Lower Limb Flashcards
(70 cards)
Why does the lower limb flex posteriorly?
Internal rotation during development
What movement is not allowed in the lower limb as to increase stability?
Pronation/supination
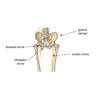
What is the socket of the femur called?
Acetabulum
What are the equivalent of tubercles (for muscle attachment) in the lower limb?
Trochanters
What bony arrangement does the neck of the femur lack that makes it a site of weakness?
Trabeculae
The distal tibia becomes what structure?
Medial malleolus
Does the lateral malleolus or medial malleolus extend further down the leg?
Lateral
Which of the two leg bones has most of the muscle attachments?
Fibula
What bone forms the heel and what other bone sits above it?
Calcaneus - heel
Talus sits above
The line of gravity of the body is posterior to the hip joint but anterior to what two parts of the leg?
knee
ankle
What kind of joint is the sacroiliac joint?
Plane synovial
What joins pubis together anteriorly? What does it make this joint type?
Cartilage
Cartilaginous
What ligament twists medial inferiorly at the hip joint in hip extension?
Iliofemoral ligament
What ligament is underneath the iliofemoral ligament?
Pubofemoral ligament
What structures along the femur neck make it a dangerous place to fracture?
Longitudinally organised vessels
What are the two joints in the one knee joint capsule?
What type are they?
Tibiofemoral
Patellofemoral
Hinge synovial
What are the semilunar fibrocartilage discs which increase contact surface at the knee joint?
Medial and lateral menisci
What are the two intracapsular ligaments of the knee?
ACL
PCL
What function does the ACL have?
Stops tibia sliding forwards
What attaches the menisci of the knee to the tibia plateau?
Horns
What are the two extracapsular ligaments of the knee?
MCL
LCL
What kind of stress does the lateral collateral ligament resist?
Varus stress
(adduction)
What is the main difference in the form of the LCL and MCL?
LCL is narrow, attaches to tibia
MCL is broad a flat, attaches to medial meniscus
What stress does the medial collateral ligament resist?
Valgus stress (abduction)