Female Reproductive System Flashcards
What is Menopause?
When the ovaries in a female run out of follicles, typically measured by the last menstrual bleed
When does Menopause typically occur in Females?
50-52 years old
What happens to the Total Number Of Follicles that a Female has After Birth?
It gradually decreases until around the 40s, when it decreases faster until there are no more
Typically at what age do Regular Menstrual Cycles typically cease, being replaced by Irregular Menstrual Cycles?
Around the mid 40s
What is the Phase before Irregular Menstrual Cycles called?
Pre-menopause
What is the Phase between the beginning of Irregular Menstrual Cycles and the Last Menstruation (Menopause)?
The menopausal transition
What is the Phase after Menopause called?
Post-menopause
Typically how long after Menopause will the follicles within the Ovaries continue to produce Hormones?
1-2 years
What is the Phase after the Ovaries stop producing Hormones called?
Ovarian senescence
What is the Phase between the beginning of Irregular Menstrual Cycles and when the Ovaries stop producing Hormones called?
Peri-menopause
During which Phase do Perimenopausal Symptoms typically occur?
Peri-menopause
The main Oestrogen hormone Post-Menopause is what? Where is it produced?
Oestrone, produced in the stromal cells of adipose tissues
Vasomotor Perimenopausal Symptoms affect what? What are some examples?
Blood Vessels
Hot Flushes and Night Sweats
What is an example of a Genitourinary Perimenopausal Symptom?
Vaginal Dryness
What is an example of a Bone Metabolism Perimenopausal Symptom?
Osteoporosis
What are some Behavioural/Psychological changes that may occur during Menopause?
Depression, Tension, Anxiety, Mental Confusion and Loss of Libido
Severely debilitating Menopausal Symptoms can be Prevented or Arrested with what?
Menopausal hormone (oestrogen replacement) therapy
What is the Downside of Menopausal Hormone Therapy?
It slightly increases the risk of breast and endometrial cancers
Approximately how many Oocytes are released over the lifetime of a Female?
Around 400
How often is a Mature Oocyte released?
Approximately every 28 days
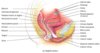
What are the Four Main Female Reproductive Organs?
- The Vagina
- The Uterus
- The Uterine (Fallopian) Tubes
- The Ovaries
Identify the Uterine/Fallopian Tube


Identify the Ovary


Identify the Uterus