MESS: Anatomy Flashcards
(60 cards)
what type of joint is pubic symphisis?
cartilagenous joint
what are fibrous joints made from?
collagen
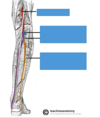
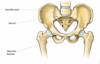
label this correctly pls


examples of hinge joints?
elbow, knee, interphalangeal (IP) joints of the hand and foot and the tibiotalar joint of the ankle



ROS(F)
ROS Friends

which bone is cribiform plate from?
ethmoid bone


C1 vertebral is called?
C2 vertebral is called?
which joint between them?
C1 is atlas
C2 is axis
pivot joint
which vertebrae has the longest spinous process?
which vertebrae have bifid spinous process?
C7
cervical: bifid spinous process
where is trochlea and capitulum on humerus?
capitulum is lateral
trochlea is medial



what are the arm condyles and epicondyles?
which epicondyle is bigger?
anterior view - can see the C and M !!
- *condyles:**
- trochlea looks like an M (medial)
- captiulum looks like a C
medial epicondlye is bigger than lateral!

which forearm bone is bigger distally and posterioly?
radius: bigger distally (thumb is bigger than little finger!)
ulnar: bigger posteriorly
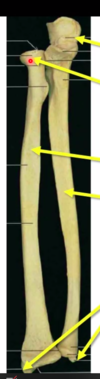
what does the ulna articulate distally with at the hand?
just the radius!
which carspals articulate with the radius?
scaphoid and lunate
what are the different names for joints in hands?
what types of joints are they?
a= Metacarpophalangeal Joint (MCP)
“proximal interphalangeal joints” (PIJ or PIP)
distal interphalangeal joints” (PIJ or PIP)
hinge joints

how many bones artiuclate to form acetabulum?
3! (hip socket)




which bone articulates with the femur and patella?
femur and tibia: tibiofemoral (not the fibula)