IP Review Tools, PPE, Basic Math Flashcards
The ancient Romans were the first to develop ______ , which contributed to the advancement of
plumbing technology.
a. the aqueduct
b. copper piping
c. a flushable toilet
d. chlorinated water
a. the aqueduct
The word plumber originates from the Latin word for ______
a. aqueduct
b. piping
c. lead
d. copper
c. lead
A ______ is an employee of a company, local government or province who makes sure that plumbing installations meet code and quality requirements.
a. master plumber
b. journey plumber
c. safety manager
d. plumbing inspector
d. plumbing inspector
A plumbing apprentice is enrolled in a plumbing apprentice program. In a typical year the apprentice will complete approximately ______ of on-the-job training.
a. 1000 hours per year
b. 2000 hours per year
c. 4000 hours per year
d. 8000 hours per year
b. 2000 hours per year
Competency based training programs are preferred over traditional programs primarily because the main
focus of these programs is________:
a. standardized classroom training
b. registration and accreditation
c. the latest technology
d. skills versus theory
d. skills versus theory
Modern plumbers are responsible for the installation and maintenance of all of the following except ______
a. lead piping
b. water supply lines
c. drainage systems
d. gas systems
a. lead piping
The ______ phase of plumbing consists of running the pipes through the holes that have been cut i
structure’s walls, ceilings or floors.
a. trim-out
b. stack-out
c. rough-out
d. rough-in
d. rough-in
The______ is a local organization that is responsible for ensuring that apprentices receive the proper
training and that graduates are qualified.
a. Plumbers Committee
b. Board of Governors
c. Industry Training Authority
d. YMCA
c. Industry Training Authority
______ employment is an organization established by the government to enforce safety standards for all places of employment:
a. WorkSafeBC
b. The Industry Training Authority
c. The Safety Committee
d. Safe Site
a. WorkSafeBC
You find it difficult to work with one of your co-workers. As a professional you should:
a. avoid the co-worker as much as possible
b. immediately report the co-worker’s behavior to his supervisor
c. ask for reassignment to another project
d. attempt to work out your differences with the co-worker
d.attempt to work out your differences with the co-worker
Suppose you notice a faulty electrical hookup at work. The first things you should do is _______
a. rewire the faulty hookup yourself
b. report the problem to your supervisor
c. contact WorkSafeBC to report the problem
d. give your coworker a chance to notice the problem
before reporting it.
b. report the problem to your supervisor
The term ______ refers to vertical straightness.
a. level
b. square
C. plumb
d. tolerance
C. plumb
One of the primary uses of a _______ is to mark and test right angles.
a. spirit level
b. framing square
c. chalk box
d. folding rule
b. framing square
Each of the following activities except_____requires the use of eye protection equipment.
a. welding
b. soldering
c. chiseling
d. leveling
d. leveling
A chop saw uses a wheel to cut _______
a. light gauge material
b. heavy gauge material
c. medium gauge material
d. any gauge material
d. any gauge material
If you notice that a pipe looks mashed after you cut it with a pipe cutter, you should _____
a. apply lubricating oil to the moving parts
b. use soapstone before making the cut
c. replace the cutting wheel
d. discard the pipe cutter and purchase a new one
c. replace the cutting wheel
Some cutting devices are designed to cut a______ : an opening slightly wider than the blade’s thickne
a. burr
b. kerf
c. chuck
d. tolerance
b. kerf
A reaming tool is used to remove a ________
a. burr
b. kerf
c. chuck
d. tolerance
a. burr
______ are used to cut threads on the end of two pipes so that they can be screwed together.
a. Tube cutters
b. Reciprocating saws
c. Pipe cutters
d. Dies
d. Dies
If you install pipe that will remain exposed you must use scratches on the pipe _______to prevent leaving jaw marks or scratches on the pipe.
a. slip joint pliers
b. a yoke vise
c. a strap wrench
d. pipe tongs
c. a strap wrench
Letter A in Figure 1 represents
a. face
b. back
c. centre point
d. centreline

d. centreline
Letter B in Figure 1 represents the
a. face
b. back
c. centre point
d. centreline
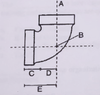
c. centre point
Letter C in Figure 1 represents the
a. fitting allowance
b. engagement
c. face-to-back measurement
d. centre-to-face measurement

b. engagement
Letter D in Figure 1 represents the______of the fitting.
a. fitting allowance
b. thread-in
c. face-to-back measurement
d. centre-to-face measurement

a. fitting allowance






























































