Glycolysis Flashcards
What are the moleucles that are oxidized to produce ATP, Heat, CO2 and water ?
Where are the exceeds stored as an where ?

Which of the macro molecule produces the most fuel ?

The composition of the body fuel stores are ?

What occurs during energy production by oxdiation of . vs energy utilizaiton ?

What happens to excess dietary fuel ? What about fasting ?

What does this mean ?



What connection with BMI ?

Where are Dietary Triacyglycerols digested ? What enzymes do ? Where is bile salt made , and what is it made of ? Where is it reabsorbed ?

To break down proteins, what is the fuction of parietal cells ? Chief cells ? What connection with HCL. What is the role of Chymotrypsin , trypsin, ?
What is the fuction of exopeptidases ?
What is the role of proteases , where is it produced ?
chief pepsi
pH= pariental cells regualte PH
PC=Chief cells

What is Achlorhydria and hypochlorhydria ? What effect does on parietal cell and H2- receptor ? which rare diease is it seen ? or infection ? What symptom ?

What is the fuction of the H2-receptor of Achlorhydria and hypochlorhydria ?

What is celiac diease?
silly intestine, hiding

Where does starch come from, and what does it break into?
Sucrose
lactose

What are the digestion enzymes of the intestinal cells that break down carbohydrates ?

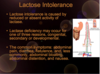
What is lactose intolerance ? reason it is caused ? Symtops
What is glycolysis the principle of ? Where does it take place ? What about RBC ? How does glucose travel ? What does insulin stimulate ?

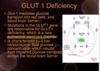
What is Glut 1 Deficiency ? What kind of mutation ? What is characterized ?