Intro to Anatomy and the Nervous System Flashcards
(18 cards)
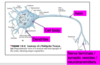
Name the parts of a neuron
What Does Grey Matter Consist of?
Cell Bodies
What does white matter consist of?
Axons, mostly covered in myelin - makes them appear white.
What is myelin composed of in the peripheral nervous system vs. the central nervous system?
Peripheral nervous system: Myelin produced by Schwann Cells
Central nervous system: Myelin produced by oligodendrocytes
What cells most often give rise to brain tumors?
glial cells in the brain often give rise to gliomas (glial cell tumor)
What surrounds both the brain and the spinal cord?
The Cerebrospinal fluid and the meninges.
What makes up the Central Nervous System?
The brain and the spinal cord
What makes up the peripheral nervous system?
Every nerve outside of the cranial/spinal nerves.
the peripheral nervous system includes the brachial and lumbar plexus.
Directions of nerve impulses?
Afferent vs. efferent
Afferent = sensory = towards the CNS
Efferent = motor= away from the CNS *think “EWWW! Get away!”
Natures of perception
somatic vs visceral
Somatic sensation - we are acutely aware of these and they are easily localized - generally originate in the body wall structures
Visceral sensation - either imperceptible or only vaguely localized. These are from blood vessels or internal organs (viscera)
What does the term ‘Decussation’ refer to?
It refers to the crossing over of our brain function
ie) the left side of the brain controls the right side of the body and vice versa.
What are the three layers of the brain and spinal cord?
Collectively this is refered to as the meninges
which is composed of three layers.
1) dura mater (outer)
2) Arachnoid ( below this layer is the subarachnoid space where fluid circulates)
3) Pia mater (most inner)
Purpose of the Ventricular system in the brain
The ventricles are hallow and Cerebral spinal fluid passes through these ventricles and into the sub arachnoid space - acting as a shock absorber for the brain.
What are the regions of the spinal cord and how many nerves exit from each region?
8 cervical (C1-8) - neck and upper limb
12 Thoracic (T1-12) - upper limb and thorax
5 Lumbar (L1-5)- abdomen and lower limb
5 Sacral (S1-5)- lower limb and perineum
What level does the spinal cord end?
L1 and L2
What is the most distal part of the spinal cord called?
the Cauda Equina
Parasympathetic effects vs. Sympathetic Effects?
Parasympathetic (parachute slows things down)
- slows heart rate
- Relaxes gut tube
- Sphincters open
- Constricted pupil
Sympathetic
- Speeds up heart rate
- Blood pressure rises
- blood vessels dilate
- dilates pupils
- sphincters clos
What levels does the sympathetic nervous system stem from?
From T1- L2


