Hand Flashcards
(33 cards)
What are the four types of joints in the hand?
Carpometacarpal joint
Metacarpal phalangeal joint
proximal interphalangeal joint
Distal interphalangeal joint
Which digit only has 2 phalanges?
Thumb (1st digit)
What is the most commonly fractured carpal bone?
scaphoid
where does a scaphoid commonly fracture?
along the long axis
Describe the 1st carpmetacarpal joint
synovial joint - saddle type
wide range of movements here including flexion, extension, abduction, adduction, opposition -
this joint is involved in the Bennet’s fracture

What muscles compose the long flexors of the finger?
Flexor digitorum profundus
Flexor digitorum superficialis
*both median nerve*
What joints does flexor digitorum profundus act on?
EVERY joint in the hand!

What are the Thenar muscles?
OAF
O= opponens pollicis
A= abductor pollicis brevis
F= flexor pollicis brevis
What are the two heads of adductor pollicis called?
- Transverse head of adductor pollicis
- Oblique head of adductor pollicis

What is the nerve supply to the thenar muscles?
Remember thenar muscles = opponens pollicis, abductor pollicis brevis, and flexor pollicis brevis - nerve suppy = median nerve
Deep to these thenar muscles is adductor pollicis whos nerve supply is the ulnar nerve!
What are the hypothenar muscles? What is their nerve supply?
Abductor digiti minimi
flexor digiti minimi
opponens digiti minimi
(ulnar nerve)
What are the roots of the ulnar nerve?
C8 and T1
What tendon do the lumbricals arise from?
They arise from the flexor digitorum profundus tendons
What is the function of the lumbricals?
What are their innervations?
flex the metacarpal phalangeal joint and extend the interphalangeal joints
innervated by median nerve on radial side
innervated by ulnar nerve on ulnar side
What are the inerossei muscles? What action are they responsible for? What is their nerve supply?
They are responsible for the adduction/abduction of your fingers
you have dorsal interossei and palmar interossei (PAD and DAB)
nerve supply = ulnar nerve (C8 T1)

What lies under the carpal tunnel?
Flexor digitorum superficialis
flexor digitorum profundus
median nerve
flexor pollicis longus tendon
What structures pass over the flexor retinaculum?
ulnar artery
ulnar nerve
palmar cutaneous branch of ulnar nerve
tendon of palmaris longus
palmar cutaneous branch of median nerve
What are the clinical symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome?
tingling/numbness of the first 3 and half digits -
wasting of the thenar eminence due to inability of OAF
opponens pollicis, abductor pollicis brevis, flexor pollicis brevis

What is the purpose of the finger synovial sheath?
what are the implications?
the synovial sheaths reduce friction in your fingers - but they can also spread infection
what structure overlies the long flexor tendons in the palm?
the palmar aponeurosis
Where does the palmar aponeurosis spred from?
it spreads from the flexor retinaculum and the palmaris longus tendon to the bases of the proximal phalances
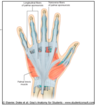
With is Dupuytren’s contracture?
common problem that results in fibrosis of the palmar aponeurosis- leading to shortening/thickening of the digital bands that pull the digits (4th and 5th especially) to varying degrees of flexion. Surgery is required to correct this deformity
How does the ulnar artery enter the hand?
it ents anterior to the flexor retinaculum between pisiform and hook of hamate (Guyon’s canal)
It divides into superficial and deep branches
it is the man contributor to the superficial arch


