Drug Excretion Flashcards
drug excretion
drugs are eliminated either as unchanged via renal excretion or convered to metabolites in the liver
excrete through urin, bile, or fecal routes
also excretion from lung as gas or breast milk
renal excretion of drugs and the three processes involved
90% of 300 drugs in a study were recovered to a significant extend in the urine
three processes include glomerular filtration, tubular secretion, and passive tubular reabsorption
glomerular filtration
glomerulus acts as a dialyzing membrane
three layers contribute to the glomerular filtration barrier that serve as size and charge-sensitive filtration systems
about 20% of of the plasma is filtered by glomerulus
drugs bound to proteins such as albumin are not filtered because albumin is too big

three layers of the glomerular filtration barrier
capillary endothelium with fenestrae of 60-100 nm (effective pore of 15nm)
negatively charged glomerular basement membrane that is also porous
epithelial podocytes that form interdigitating foot processes with filtration slits of 25-60 nm, effective pore size of <6nm
these layers form a size- and charge-sensitive filter
renal drug excretion vs. glomerular filtration
about 80% of filtered ionized drug gets excreted
drug secreted due to filtration alone = GFR x fd (free drug concentration)
net secretion if total renal secreted drug > GFR x fd
net reabsorption if total renal secreted drug < GFR x fd
tubular secretion
occurs at the proximal tubules
80% of ionized drug is excreted
some tightly bound drugs, though not filtered will be actrively secreted when it dissosciates
transporters in renal secretion
two families of solute carriers on the basolateral side include OATs and OCTs
ABC transporters and SLC transporters on the apical side (urin side) for exporting the drug to the urine
drugs carried by organic cation transporters (OCTs)
for weak bases such as procaine, quinidine, and histamine
SLC 22 family transporters OCT1 and 2 mediates facilitated diffusion
on the apical membranes ABC (MDR1) transporters, organic cation/carnitine ttransporters (OCTN1 and 2), and OCT3 transporters
drugs carried by organic anion transporters
for weak acids such as penicillin, cephalosporin, and probenecid
OAT1 and OAT3 (SLC22A) are on the basolateral membrane, coupled with alpha-ketoglutarate
MRP2 and MRP4 on the apical side of the membrane, transports OA- into the urine
NPT1/SLC17A1 mediates transport of phosphates usch as PAH, probenicid and penicillin go into the urine
passive tubular reabsorption
occurs in the distal tubule
drug transport across is bidirectional, but the net movement is reabsorptive
due to concentrated urine to increase drug concentration of ionized and non-ionized forms
involves passive diffusion of non-ionized drugs
probenecid
a drug that competes with the transport system of penicillin, effectively prolonging its time in the body
method of enhancing excretion of weak acids
alkalization of uring wiht NaHCO3 intravenous injections
accelerates excretion of weak acids such as barbiturates by increasing the negatively charged form of the drug
method of enhancing the excretion of weak bases
acidification of uring with arginine-HCl
increases the positively charged form of the drug
factors other than state of drug that affect renal excretion
renal diseases that decrease glomerular filtration decrease drug excretion
drug binding delays excretion if not actively secreted
alteration of drug metabolism influences drug excretion
diuresis increases excretion due to decrease in transit times in tubules
transporters and nephrotoxicity
some drugs such as HIV drugs adefovir and cidofovir are toxic to neprhons
excretion of drugs >300Da
excreted through the bile
drug excretion through the bile
drug passes through the enterohepatic recirculation through sinusoids in the liver
albumin and albumin-bound drugs easily go through the liver fenestrae, which are 150 to 175 nm in diameter
from there, a variety of transporters will transport the drug into the bile

ABC5/8
a dimer that exports cholesterol and pytosterols into the bile
defects in either ABC5 or 8 gene causes sisterolemia
xanthomas and premature onset of atherosclerosis may result
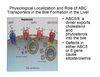
OATP1B1
pump found in liver cell
if defective, will lead to an increased blood concentration of statins
enterohepatic cycle
drugs are metabolized in the liver to form glucuronides
they enter the bile to a large extent
these modified drugs can be cleaved by bacterial beta-glucuronidases in the colon to liberate the drug molecule, which is then reabsorbed
effect of enterohepatic recirculation on plasma time concentration of estrone
several stabilizations of the hormones over time
if taken with antibiotics such as minocycline, will inhibit the time that the drug stays in the system
could result in unexpected pregnancies


