*
- Image: BL IVH & Dilated Vt*

Choroid plexus cyst are identified ⬜ trimester and a marker for ⬜ in babies
________________
How do they affect the baby?
2ND
________________
Aneuploidy
________________
does NOT affect baby. Regressess spontaneously and is benign
Dark holes = Cyst

What are the 7 major complications of Newborn Prematurity
Less than 32 weeks gestation specfically
“Premies stay BURPPIN”
Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia
UcantBreathe (Neonatal Respiratory Distress Syndrome)
Retinopathy
- *P**atent Ductus Arteriosus
- *P**alsy CEREBRAL
Intraventricular Hemorrhage
Necrotizing Enterocolitis (⬆︎gastric residual volume with abd distension)
How do Traumatic Carotid Injuries occur?-3 ; Dx-2

Image: Carotid Dissection
- Penetrating Trauma
- Oropharyngeal trauma (falling w/object in mouth)
- Neck Strain (yoga, sports)
Dx = CT angio vs MR angio
These will present like Strokes

[DLB (Dementia with Lewy Bodies)] Tx
Rivastigmine AChinesterase inhibitor
What are the hallmark pathological findings for Alzheimers-2
[Tau Neurofibrillary tangles] & [Neuritic Senile Plaques]

Most serious complication of Guillain Barre? How do you determine when this complication gets really bad?
Respiratory Failure; FVC ≤ 20 mL/kg via SPIROMETRY means intubate!

HR, BP, Quadriparesis, FACIAL palsy are other serious complications
Levodopa is used to treat Parkinson’s Disease
Early SE?-3 ; Late SE
Early SE (HAD) = Hallucinations/Agitation/Dizziness
Late SE (5-10 yrs post tx) = Involuntary mvmnts
Dx for VitB12 deficiency - 3
- [⬆︎ Methylmalonic Acid levels]
- CBC showing Macrocytic Anemia
- Serum Vitamin levels
There are 3 Main causes of Spinal Cord Compression
Dx for Spinal Cord Compression-3

- MRI
- Classic S/S (BLE weakness, Worst w/spinal extension, better w/flexion, UMN signs)
- Positive Straight Leg

Note: In Acute Cord Compression, pts will have spinal SHOCK x3days = AReflexia and Flaccid paralysis
HemiNeglect Syndrome
Stroke in R Parietal Cortex (NonDominant hemisphere) –> Neglect of anything on the Left side
This is only in R handed people. It’s opposite for L handed
[Juvenile Myoclonic Epilepsy] CP
________________
Demographic?
Generalized Seizures +/- Absence seizures, most frequently in 1st hour after waking
________________
Teens
Lennox Gastaut CP-2
Lennox Gastaut
- Lala Land Retarded before 5 yo
- Generalized Tonic Clonic Seizures SEVERE