Cardiac Introduction Flashcards
Brain
Blood Flow
consumption
Flow: 13%
consumption: 21%
Coronary circulation
flow
O2 consumption
Flow: 4%
O2 consumption: 11%
Liver
Blood flow
and consumption
Flow: 24%
O2 consumption 23%
skeletal muscle
flow and O2 consumption
Flow: 21%
O2 consumption: 27%
Kidney
Flow and O2 consumption
Flow: 20%
O2 consumption: 7%
Skin and other organs
Flow and O2 consumption
Flow: 18%
O2 consumption: 11%
visceral pericardium
the inner layer of the pericardium closes to the heart
Parietal pericardium
the outer layer of the paricardium
Pathway of blood through the heart
- deoxygenated blood enters Right atrium from the Venae cavae.
- through tricuspid valve to Right ventricle
- through pulmonary valve to pulmonary trunk/arteries
- Alveoli of the lungs to become oxygenated
- through pulmonary veins into left Atrium
- through mitral valve into left ventricle
- through aortic valve into aorta
- out to systemic circuit
Fossa Ovalis
- Where the Foramen Ovale was during fetal development
- In Right Atria on septal wall between Right and Left Atrium
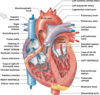
Cordae tendineae
Connect the papillary muscles to the tricuspid and mitral valve.
Prevent the prolapse of the valves up into the atria while ventricle is contracting and pressure is much higher in Ventricle than in the atrium

attributes of arteries
- deliver blood under high pressure
- thick walled
- no valves
- more elastic closer to heart in bigger arteries
- more muscular farther from heart as arteries get smaller
attributes of Veins
- Collection of blood under low pressure
- thinner walled
- valves to facilitate blood return to the heart
- total volume of veins is much greater than arteries
Poiseuille’s law
R = (n*L*8)/(πr4)
n = viscocity
L = vessel length
r = vessel radius

Poiseuilles Law
change in radius
change in R is non-linear
Smaller radius has exponentially more resistance
Poiseuille’s Law
Change in length
change in length is linear
vessel becomes twice as long, resistance becomes twice as hard
Poiseuille’s law
change in viscocity
Change is viscocity is linear
blood becomes twice as viscous, resistance is twice as hard

- as the arterioles become smaller branches, the area increases and velocity slows
- total resistance is lower than each individual resistance
- Velocity of veins is slower than arteries because area is greater
- V1*A1=V2*A2
What causes turbulent flow?
- increased velocity
- a bigger tube
- a tube getting smaller
- merging
- interference
Laminar flow is more likely in…
- small tubes
- higher viscocity


