Disorders of the Cervix Flashcards
(25 cards)
what are the disorders of the cervix?
- Cervical intraepithelial neoplasia
- Cervical cancer
what is this?

normal cervix
what is this?

normal endo and exocervix

what is the purpose of the Cervix?
what are its 2 portions?
connects the uterus to the vagina.
- exocervix: part that protrudes into the vagina, covered in squamous epithelium
- endocervix: canal that leads to endometrial cavity and is line with mucus secreting columnar cells
what part of the cervix can cancer develop?
where is that?
what cancer develops here?
what procedure is done to check here for cancer?
T (transformation) zone, area that undergoes squamous metaplasia, its where edocervical epithelium meets the acid pH of vagina
squamous dysplasia
pap smear
what is this?

koilocytosis in squamous cells
what is Cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN)?
what part of the epithelium does it involve mainly?
how do you notice neoplasia?
where do changes happen?
- disordered growth of cervical epithelium
- squamo-columnar junction
- disordered growth (loss of polarity) and nuclear hyperchromatism
- changes begin at the basal layer and extend outward.
what is this?

carcinoma in situ (intact bas. membrane)
Majority of cases of Cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) are associated with what?
HPV types 16, 18, 31, 33
CIN is classified into 3 types depending on extent of epithelial involvement, what are these?
- CIN 1: Mild dysplasia of lower third of epithelium.
- CIN 2: Moderate dysplasia in lower two thirds of the epithelium
- CIN 3: Severe dysplasia to carcinoma in situ of entire thickness of epithelium
what is this?

squamous cell carcinoma of the cervix
what is this?

cervical cancer producing hydronephrosis
what is this?

exophytic ulcerated squamous cell carcinoma
what is this?
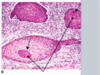
keratin pearls found in squamous cell carcinoma of cervix
what are the risk factors for CIN?
how do you screen?
early age sexual activity
multiple high risk partners
high risk HPV types
pap smear
what are the Clinical Findings for Cervical intraepithelial neoplasia?
- Dysplasia is not usually visible to naked eyes
- 1% acetic acid wash applied to cervix, dehydrates cells and reveals “acetowhite” areas that correspond to dysplasia
what are the Cervical Carcinomas?
- Squamous cell carcinoma*******
- Adenocarcinoma
what is this?


what is the third most common cancer of lower female genital tract?
what are its risks?
cervical carcinoma
- early age sexual activity, especially with high risk partners
- HPV
what are the high risk HPV serotypes for Cervical carcinoma?
what proteins of the serotypes are important in cervical cancer?
16, 18, 31, 33
protein E6 (binds to p53) and E7 (binds to Rb)
what are the symptoms found in cervical cancer?
- Postcoital vaginal bleeding
- Dyspareunia
- Malodorous discharge
what are the signs of cervical cancer?
Friable, raised, reddened or ulcerated area visible on cervix
how do you diagnose cervical cancer?
how do you prevent it?
pap smear
colonoscopy
hpv vaccine: gardasil (hpv 6,11, 16,18
cervarix (hpv 16, 18)


