Neuro images Flashcards
(21 cards)
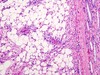
Globoid cells in Krabbe disease (AR and a galcotocerebrosidase deficiency)

Cingulate (subfalcine) herniation under the falx cerebri
-compress the ACA

Downward transtentorial (central) herniation

Uncal herniation
the uncus: medial temporal lobe.
compresses:ipsilateral CN III (blown pupil and down and out gaze), ipsilateral PCA(contralateral homonymous hemianopsia), contralateral crus cerebri (ipsilateral paralysis, “false localization”

Cerebellar tonsillar herniation into the foramen magnum
-coma death result when these herniations compress the brain stem (and inhibit respiration)

angiofibromas
assoc. Tuberous sclerosis

ash leaf spots assoc. tuberous sclerosis

renal angiomyolipoma assoc. tuberous sclerosis
cafe au lait spots
assoc with NF1

lisch nodules (pigmented iris hamartomas) assoc with NF 1

Glioblastoma multiforme (grade IV) astrocytoma
- common, highly malignant primary brain tumor
- 1 year median survival
- found in cerebral hemispheres
- can cross the corpus callosum (butterfly glioma)
- stains astrocytes for GFAP
- pseudopalisading pleomorphic tumor cells-border central areas of necrosis and hemmorrhage

Meningioma
-common typically bening primary tumor of adults
0most often occurs in convexities of hemispheres nears surface of brain and parasagital region.
- arrises from ARACHNOID cells, may have a dural attachment
- often asymptomatic, may present with seizures or focal signs
- resect or radiosurgery
- women
- Spindle cells concentrically arranged in whorled patter, psammoma bodies (laminated calcifications)

Meningioma types

Hemangioblastoma
- adult
- most often cerebellar
- assoc. with VHL sundrome when found with retinal angiomas
- can produce EPO –> secondary polycythemia
- closely arranged, thin walled capillaries with minimal interleaving parenchyma

Schwannoma
- Usually found at cerebellopontine angle
- schwann cell origin
- S-100 postive, often locallized to CN VIII –> acoustic shwannoma (acoustic neuroma).
Resectble or treated with stereotactic radiosurgery
Bilateral acoustic schwannomas are found in NF-2

Oligodendroglioma
- adult
- relatively rare, slow growing
- most often FRONTAL lobes
- chicken wire capillary patter with fried egg cells (round nuceli with clear cytoplasm)
- often calcified oligodendroglioma

Piliocytic (low grade) astrocytoma
- kids
- usually well circumscribed
- found in posterior fossa (cerebellum)
- could be supratentorial
- GFAP postive
- bening
- rosenthal fibers (esosinophilic. corkscrew fibers)

medulloblastoma
- kids
- highly malignant cerebellar tumor
- a form of primitic NEUROECTODERMAL tumor
- can compress the 4th ventricle causing hydrocephalus
- can send drop mets to spinal chord
- horner wright rosettes and small blue cells
gross: solid

ependymoma
ependymal cell tumors most commonly found in the 4th ventricle
- kids
- can cause hydrocephalus
- poor prognosis
perivascular rosettes and rod shaped blepharoplasts (basal ciliary bodies) found near nucleus

cranipharyngioma
- bening childhood turmor, may be confused with a pituitary adenoma
- most common supretentorial tumor
- rerived from rathke pouch remnant
- clacification is common
- tooth enamel like histo



