Brain Structure Flashcards
(45 cards)
What are the four main regions of the forebrain?
The Frontal, Temporal, Parietal and Occipital Lobes
What are the four main landmarks which divide the forebrain into its four main regions?
The Central Sulcus, The Lateral Fissure, The Pre-Occipital Notch and the Superior end of the Parietal-Occipital sulcus
Identify the Pre-Occipital Notch


What is the Blue area of the forebrain called?

The Frontal Lobe
What is the Yellow area of the forebrain called?

The Parietal Lobe
What is the Pink area of the forebrain called?

The Occipital Lobe
What is the Green area of the forebrain called?

The Temporal Lobe
Where are the Supramarginal and Angular Gyri?

Sitting on the posterior and inferior side of the parietal lobe (Mc’Donald’s “M”)
Where are the Primary and Secondary Visual Cortices?

In the Occiptal Lobe
Where are the Primary Auditory Cortex and Wernicke’s area?

Along the superior border of the temporal lobe
Where is the Broca’s area located?

Along the Posterior border of the Pre-Motor Cortex, in front of the Pre-Central Gyrus
Where is the Exner’s Area located?

Along the Posterior border of the Pre-Motor Cortex, in front of the Pre-Central Gyrus and above the Broca’s Area
Where is the Postcentral Gyrus/Primary Somatosensory Cortex?

On the posterior side of the Central Sulcus
Where is the Precentral Gyrus/Primary Motor Cortex?

On the anterior side of the Central Sulcus
What Connects the Broca’s and Wernicke’s areas?

The Arcuate Fasiculus
What is the structure Below the Purple region?

The Corpus Callosum
What is the Purple Region?

The Cingulate Gyrus
What is the Sulcus between the Green and Pink Regions?
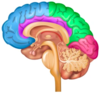
The Parieto-Occipital Sulcus
What Sulcus runs through the Pink region?

The Calcarine Sulcus
What area of the Occipital Lobe can be identified through looking for the Calcarine Sulcus?
The Primary Visual Cortex
What is the structure below the occipital lobe?
The Cerebellum
What Structuresare part of theForebrain Diencephalon?
The Thalamus, Hypothalamus, and Pituitary Gland
What Structures are part of the Mid Brain?
The Cerebral Peduncles, Cerebral Aqueduct and the Superior and Inferior Collilculi
What Structures are part of the Forebrain?
Cingulate Gyrus, Corpus Callosum, The 4 Lobes,






















